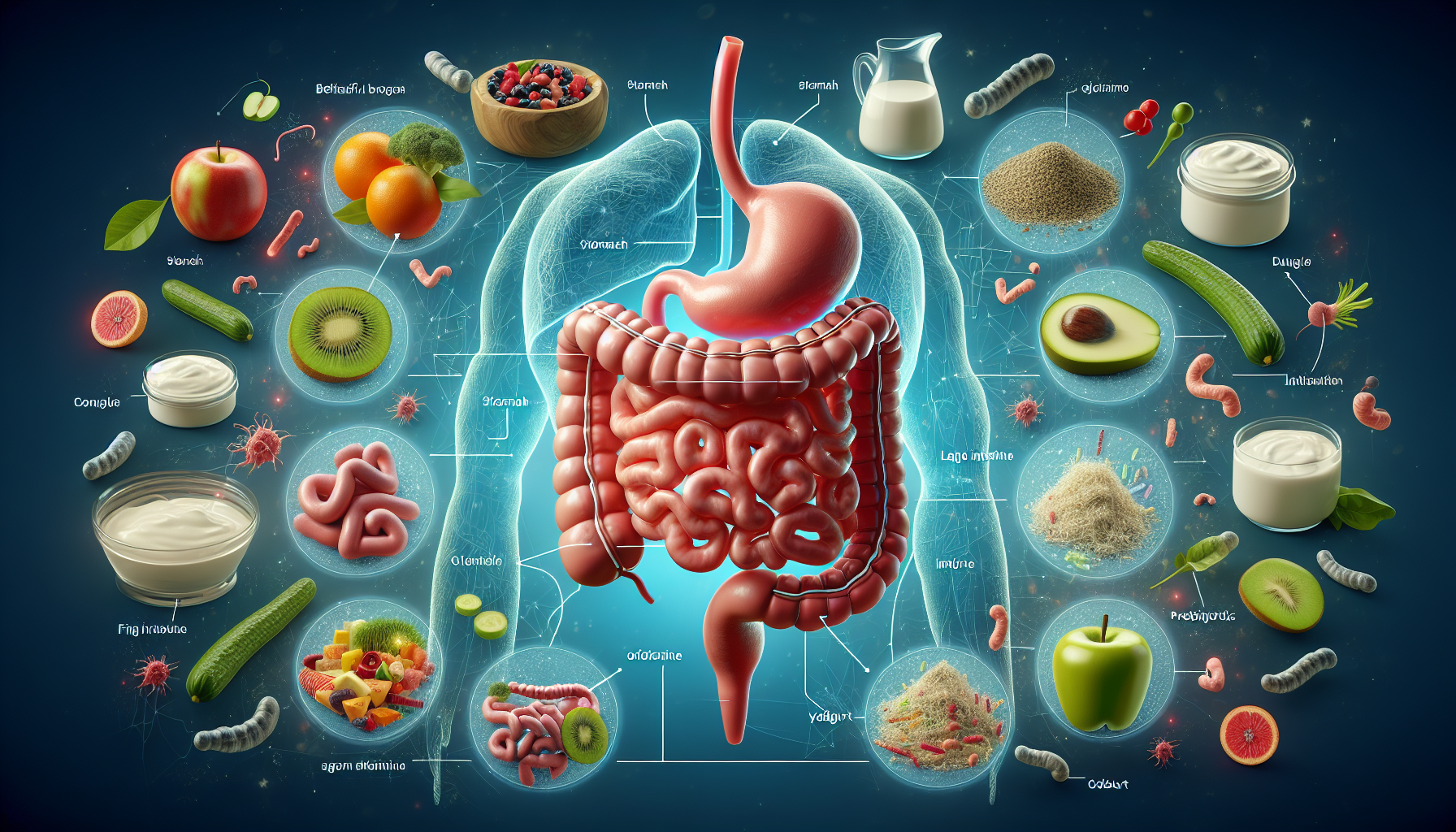
Gut health is a critical aspect of overall wellbeing that often goes unnoticed until problems arise. The digestive system, or the ‘gut’, is not only responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients but also plays a vital role in the immune system, mental health, endocrine functions, and even the condition of your skin. This holistic influence of gut health on our bodies and minds underscores its significance.
When discussing gut health, it is essential to understand the complex system of bacteria living in the digestive tract, known as the gut microbiome. This community of microorganisms can be thought of as a bustling city within our bodies, carrying out essential functions that contribute to our overall health.
Gut Microbiome: The Unsung Hero of Health
The gut microbiome consists of trillions of bacteria, both beneficial and harmful. Maintaining the right balance of these bacteria is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, and the production of key vitamins, such as Vitamin K and some B vitamins. Research has also linked the gut microbiome to broader aspects of health, including mental health and chronic diseases.
A well-balanced microbiome can be nurtured through a variety of means, one of which is the use of CBD. While research is still ongoing, preliminary studies suggest that CBD may have an impact on the gut microbiome, influencing inflammation and the overall health of the digestive system.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut is often referred to as the second brain due to the enteric nervous system—millions of neurons that line the gastrointestinal tract and communicate with the central nervous system. This connection is so strong that the state of your gut can influence your mood and cognitive functions, giving rise to the concept of the "gut-brain axis." This is why managing stress is crucial, as chronic stress can upset your digestive system, leading to a range of health issues.
Immunity and the Gut
The gut plays a substantial role in the body’s immune response. A significant portion of the immune system is housed in the digestive tract. A healthy gut helps to ensure an effective immune response to pathogens, whereas an imbalanced gut microbiome can lead to a weakened immune system, making you more susceptible to infections and disease.
For a more in-depth understanding of the immune system’s relationship with the gut, consider reading about The Relationship Between Digestive Health and Immunity.
Dietary Fiber: A Cornerstone of Gut Health
One of the most important elements for a healthy gut is dietary fiber. Found in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, fiber serves as a prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in the gut. The fermentation of fiber by these bacteria produces short-chain fatty acids, which have been shown to support gut health and reduce inflammation.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria that add to the population of good bacteria in your digestive system. These can be found in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, or taken as supplements. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that feed these beneficial bacteria. Both are essential for maintaining a healthy gut ecosystem.
For more information on nurturing a healthy gut microbiome, you might want to explore Probiotics and Prebiotics: Nourishing a Healthy Gut Microbiome.
The Role of Hydration in Gut Health
Hydration is another key factor in digestive health. Water helps dissolve fats and soluble fiber, allowing these substances to pass through more easily. Moreover, staying hydrated ensures that the mucosal lining of the intestines remains intact, which is essential for nutrient absorption and preventing pathogens from entering the bloodstream.
The importance of hydration in digestive health is further explained in The Role of Hydration in Maintaining Digestive Health.
External Resources for Further Reading
To delve deeper into the specifics of fiber’s role in gut health, The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition provides peer-reviewed articles and studies on dietary fiber and its health implications.
Those interested in the gut-brain axis and its impact on mental health can find valuable insights at the International Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility, a resource dedicated to the study of gut-brain interactions.
For data on the gut’s immunity functions, the National Institutes of Health offers a plethora of research articles and information on the immune system and the human microbiome.
Conclusion
The significance of gut health extends far beyond the process of digestion. It is intricately connected to various aspects of our overall health, from mental wellbeing to immunity. By incorporating a balanced diet rich in fiber, staying hydrated, managing stress, and possibly integrating supplements like probiotics, prebiotics, and even CBD, we can support our gut health and, by extension, our overall wellbeing.
Gut health is an ongoing journey, and understanding its importance is the first step towards a healthier, happier life.