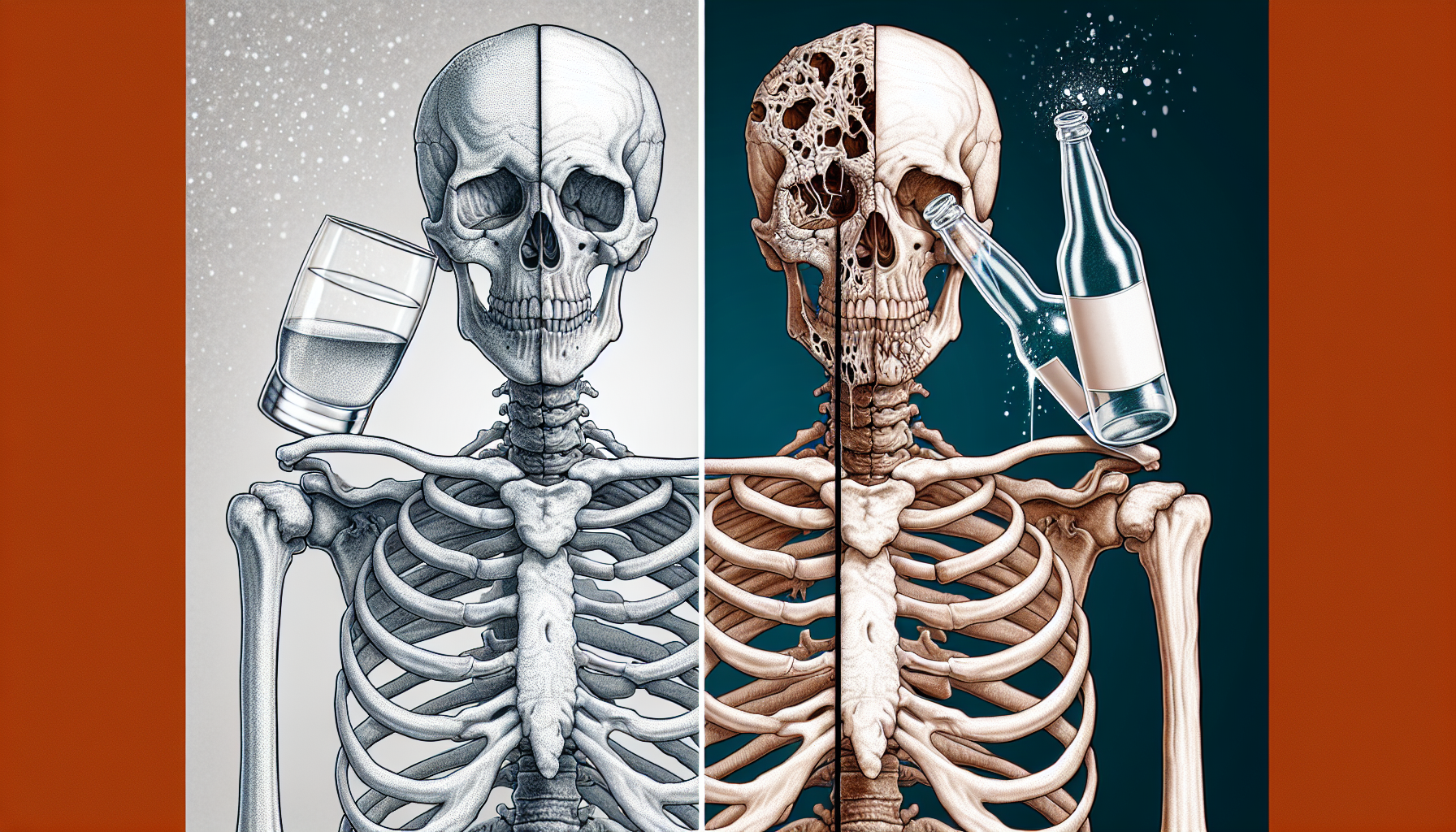
Excessive alcohol consumption is a widely recognized health hazard, known to affect various systems within the body, including the liver, brain, and cardiovascular system. However, its impact on bone health is often overlooked, despite the critical role that bones play in our overall well-being. The skeletal system not only provides structural support but also aids in the protection of internal organs, the anchorage of muscles, and the storage of essential minerals. Understanding the influence of alcohol on our bones is vital in maintaining long-term health and preventing osteoporosis and fractures.
