Omega-3 fatty acids are renowned for their myriad of health benefits, including their ability to support cardiovascular and brain health. However, recent research has unveiled another important facet of these polyunsaturated fats: their significant role in maintaining and improving bone density and joint health. This article delves into the science behind Omega-3s and their impact on skeletal integrity, offering insights into how these essential nutrients can be integrated into one’s diet for optimal bone and joint function.
Understanding Bone Density and Its Importance
Bone density refers to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones. It is a critical indicator of bone strength and overall skeletal health. Healthy bone density is crucial as it helps prevent osteoporosis and reduces the risk of fractures. The maintenance of bone density is a dynamic process involving the interplay of various nutrients, hormones, and lifestyle factors. Exploring the role of antioxidants in bone repair and regeneration provides a deep dive into how different nutrients contribute to bone health.
The Link Between Omega-3s and Bone Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), are found in high concentrations in fish oil and have been shown to influence bone density. These fats assist in the regulation of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption, respectively. Omega-3s can modulate the production of inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins, which, when produced in excess, can lead to increased bone loss.
Research indicates that a higher intake of Omega-3s is linked to improved bone density. For instance, a study published in the "American Journal of Clinical Nutrition" found that increased Omega-3 intake was associated with enhanced bone mineral density in older adults.
Joint Health and Omega-3s: Easing the Burden of Arthritis
Joint health is another area where Omega-3s exhibit beneficial properties. These fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects that can alleviate symptoms of arthritis, such as joint pain and stiffness. By incorporating Omega-3s into the diet, individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may experience a reduction in joint inflammation, leading to improved mobility and a reduced need for nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Integrating Omega-3s into Your Diet for Bone and Joint Health
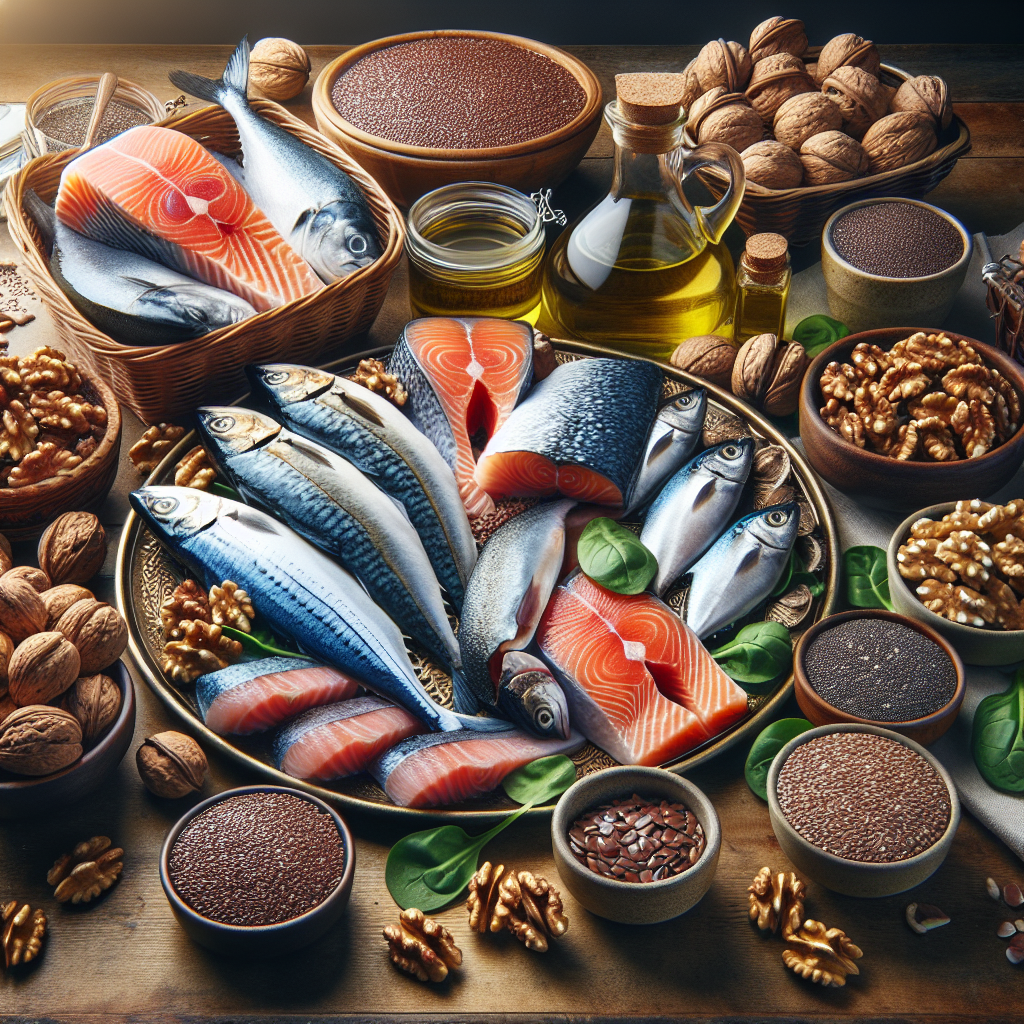
To harness the benefits of Omega-3s for bone and joint health, it is essential to include Omega-3-rich foods in your diet. Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources. For those who do not consume fish, algae-based supplements are a viable alternative. Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts also provide a plant-based source of Omega-3s, primarily in the form of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), which the body can partially convert to EPA and DHA.
The Role of Exercise in Conjunction with Omega-3s for Bone Health
While Omega-3s play a critical role in bone and joint health, they should be part of a broader approach that includes regular exercise. Weight-bearing and muscle-strengthening exercises are particularly beneficial for bone density. For more information on optimizing physical activity for bone health, Optimizing Bone Health in Children: The Role of Physical Activity offers valuable insights.
Omega-3 Supplementation: Things to Consider
For those considering Omega-3 supplements, it is important to choose high-quality products and to be aware of the correct dosage. Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended to determine the appropriate amount based on individual health needs and to avoid potential interactions with other medications.
External Resources Supporting Omega-3s for Bone Health
Several high-quality, niche resources provide further evidence of the role of Omega-3s in bone density and joint health:
- A systematic review in the Journal of Osteoporosis discusses the potential of Omega-3 fatty acids in preventing osteoporosis.
- The Arthritis Foundation offers detailed guidance on how the fatty acids in fish can help with arthritis symptoms.
- Research published in Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids investigates the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids on bone metabolism.
Conclusion
The role of Omega-3 fatty acids in bone density and joint health is an evolving field with promising potential. As part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle, Omega-3s can contribute significantly to maintaining strong bones and flexible joints. Whether through natural food sources or supplementation, increasing the intake of these essential nutrients could be a strategic move for those looking to support their skeletal health as they age.
For further reading on related topics, articles such as Nutrients That Support Bone Health Beyond Calcium and Vitamin D and Combating the Risk of Osteoporosis Through Diet and Exercise delve into additional strategies to enhance bone health.
Incorporating Omega-3s into your health regimen could not only benefit your bones and joints but also contribute to overall wellness. As always, it is crucial to take a comprehensive approach to health, considering all aspects of diet and lifestyle for the best outcomes.