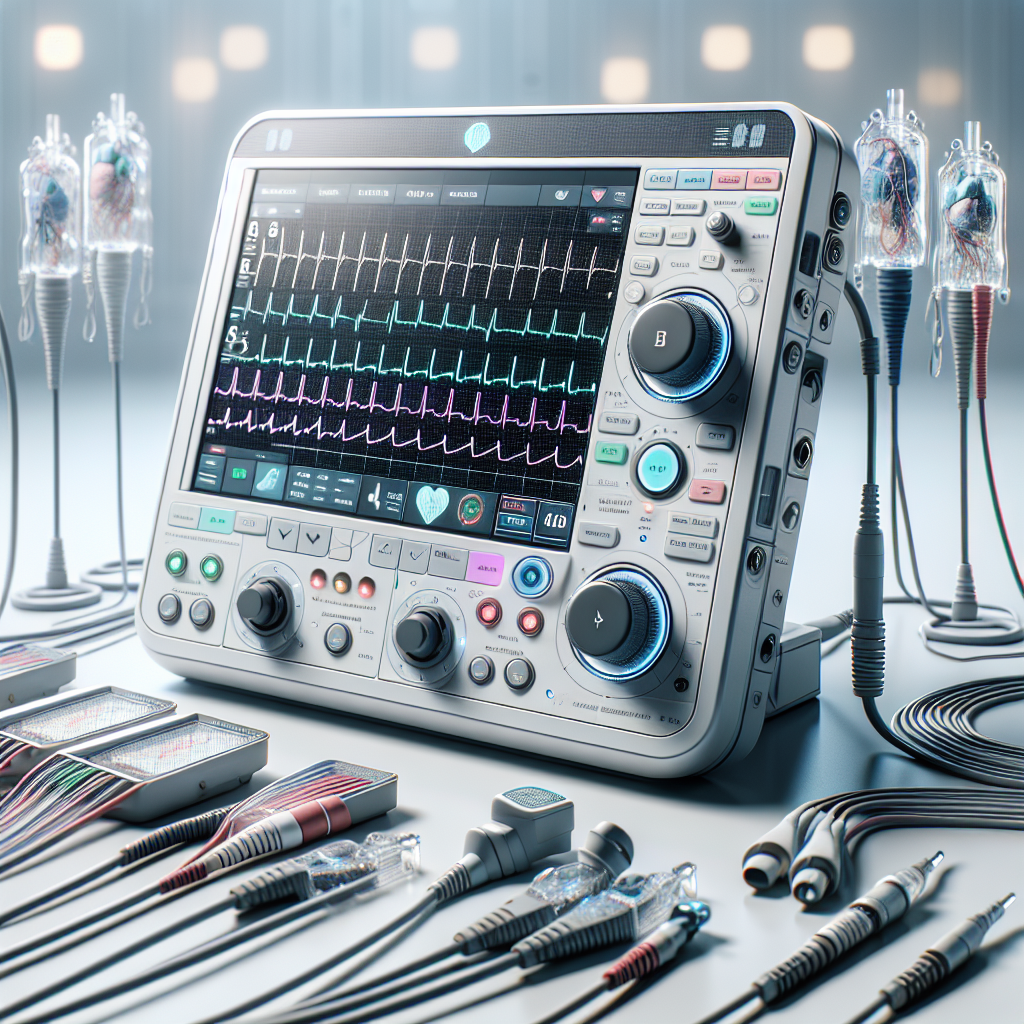
The heart is not just the seat of our emotions but also a critical organ that demands vigilant care and attention, particularly as we navigate through the hurdles of modern life that put us at risk for heart disease. With heart disease being a leading cause of death globally, early detection and management are crucial in changing this dire statistic. Among the myriad of tools available for heart health assessment, the electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) stands out as an essential, non-invasive method to monitor the heart’s activity and detect potential problems early on.
What is an Electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram is a simple test that records the electrical activity of the heart. It is a reflection of the complex symphony of electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat. By placing electrodes on the patient’s skin, the ECG machine creates a graph of the heart’s electrical activity, which can reveal a wealth of information about heart health.