Alcohol’s Impact on the Skeletal System
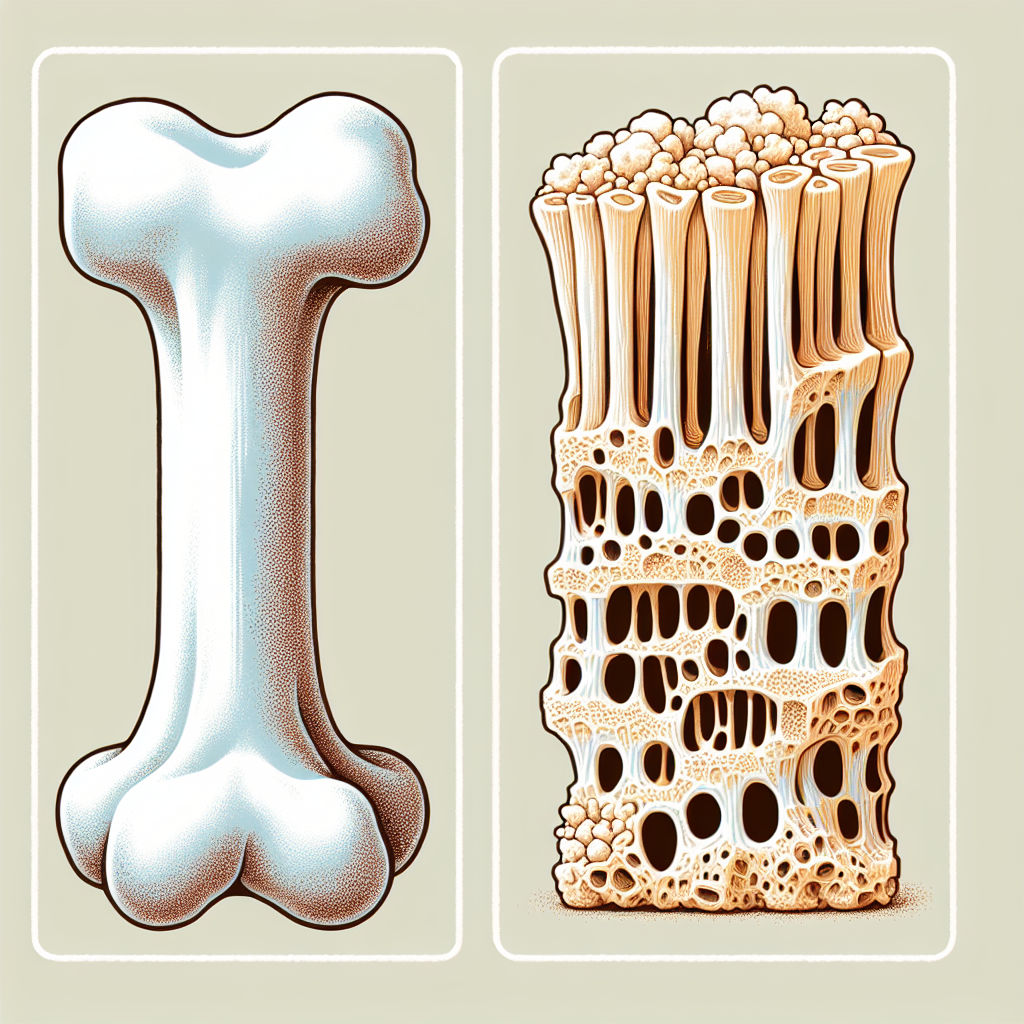
Excessive alcohol intake disrupts the balance of bone remodeling, a natural process where old bone tissue is replaced by new bone tissue. This disruption can lead to decreased bone density and an increased risk of fractures. Alcohol affects the bones in several ways:
-
Inhibiting Osteoblast Activity: Osteoblasts are cells responsible for forming new bone. Alcohol can suppress the function and proliferation of these cells, leading to diminished bone formation.
