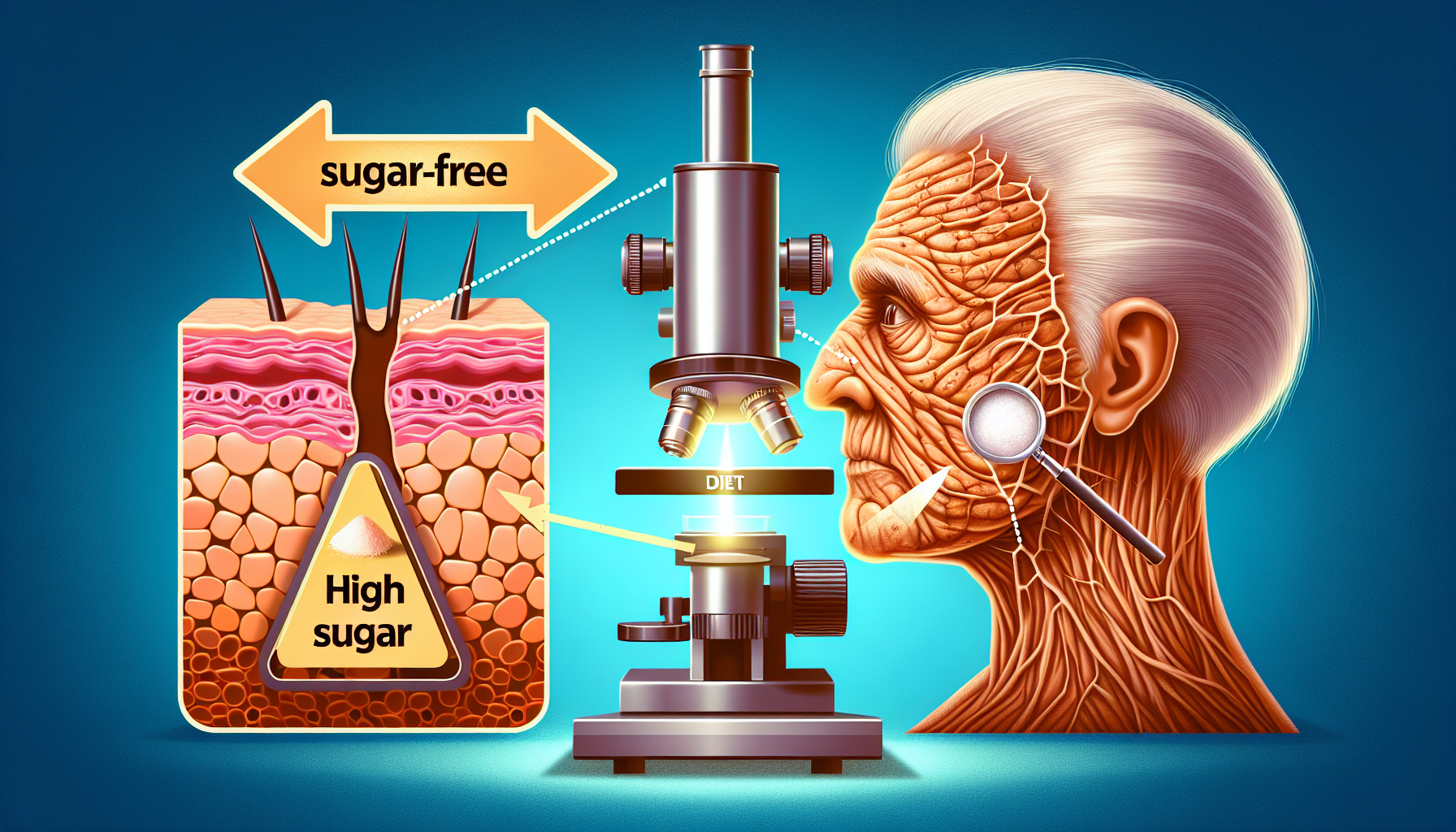
Sugar, a pervasive ingredient in many of our daily diets, is not just a concern for our waistlines but also for our skin’s health and appearance. The sweet culprit behind many health issues can also accelerate the aging process of our skin, leading to wrinkles, sagging, and a dull complexion. In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll delve into the mechanics of how sugar impacts skin aging and provide actionable tips to mitigate these effects and maintain youthful, radiant skin.
