Hyperthyroidism is a condition characterized by an overproduction of thyroid hormones, which can have far-reaching impacts on various bodily functions. One of the lesser-known but significant effects of hyperthyroidism is its impact on bone density. This article delves into the intricate relationship between hyperthyroidism and bone health, exploring the pathophysiology behind the condition, its implications, and strategies to mitigate its effects on the skeletal system.
The Thyroid-Bone Density Connection
The thyroid gland plays a pivotal role in metabolism, growth, and development. Thyroid hormones, particularly thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), influence the rate at which your body uses energy and the sensitivity of your body to other hormones. However, when the thyroid is overactive, it leads to a condition known as hyperthyroidism, which can accelerate your body’s metabolism, causing unintentional weight loss and a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
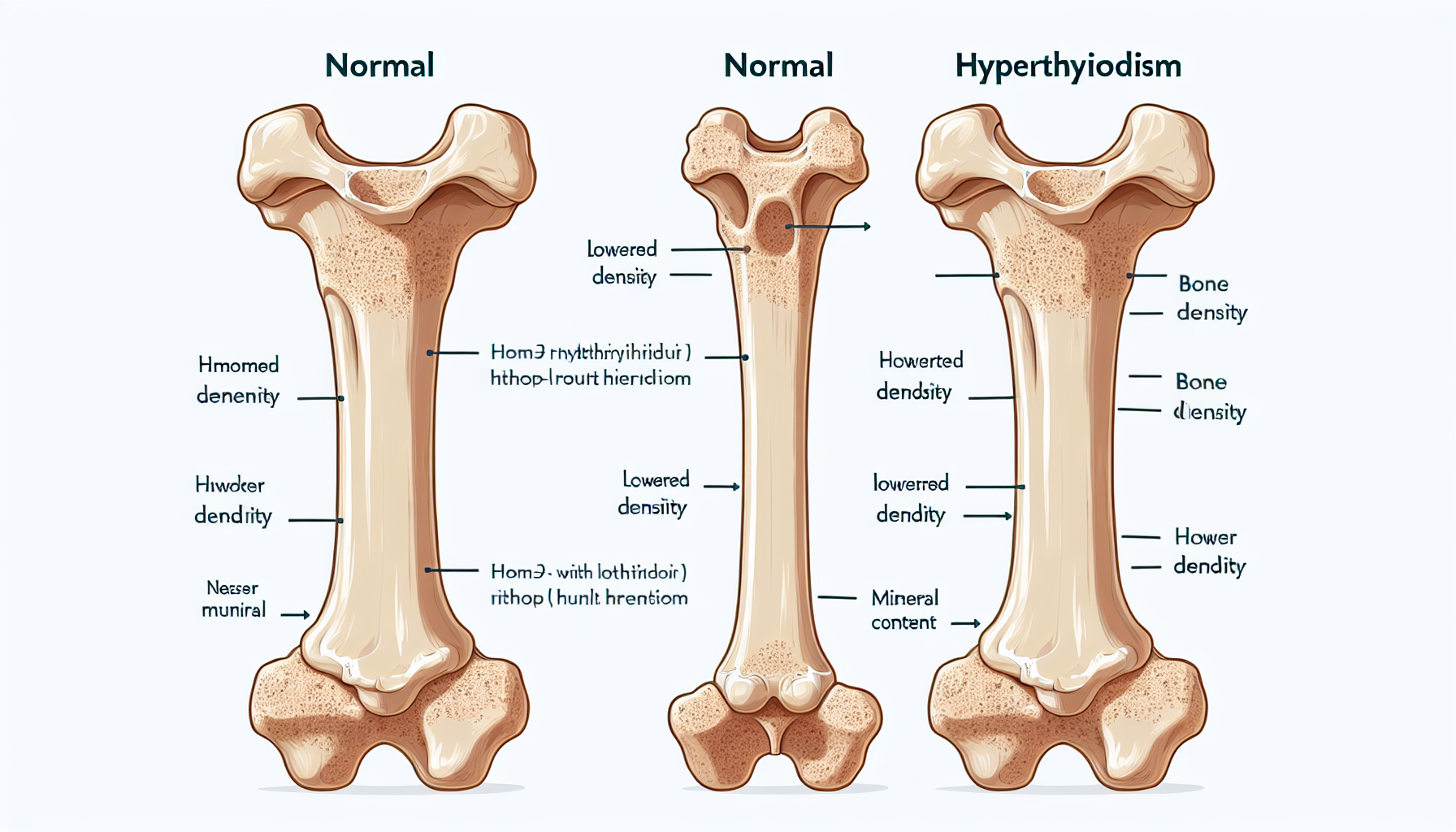
Beyond these well-known symptoms, hyperthyroidism also affects bone remodeling—a process where old bone tissue is replaced by new tissue. Thyroid hormones have a direct impact on osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption, respectively. In hyperthyroidism, there’s an increase in bone resorption rates, leading to a decrease in bone density and potentially increasing the risk of fractures.
