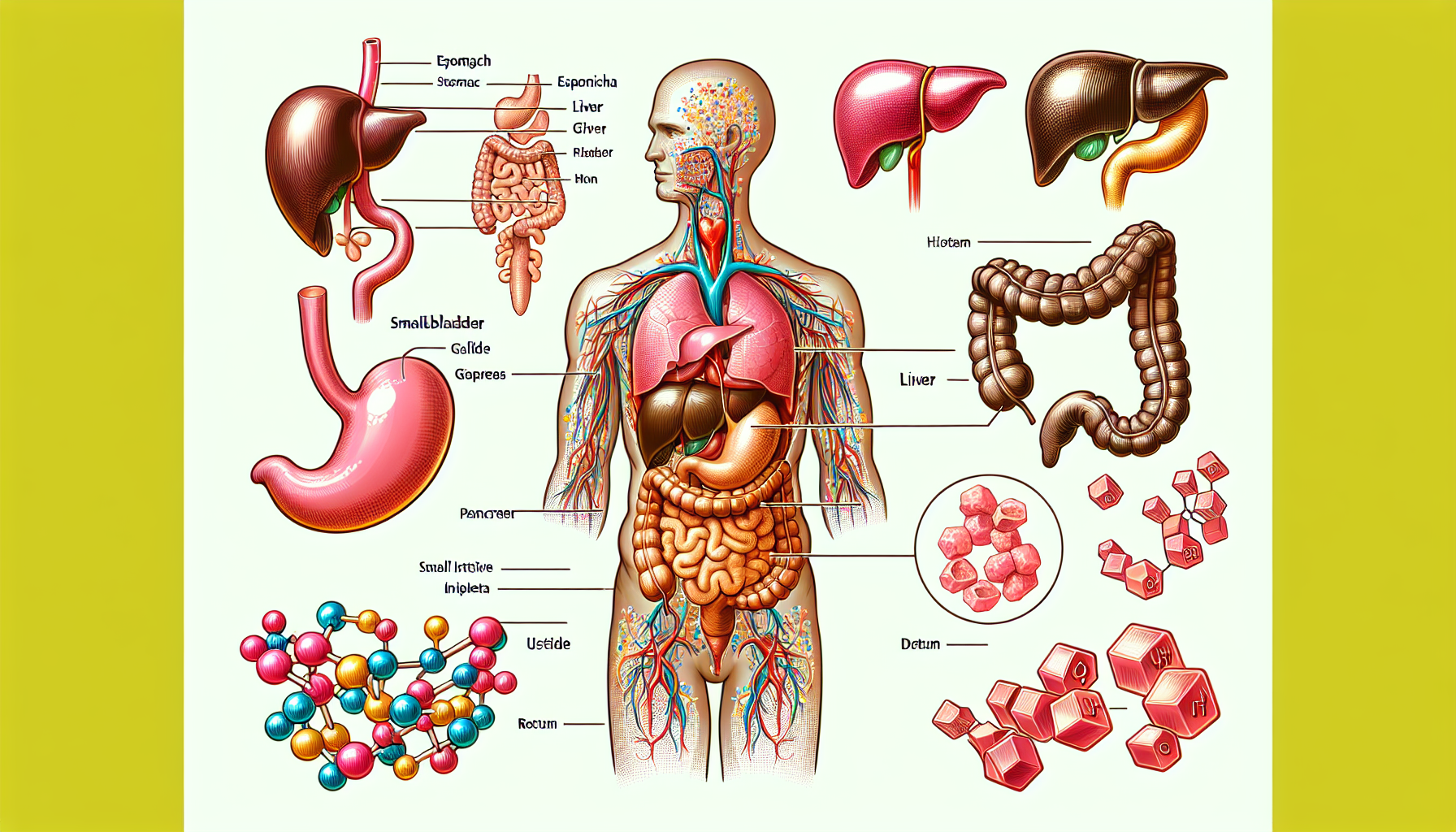
Cholesterol is a fatty substance that’s vital for the normal functioning of the body. While it’s often discussed in the context of cardiovascular health, its impact on digestive health is equally significant but less frequently acknowledged. Cholesterol plays a critical role in digestion, from forming bile acids that help digest fat to influencing the structure and function of cell membranes in the digestive tract.
