Dysbiosis is a term that has been gaining attention among health professionals and the general public alike. It refers to an imbalance in the microbial communities within the human body, particularly the gut. A healthy balance of these microorganisms is crucial for not only digestive health but also overall well-being. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes and treatments of dysbiosis, and explore how maintaining a balanced gut microbiota can lead to improved health outcomes.
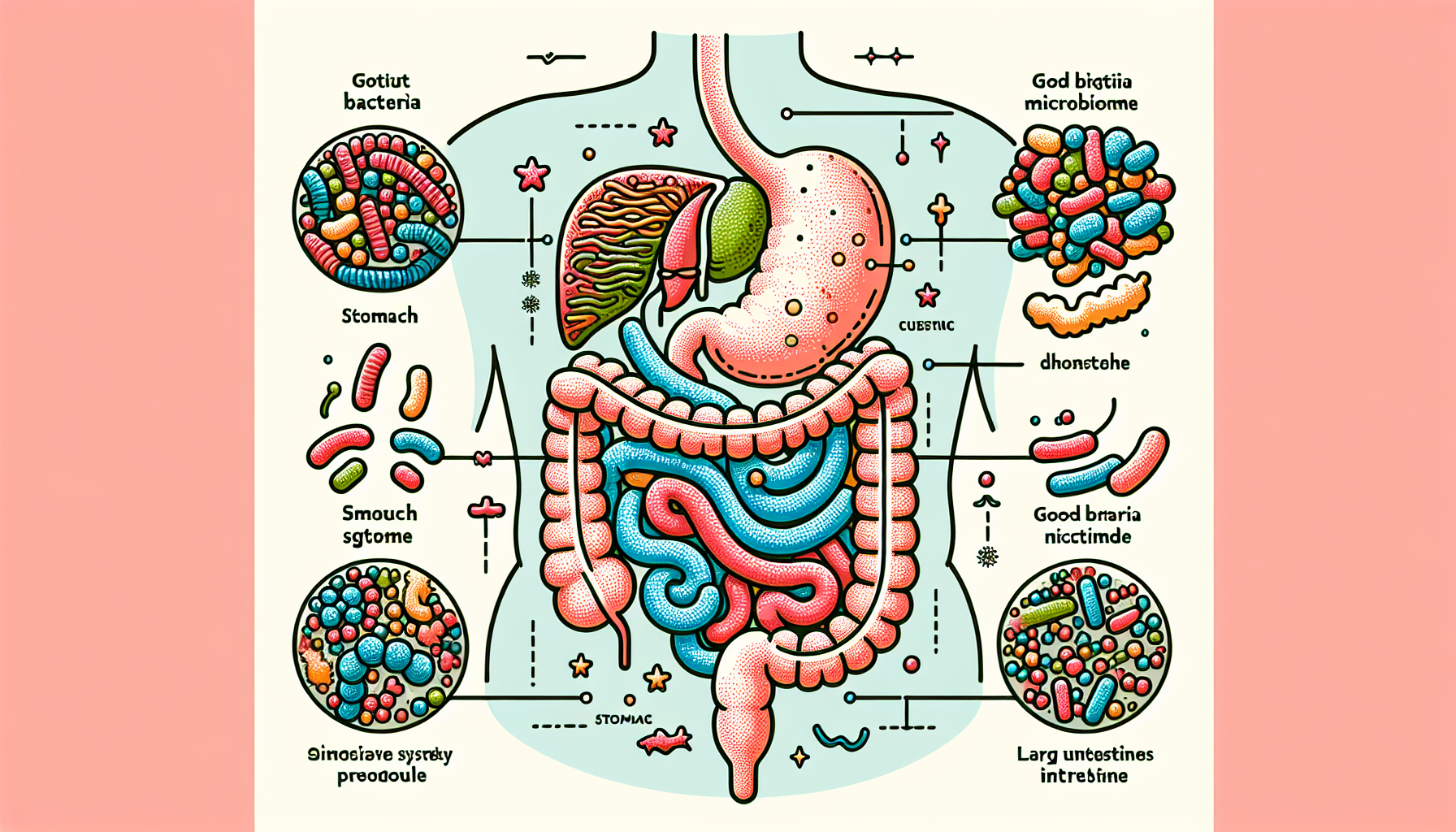
The Balance of Gut Microbiota
The human gut is home to a complex community of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms, collectively known as the microbiota. These microorganisms play a vital role in digestive health, aiding in the breakdown of food, absorption of nutrients, and the production of essential vitamins. They also contribute to the body’s immune function and can influence mood and energy levels.
