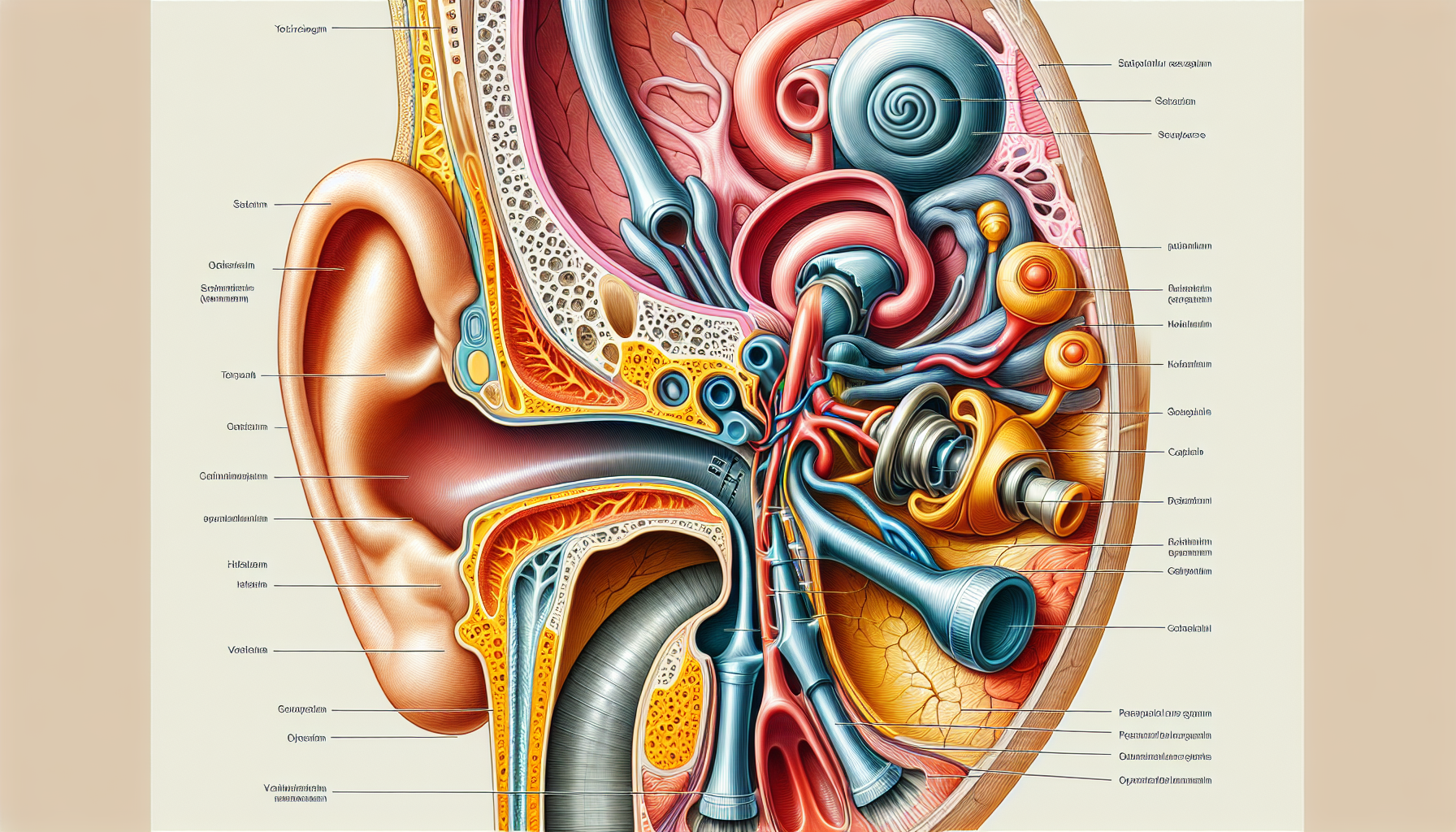
The vestibular system, a key component of our sensory apparatus, plays a critical role in our ability to interpret our environment and maintain balance. It is the sensory system that provides the leading contribution to our sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Understanding the intricacies of vestibular health is not only vital for maintaining everyday function but is also crucial for those with sensory processing disorders.