How Cholesterol Affects Digestive Health
Cholesterol is essential for the production of bile, a fluid produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile acids, which are components of bile, emulsify fats in the diet, which is crucial for their digestion and absorption in the intestines. Without adequate cholesterol, bile acid production can be compromised, leading to difficulties in processing dietary fats, which can contribute to various digestive disorders.
Bile Acid Synthesis and Digestive Function
Cholesterol is converted into bile acids by the liver cells. These acids are then released into the small intestine where they play a pivotal role in breaking down fats so that they can be absorbed by the body. A deficiency in bile acids can lead to fat malabsorption and symptoms such as diarrhea and steatorrhea (the excretion of abnormal quantities of fat with the feces due to reduced absorption of fat by the intestines).
Cholesterol and the Cell Membranes
Every cell in the body, including those in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, is surrounded by a membrane that contains cholesterol. This cholesterol is crucial for maintaining the integrity and fluidity of cell membranes. It influences nutrient transport and cellular communication, which are vital for the proper functioning of the digestive system.
The Role of Diet in Cholesterol and Digestive Health
Diet plays a crucial role in managing cholesterol levels and, by extension, digestive health. Consuming a diet high in fiber, particularly soluble fiber, can help reduce the absorption of cholesterol in the intestines and promote a healthy balance of gut flora, essential for optimal digestive function.
Foods That Affect Cholesterol and Digestive Health
Certain foods can influence cholesterol levels and digestive health positively or negatively. For instance, high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help lower cholesterol levels. In contrast, foods high in saturated fats and trans fats can increase cholesterol levels, potentially leading to digestive issues.
The Impact of High Cholesterol on Digestive Diseases
High cholesterol levels can lead to the development of gallstones, which are primarily made of hardened cholesterol. Gallstones can cause significant digestive discomfort and may necessitate medical intervention.
For more insights into how dietary choices influence digestive health, readers can explore Evaluating the Role of Diet in Peptic Ulcer Disease, which provides a deeper understanding of the connection between nutrition and digestive conditions.
Cholesterol, Digestive Disorders, and Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota, the community of microbes residing in our intestines, has a profound influence on both cholesterol metabolism and digestive health. Certain gut bacteria can metabolize cholesterol, potentially reducing its levels in the body.
The Interplay Between Cholesterol and the Microbiome
Research suggests that the gut microbiome can influence cholesterol levels by affecting how much cholesterol is absorbed from the diet into the bloodstream and how much is excreted. A healthy microbiome, promoted by a diet rich in prebiotics and probiotics, can therefore support the management of cholesterol levels and enhance overall digestive health.
Understanding the role of the microbiome is further explored in The Impact of Sleep Patterns on Digestive Health, which discusses how lifestyle factors can affect gut bacteria and consequently, digestive health.
Probiotics and Cholesterol
Probiotic foods and supplements can have a positive effect on cholesterol levels. Certain strains of probiotics have been shown to help reduce cholesterol by breaking it down or by preventing its absorption in the intestine.
For a comprehensive understanding of gut flora and its benefits, reading about Strategies to Enhance Gut Flora and Promote Digestive Balance is recommended.
Managing Cholesterol for Optimal Digestive Health
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels is crucial for digestive health. Here are some strategies to achieve this:
- Diet: Adopting a diet low in saturated fats and rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help manage cholesterol levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), the "good" cholesterol, which helps remove excess cholesterol from the body.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage cholesterol levels effectively. Statins are commonly prescribed to lower low-density lipoprotein (LDL), the "bad" cholesterol, levels in the blood.
- Supplements: Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, niacin, and soluble fiber, may help manage cholesterol levels. However, always consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
For more information on supplements and their role in managing cholesterol, visit Medication & Supplements.
External Resources Supporting the Connection Between Cholesterol and Digestive Health
- The American Heart Association’s Guide to Dietary Fats
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases on Gallstones
- The Impact of Probiotics on Cholesterol Levels
- Gut Microbiota for Health by the European Society for Neurogastroenterology & Motility
- Exercise and its Effects on Serum Cholesterol
In conclusion, cholesterol and digestive health are intricately connected. Cholesterol is not only pivotal in the digestion and absorption of fats but also influences the integrity of the GI tract and the composition of the gut microbiota. Maintaining balanced cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and, when necessary, medication and supplements is essential for ensuring a healthy digestive system. Understanding this connection can lead to more comprehensive health strategies that encompass both heart and digestive wellness.