The Glycation Process and Its Role in Skin Aging
Glycation is a natural chemical process in which sugar molecules bind to proteins or lipids without the controlling action of an enzyme. In the context of skin health, this reaction primarily involves glucose and collagen or elastin—the proteins that give skin its firmness and elasticity. When glycation occurs, it results in the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which have significant implications for the skin.
AGEs compromise the structural integrity and regenerative abilities of collagen and elastin, leading to the premature appearance of aging signs such as wrinkles, fine lines, and a loss of firmness. Moreover, AGEs exacerbate oxidative stress and inflammation, further damaging skin cells and accelerating the aging process.
For a deeper understanding of skin health and the factors that contribute to its vitality, readers may explore Avix Health’s comprehensive guide on skin health, which provides a wealth of information on maintaining a healthy and youthful complexion.
Diet and Skin: The Sugar Connection
The modern diet, often high in processed foods and added sugars, can lead to an overabundance of glucose in the body, exacerbating the glycation process. Not only does this increase the production of AGEs, but it also can trigger a cascade of skin issues. Studies have shown that a diet high in sugar can disrupt the balance of the microbiome, increase sebum production, and inflame skin conditions like acne.
To mitigate these effects, it is essential to maintain a diet that supports skin health by reducing sugar intake and including nutrient-rich foods that combat glycation. Foods high in antioxidants, like berries, nuts, and green leafy vegetables, can help protect the skin from oxidative stress, while those rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish and flaxseed, can help maintain the skin’s lipid barrier and reduce inflammation.
Strategies to Counteract Sugar-Induced Skin Aging
Optimize Your Diet
A balanced diet is a cornerstone of skin health. Focus on incorporating foods that are low in sugar and high in antioxidants. Consider reading more about the role of diet in managing specific skin conditions, such as rosacea, to tailor your diet to your skin’s needs.
Skin Care Products and Ingredients
Topical products can also play a pivotal role in fighting the effects of sugar on the skin. Ingredients such as retinol, which is known for its skin-rejuvenating properties, can stimulate collagen production and accelerate cell turnover. To learn more about the benefits of retinol and other active ingredients, delve into the article on retinol for skin rejuvenation.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to diet and skincare, lifestyle factors such as exercise can promote skin cell renewal and overall skin health. Engaging in regular physical activity increases blood flow, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the skin. For insights on the connection between exercise and skin health, examine the link between exercise and skin cell renewal.
Professional Treatments
Professional treatments like chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion can help reverse some of the damage caused by glycation by removing dead skin cells and stimulating collagen production. Consult with a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for your skin type and concerns.
External Resources for Further Exploration
For those seeking to expand their understanding of glycation and skin aging, the following resources offer niche and specific insights:
- A detailed exploration of the glycation process and its influence on skin can be found in the research published by the International Dermal Institute.
- The American Academy of Dermatology provides guidance on building a skin care routine that includes products to combat glycation and its effects.
- The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology offers a collection of studies addressing the impact of diet on skin health, including the role of sugar.
Conclusion
The relationship between sugar consumption and skin aging is intricate and undeniable. By understanding the glycation process and its detrimental effects on skin health, individuals can take proactive steps to protect and rejuvenate their complexion. A combination of dietary adjustments, targeted skincare, lifestyle changes, and professional treatments can collectively counteract the aging effects of sugar on the skin.
As you continue to navigate the journey of skin care and health, remember that knowledge is power. Stay informed, make conscious lifestyle choices, and invest in quality products that align with your skin’s needs. The path to healthy, youthful skin is a holistic one, embracing all aspects of well-being.