Causes of Dysbiosis
Several factors can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiota, leading to dysbiosis. These include:
- Antibiotic Use: While antibiotics are essential for treating bacterial infections, their overuse or misuse can harm beneficial gut bacteria.
- Poor Diet: A diet high in processed foods and low in fiber can negatively affect gut microbiota.
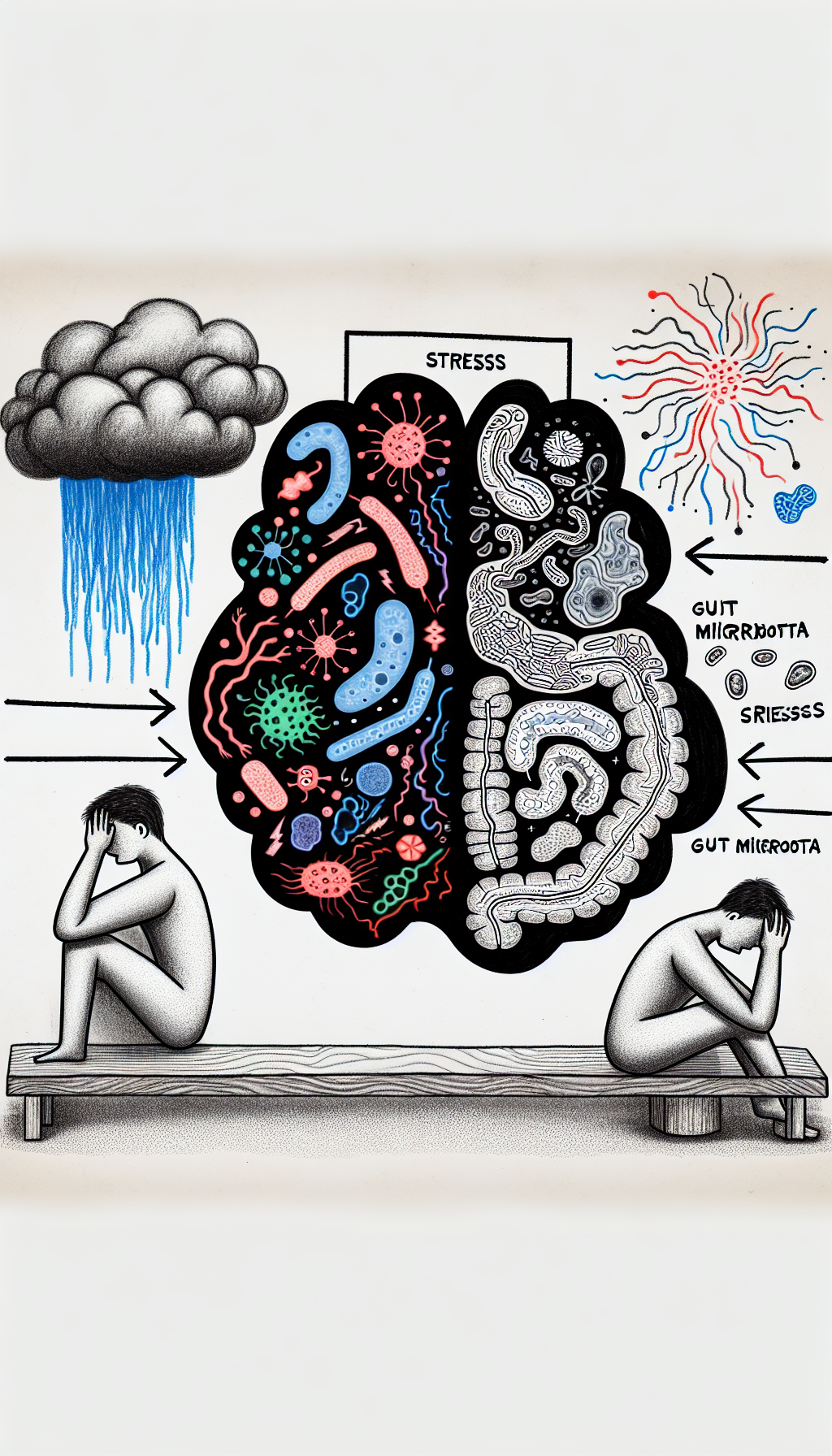
- Chronic Stress: Stress has been shown to alter the composition and function of the gut microbiota.