For those seeking to understand the broader context of bone health, our comprehensive guide on Bone Health provides valuable insights into maintaining a healthy skeletal system.
Assessing the Impact
The effect of hyperthyroidism on bone density is more pronounced in certain groups, particularly postmenopausal women and elderly patients, who are already at a higher risk for osteoporosis. Studies have shown that individuals with untreated hyperthyroidism have lower bone mineral density (BMD) compared to their euthyroid counterparts.
Furthermore, the duration and severity of hyperthyroidism also contribute to the extent of bone loss. The longer a person remains hyperthyroid, the greater the potential for significant bone density reduction.
Prevention and Treatment
The management of hyperthyroidism is crucial for the preservation of bone density. Treatment options include antithyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery. By bringing thyroid hormone levels back to normal, it’s possible to slow down or even halt the progression of bone loss.
In conjunction with medical treatment, lifestyle modifications can be beneficial. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health, as is engaging in regular weight-bearing exercises. For further reading on the role of diet and exercise in combating osteoporosis, consider our article on Combating the Risk of Osteoporosis Through Diet and Exercise.
Additionally, smoking cessation and reducing alcohol consumption can also help in maintaining bone density. For those interested in the impact of lifestyle choices on bone mass, the article The Influence of Lifestyle Choices on Bone Mass and Health is a valuable resource.
Monitoring Bone Health
Regular bone density screenings are important for those with hyperthyroidism. These tests can help detect early bone loss, allowing for timely intervention. It is also essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their thyroid levels and ensure that they remain within a healthy range.
For those undergoing treatment for hyperthyroidism, repeat bone density tests can be a useful tool to assess the effectiveness of the interventions and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Complementary Strategies
In addition to conventional treatments, certain nutritional and lifestyle interventions can play a supportive role in managing bone density issues. The intake of omega-3 fatty acids, for example, has been associated with improved bone density. Readers can explore this topic further in the article Role of Omega-3s in Bone Density and Joint Health.
Moreover, patients with hyperthyroidism should also be aware of the potential impact of other factors such as chronic stress and sleep disorders on bone density. Informative resources can be found in articles such as The Impact of Chronic Stress on Bone Density and Health and The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Bone Metabolism.
External Resources for Further Reading
To enrich your understanding of the effects of hyperthyroidism on bone density, consider the following external resources:
- The Endocrine Society’s guidelines on thyroid disease and bone health provide a thorough overview of clinical recommendations for managing bone risks associated with thyroid disorders. (Endocrine Society Guidelines)
- A scholarly article on the molecular mechanisms by which thyroid hormones affect bone cells can offer a deeper dive into the pathophysiology of bone loss in hyperthyroidism. (Molecular Mechanisms in Bone Cells)
- Patient advocacy groups like the Thyroid Foundation of America offer support and information that can help patients navigate the challenges of living with hyperthyroidism, including its impact on bone health. (Thyroid Foundation of America)
In conclusion, hyperthyroidism has a significant impact on bone density, which can lead to an increased risk of fractures and osteoporosis if not adequately managed. Understanding the interplay between thyroid function and bone health, alongside implementing effective treatment strategies, is crucial for maintaining a robust skeletal system. By staying informed and proactive, individuals with hyperthyroidism can take meaningful steps toward protecting their bones and overall well-being.