The ECG’s Role in Heart Disease Detection
The detail within an ECG readout allows physicians to observe abnormalities that might indicate various forms of heart disease. Here are several ways an ECG can be beneficial:
Identifying Irregular Heart Rhythms
Irregular heart rhythms, or arrhythmias, can lead to complications such as stroke or heart failure. An ECG can detect these irregularities, whether they are too fast, too slow, or erratic, helping to guide further investigation or immediate treatment.
Uncovering Heart Attack Evidence
During a heart attack, the heart muscle is damaged due to a lack of blood flow. This damage alters the electrical signals in the heart, which an ECG can detect. An early ECG can be instrumental in guiding emergency treatment and improving outcomes.
Detecting Structural Abnormalities
Changes in the size and position of the heart chambers can affect the ECG waveform. Cardiomyopathy and other structural heart conditions can be suggested by specific patterns seen on an ECG.
Monitoring the Effects of Heart Medication
Certain medications that affect the heart’s electrical activity can be monitored using serial ECGs to ensure they are working correctly and to adjust dosages if necessary.
Preoperative Assessment
Before surgeries, an ECG can assess the risk of heart complications during the operation, especially in patients with known heart conditions or significant risk factors.
Prognosis and Follow-Up
After a cardiac event, ECGs are used to monitor recovery and guide rehabilitation and secondary prevention strategies.
Electrocardiograms in Context – Complementary Resources
While ECGs provide vital information, they are one element of a comprehensive cardiovascular health strategy. To further understand the context within which ECGs operate, it’s essential to explore additional resources that delve into various aspects of heart health.
Cardiovascular Health is a cornerstone resource that provides an overview of heart-related issues and strategies to maintain heart health, acting as a companion to understanding the broader implications of ECG findings.
For those looking to understand the impact of lifestyle on heart health, resources such as The Benefits and Risks of Running for Heart Health can be very insightful. It explores how physical activity influences cardiovascular well-being and where ECGs might fit into a fitness regimen.
Moreover, the relationship between chronic conditions and heart health cannot be overstated. Articles like The Interplay Between Blood Sugar Levels and Cardiovascular Health provide a nuanced view of how systemic health issues can affect the heart.
In the realm of patient education, resources like The Role of Patient Education in Managing Cardiovascular Disease emphasize the importance of understanding one’s condition and the various diagnostic tools, including ECGs, to better manage heart disease.
Advanced Interpretations and Technological Innovations
The ECG is not a standalone diagnostic tool but part of a broader diagnostic process. For more nuanced interpretations, cardiologists might employ additional tests, such as echocardiograms or stress tests. These resources are often discussed on niche medical platforms and in specialized publications that cater to healthcare professionals.
Recent advancements in ECG technology have also enabled remote and continuous monitoring of the heart’s electrical activity through mobile health devices. These innovations are covered in depth on platforms focusing on Exploring the Role of Mobile Health in Cardiovascular Prevention, providing insights into the future of heart disease management.
External Resources for In-depth Understanding
For those seeking a deeper dive into the technical aspects of ECG interpretation, there are several high-quality, niche resources available:
-
The Journal of Electrocardiology offers peer-reviewed articles that delve into the clinical and experimental aspects of electrocardiography.
-
ECG Wave-Maven is a tool from Harvard Medical School that presents a wide array of ECG cases, fostering a deeper understanding of ECG readings and their implications.
-
The Heart Rhythm Society provides extensive resources on arrhythmias and electrocardiography, supporting both patients and medical professionals in understanding heart rhythm disorders.
-
For a historical perspective and foundational knowledge, the British Heart Foundation offers resources that detail the evolution of ECG and its role in modern medicine.
-
The American Heart Association is a trusted resource for guidelines on cardiovascular health and the use of ECG in various clinical scenarios.
Conclusion
Electrocardiograms serve as a critical tool in the early detection and management of heart disease. They provide a window into the heart’s electrical activity, allowing clinicians to diagnose and treat arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular conditions effectively. As we continue to advance technologically, the role of ECGs in both clinical settings and personal health monitoring is likely to expand, offering greater insight and control over our heart health.
In conclusion, whether you are a healthcare professional, a patient, or someone interested in understanding heart health, the ECG is a fundamental aspect of cardiovascular care. By combining the information provided by ECGs with a holistic understanding of heart health, including lifestyle, nutrition, and education, we can improve outcomes and lead healthier, heart-conscious lives.