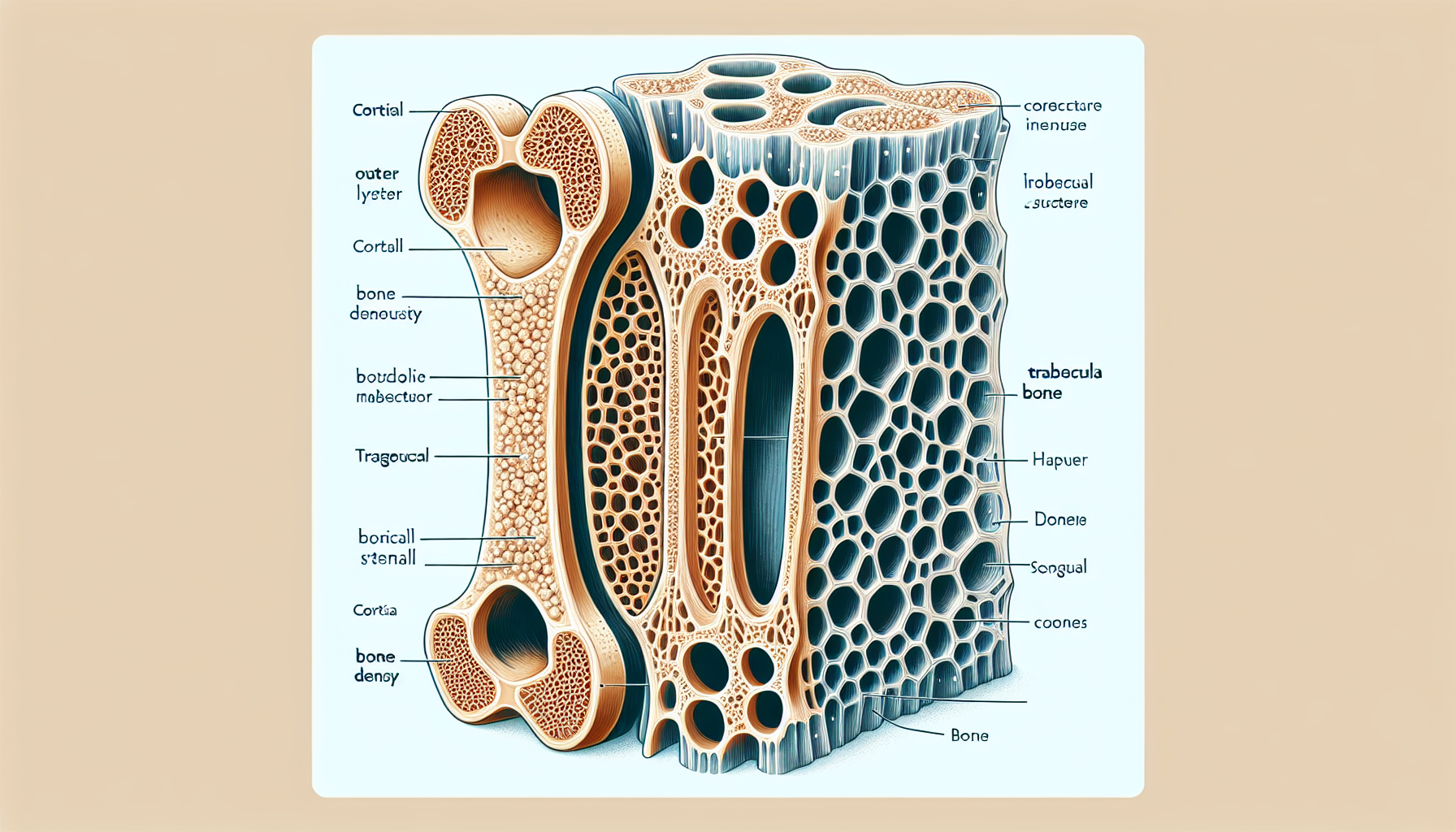
Bone health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, often overlooked until problems arise. Our bones are living tissues that continually remodel themselves, balancing between bone formation and bone loss. This balance is essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones throughout our lives. A holistic understanding of bone health encompasses the role of nutrition, exercise, hormonal balance, and genetics—all of which contribute to the integrity of our skeletal system.