Vestibular System: The Body’s Balance Center
The vestibular system is located within the inner ear and is responsible for detecting changes in head movement and position. It works in harmony with other sensory systems, like the visual system and proprioception, to maintain postural equilibrium and orientation. The system is composed of the semicircular canals, which sense rotational movements, and the otolith organs (the utricle and saccule), which detect linear accelerations.
When vestibular function is compromised, individuals may experience symptoms such as dizziness, vertigo, balance issues, and difficulty with motor skills. These symptoms can have a profound impact on day-to-day activities and overall quality of life.
The Connection Between Vestibular Function and Sensory Health
The vestibular system’s role extends beyond balance and spatial awareness; it is deeply intertwined with overall sensory health. Sensory processing refers to the way the nervous system receives messages from the senses and turns them into appropriate motor and behavioral responses. Proper vestibular function is essential for adequate sensory processing. It is the foundation upon which the body builds its understanding of the sensory environment.
Disorders related to vestibular health can lead to or exacerbate sensory processing disorders (SPD). People with SPD may find it difficult to process and act upon information received through the senses, which can lead to considerable challenges in performing countless tasks.
Vestibular Health’s Impact on Development and Daily Life
Vestibular health is especially important in childhood development. Children learn to interact with their environment largely through movement and balance. The role of sensory play in childhood development is well-documented, and activities that stimulate the vestibular system are a key part of this.
In adults, vestibular disorders can affect various aspects of daily life, including the ability to focus and maintain concentration. This is particularly significant for individuals with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), as highlighted in the article discussing sensory health strategies for people with ADHD.
Diagnosing Vestibular Disorders
Diagnosing vestibular disorders starts with a thorough evaluation by a healthcare provider, often including a detailed history and physical examination, as well as specialized tests. These tests can range from simple bedside examinations to more complex assessments like videonystagmography (VNG) or rotary chair testing.
Early diagnosis and intervention are vital to manage symptoms and improve outcomes. For instance, vestibular rehabilitation therapy (VRT) is a specialized form of therapy aimed at alleviating primary and secondary problems caused by vestibular disorders.
Treatment and Management of Vestibular Disorders
Treatment for vestibular disorders varies based on the underlying cause and the symptoms presented. Options include:
- Vestibular rehabilitation therapy
- Medications to relieve symptoms like nausea or dizziness
- Surgical interventions in certain cases
- Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and stress management
Additionally, technologies for managing sensory processing disorders have advanced, offering new avenues for coping with the challenges brought on by vestibular dysfunction.
The Role of Exercise in Vestibular Health
Exercise plays a critical role in maintaining vestibular health. Activities that challenge the body’s balance and spatial orientation can help to keep the vestibular system finely tuned. Effective sensory diet exercises for various ages include those that incorporate balance, coordination, and spatial orientation, all of which engage the vestibular system.
Understanding the Broader Impact of Vestibular Health
The effects of vestibular dysfunction extend beyond physical symptoms. It can also affect emotional and mental health, contributing to feelings of anxiety and depression. Addressing vestibular health is, therefore, a holistic process that can involve multiple therapeutic approaches, including cognitive-behavioral therapy and mindfulness practices.
External Resources for Further Reading
For those interested in exploring vestibular health and sensory processing further, the following resources provide valuable information:
- Vestibular Disorders Association (VEDA) offers resources for understanding vestibular disorders, including diagnostic tools and treatment options.
- The American Occupational Therapy Association provides insights into how occupational therapy can assist with vestibular health and sensory processing disorders.
- The Sensory Processing Disorder Foundation offers a wealth of information on sensory processing issues and strategies for coping with them.
- The International Society for Neurofeedback & Research presents research on neurofeedback and its potential benefits for those with vestibular and sensory processing disorders.
Conclusion
Vestibular health is a cornerstone of sensory processing and overall well-being. By understanding its role and the effects of its dysfunction, individuals and healthcare professionals can better approach the challenges associated with sensory processing disorders. Through early diagnosis, effective treatment, and ongoing management, individuals with vestibular disorders can achieve improved quality of life and greater success in their daily activities. The nexus of vestibular health and sensory processing is a field ripe with opportunities for further research and development, promising even more sophisticated approaches to treatment and management in the future.