-
Increasing Osteoclast Activity: In contrast to osteoblasts, osteoclasts break down bone tissue. Alcohol can stimulate these cells, leading to accelerated bone loss.
-
Impairing Calcium Absorption: Calcium is a critical mineral for bone health. Alcohol can interfere with calcium absorption in the gut and its reabsorption in the kidneys, leading to calcium deficiencies.
-
Disrupting Hormone Regulation: Alcohol alters the production of hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol, which play a role in bone health. For example, reduced estrogen levels can lead to bone loss in women.
-
Affecting Nutrition: Heavy drinkers often have poor diets, lacking essential nutrients for bone health like vitamin D and magnesium.
For a deeper understanding of the essential role of bone health and how to maintain it, consider the comprehensive resource found here.
The Intersection of Alcohol and Nutritional Deficiencies
The relationship between alcohol consumption and nutrient deficiencies is well-established. Alcohol can impair the absorption and metabolism of critical nutrients like vitamin D and calcium, which are essential for maintaining strong bones. Without sufficient vitamin D, calcium absorption is diminished, and without adequate calcium, the bones become weak and more susceptible to fractures.
Furthermore, alcohol may lead to malnutrition by replacing caloric intake with non-nutritive calories, leading to a decreased intake of foods that are beneficial for bone health. The importance of a nutrient-rich diet for maintaining bone density cannot be overstated, as highlighted in the article on Vegan Sources of Calcium and Vitamin D for Bone Health.
Lifestyle Choices and Bone Health
While the negative effects of excessive alcohol on bone health are clear, it’s also important to focus on positive lifestyle choices that can enhance bone strength. Weight-bearing exercises, for example, are known to be beneficial for bone density, as they encourage the development of new bone tissue. For more insight into how exercise affects bone health, the article on Understanding the Impact of Weight-Bearing Exercises on Bone Health offers valuable information.
The Role of Hydration in Bone Health
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health. Adequate fluid intake is essential for nutrient transportation and chemical reactions in the body, including those that involve bone tissue. Dehydration can affect the balance of minerals and impede the bone remodeling process. To learn more about the vital role of hydration in bone health, read the insights provided in The Importance of Hydration for Bone Health.
Addressing Alcohol-Related Bone Damage
If bone damage due to alcohol consumption has already occurred, it is essential to address it proactively. This includes reducing or eliminating alcohol intake, improving dietary habits, engaging in regular physical activity, and possibly incorporating supplements or medications to support bone health. Consulting healthcare professionals and considering a bone density test can provide personalized strategies for recovery and maintenance.
For those with health conditions that exacerbate bone health issues, such as rheumatoid arthritis, tailored approaches to managing bone health are necessary. The article on How to Manage Bone Health with Rheumatoid Arthritis provides guidance in such scenarios.
External Resources to Further Understand Bone Health
-
International Osteoporosis Foundation: Offers extensive information on bone health, including the risks associated with alcohol and strategies for prevention and management of osteoporosis.
-
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism: Provides research and publications on the effects of alcohol on health, including its impact on the skeletal system.
-
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: Features scientific studies and articles that discuss the relationship between nutrition, lifestyle choices, and bone health.
-
The Journal of Bone and Mineral Research: A peer-reviewed journal with articles on the latest research related to bone metabolism and the effects of various substances, including alcohol, on bone health.
Conclusion
The effects of excessive alcohol on bone health are significant and multifaceted, impacting bone density, strength, and the body’s ability to repair and form new bone tissue. By understanding these effects and making informed choices about alcohol consumption and lifestyle habits, individuals can take proactive steps toward preserving their skeletal health and overall well-being. As with any health issue, it is essential to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment.
Remember, your bones are the framework of your body, and taking care of them is crucial for a healthy, active life. Recognize the risks associated with excessive alcohol use and prioritize your bone health today.