The Importance of Calcium and Vitamin D
Calcium is the cornerstone of bone health. It is the primary mineral found in your bones, which acts as a reservoir for maintaining calcium levels in the blood, crucial for various functions. Adequate calcium intake is necessary to prevent the body from taking it away from the bones, which can lead to decreased bone density and strength. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods are traditional sources of calcium, but understanding their absorption and interaction with other nutrients is vital.
Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in calcium absorption and bone health. Without sufficient vitamin D, our bodies cannot effectively absorb calcium, which can lead to bone thinning and an increased risk of fractures. Sun exposure is a natural source of vitamin D, but due to lifestyle factors and geographical locations, many individuals may need supplements to achieve optimal levels.
For those seeking a deeper dive into the subject, The Importance of Calcium in Bone Strength provides extensive insights into the indispensable nature of calcium for our skeletal system.
Exercise and Bone Density
Physical activity is not just good for your muscles; it’s essential for your bones as well. Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, running, and resistance training, can help build and maintain bone density. During these activities, the bones adapt to the impact and the pull of muscle by building more bone cells, thus increasing strength.
For tailored exercise routines that can aid in improving bone density, consider exploring Exercise Routines for Improving Bone Density, which offers guidance on specific workouts that benefit skeletal health.
Hormones and Bone Density
Hormones significantly influence bone density, particularly estrogen in women and testosterone in men. These sex hormones can promote bone formation and slow down bone resorption. During menopause, decreased estrogen levels can lead to an accelerated bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Therefore, understanding hormonal changes at different life stages is essential for bone health management.
For a comprehensive view of how hormones affect bone density across various stages of life, the article How Hormones Affect Your Bone Density is an excellent resource.
The Role of Genetics in Bone Health
Genetics also plays a significant role in determining bone mass and susceptibility to bone diseases. Specific genetic markers can indicate whether an individual is more likely to experience bone health issues, which can be a valuable insight for preventive measures. However, environmental factors and lifestyle choices still have a substantial impact on bone health, which means that genetic predisposition isn’t the sole determinant of bone health.
For more details on this topic, delve into the research presented in The Role of Genetics in Bone Health.
Nutritional Supplements and Medications
While diet should be your primary source of essential nutrients, supplements can play a supportive role, especially when dietary intake is insufficient or specific health conditions warrant their use. Calcium and vitamin D supplements are commonly recommended for individuals at risk of bone density loss. However, the balance of supplementation should be carefully managed to avoid potential health risks associated with excessive intake.
For those who require medication to manage bone health conditions such as osteoporosis, it’s critical to understand the interactions between various prescriptions and over-the-counter supplements. Proper management can prevent adverse effects and enhance the efficacy of treatments.
A comprehensive guide on managing medication and supplements effectively can be found at Medication & Supplements.
External Resources for In-Depth Understanding
In pursuit of advanced knowledge, several niche resources can offer valuable information:
- A detailed analysis of bone remodeling and homeostasis can be found on EndocrineWeb, providing insights into the hormonal influences on bone health.
- The International Osteoporosis Foundation offers resources on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoporosis and related bone disorders.
- For those interested in genetic factors related to bone health, the National Center for Biotechnology Information provides extensive studies and findings on genetic markers and their implications.
- Research on the synergistic effects of nutrients on bone health can be explored through the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, which publishes peer-reviewed articles on bone biology and related disorders.
- Exercise and Sport Sciences Reviews presents scholarly reviews and scientific research on the impact of physical activity on bone health, among other topics.
By integrating knowledge from these resources with practical lifestyle changes and medical advice, one can develop a robust framework for maintaining and improving bone health. Remember, it’s not just about preventing issues; it’s about building a foundation that will support your overall health for years to come.