- Infections: Certain pathogens can invade and disrupt the gut ecosystem.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to toxins like pesticides can harm gut bacteria.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of dysbiosis can vary widely, but common signs include gastrointestinal issues like bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. Non-digestive symptoms may also arise, such as fatigue, skin problems, and mood fluctuations.
Diagnosing dysbiosis typically involves a detailed medical history and may include stool tests to analyze the composition of the gut microbiota.
Treatment Strategies
Treating dysbiosis involves a multifaceted approach aimed at restoring the balance of the gut microbiota:
Dietary Modifications
Adopting a diet rich in whole foods, fibers, and fermented products can nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Resources like the Harvard School of Public Health provide in-depth information on how diet influences the microbiome.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can confer health benefits, while prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed these beneficial bacteria. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics offers insights into the latest research on these supplements.
Lifestyle Changes
Reducing stress through techniques like meditation, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can positively affect gut health. The American Psychological Association discusses the connection between stress and physical health.
Medication
In some cases, antibiotics or antifungals may be necessary to target specific pathogens causing dysbiosis. Discussions with a healthcare provider are crucial to determine the appropriate course of action.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
For severe cases of dysbiosis, FMT is an emerging treatment that involves transferring stool from a healthy donor to the patient’s gut. The Fecal Transplant Foundation provides further information on this procedure.
Preventative Measures
Preventing dysbiosis is equally important as treating it. Measures include:
- Maintaining a Balanced Diet: Emphasizing a diet rich in diverse plant-based foods supports a varied gut microbiota.
- Mindful Medication Use: Only using antibiotics when necessary and completing the prescribed course can help preserve gut bacteria.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has been linked to increased microbial diversity in the gut.
The Role of Gut Microbiota in Disease Prevention
A balanced gut microbiota is not only essential for digestive health but also plays a role in preventing diseases. Research indicates that a healthy gut can protect against conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. To explore this topic further, consider reading The Role of Gut Microbiota in Disease Prevention.
Connection Between Diet and Dysbiosis
Dietary choices have a profound impact on the gut microbiota. The Mediterranean diet, for example, has been shown to have numerous digestive benefits, including promoting a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
Natural Approaches to Improve Gut Health
Incorporating natural and probiotic-rich foods into one’s diet is an effective strategy to enhance gut microbiota. To learn more about these dietary choices, the article on Using Probiotic Foods to Naturally Improve Gut Health is an excellent resource.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing dysbiosis is critical for maintaining optimal health. By addressing the causes and implementing effective treatments and preventative measures, individuals can support their gut microbiota and, consequently, their overall well-being. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that accommodates one’s unique health circumstances.
Remember, a healthy gut is a cornerstone of a healthy life, and with the right knowledge and actions, we can all strive towards better digestive health and beyond.