Gastric ulcers, also known as peptic ulcers, are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach. While they can be a source of significant discomfort and potential complications, understanding the symptoms and available treatments can empower individuals to manage their condition effectively. This comprehensive guide offers insights into recognizing symptoms, exploring causes, and treatment options for those suffering from gastric ulcers.
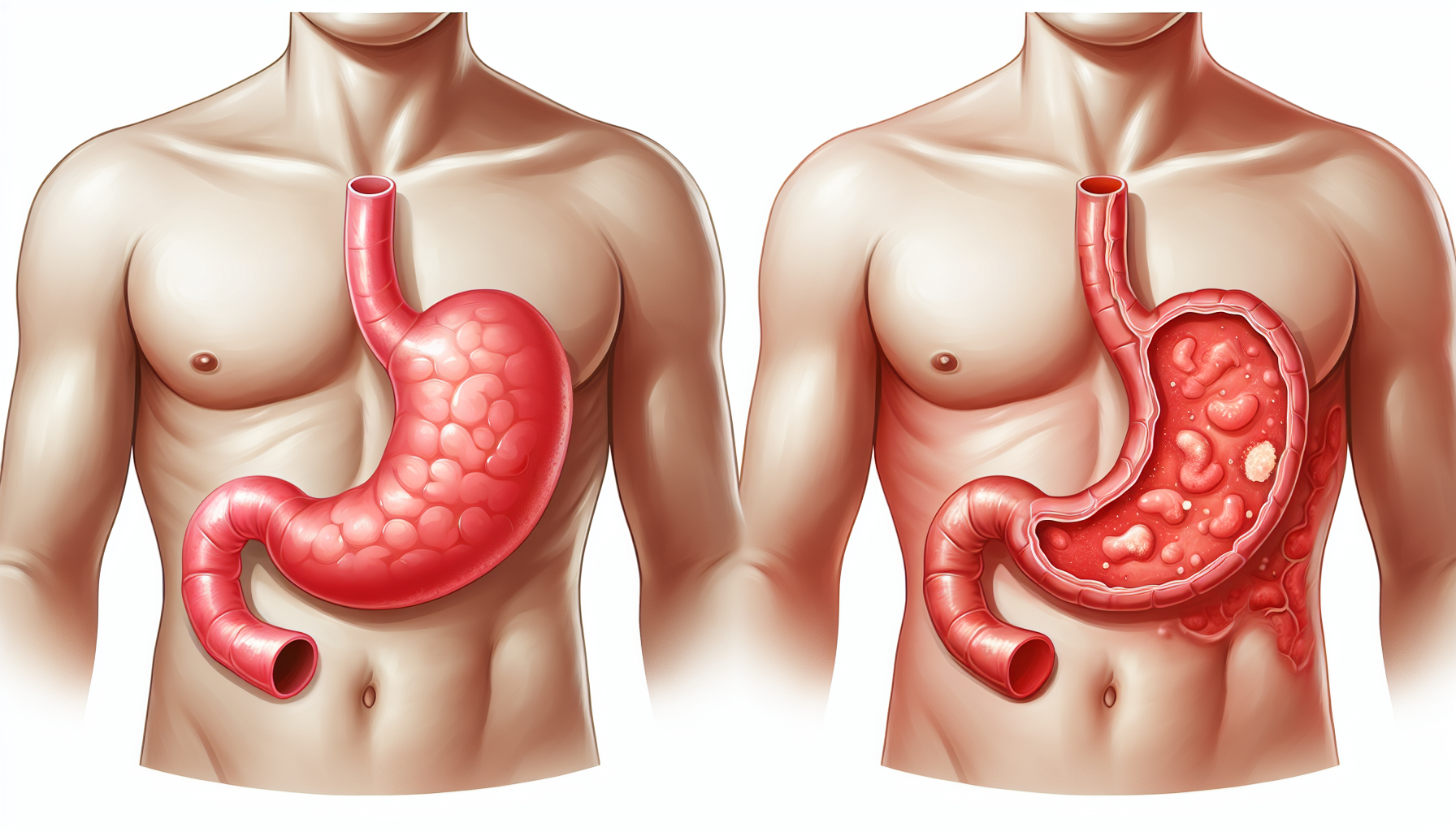
Understanding Gastric Ulcers
The stomach’s mucous layer protects it from acidic digestive juices. However, when this barrier is compromised, acids can erode the stomach lining, leading to ulcers. Several factors can contribute to this breakdown, including the overuse of certain medications, like NSAIDs, and infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
Symptoms to Watch For
Gastric ulcers can manifest through a variety of symptoms. The most common include:
- Persistent stomach pain
- Bloating and abdominal fullness
- Heartburn or indigestion (dyspepsia)
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Symptoms that worsen at night or between meals
In some cases, more severe symptoms such as vomiting blood or black stools may indicate bleeding within the stomach, which requires immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing gastric ulcers, including:
- Chronic use of NSAIDs
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Smoking and use of tobacco
- Stress (although not a direct cause, it can exacerbate symptoms)
- A family history of ulcers
Diagnostic Approaches
If you’re experiencing symptoms that suggest a gastric ulcer, it’s essential to seek a professional diagnosis. Your healthcare provider may recommend an endoscopy, a procedure where a small camera is used to view the stomach lining directly. Alternatively, non-invasive tests for H. pylori or other biomarkers can also provide valuable information.
Treatments for Gastric Ulcers
The treatment for gastric ulcers depends on the underlying cause. If H. pylori infection is present, eradication therapy typically involves a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications. For those related to NSAID use, cessation of the offending drug, alongside acid suppression therapy, can lead to healing.
Medications
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Reduce stomach acid production, creating an environment that allows ulcers to heal.
- H2-Receptor Antagonists: Another class of acid reducers, though not as potent as PPIs.
- Antacids: Over-the-counter options for immediate symptom relief.
- Cytoprotective Agents: Medications like sucralfate that protect the stomach lining.
Lifestyle Modifications
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly aid in the treatment and prevention of gastric ulcers. These include:
- Adopting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber
- Limiting spicy and acidic foods if they worsen symptoms
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques (Impact of Stress Reduction on Digestive Efficiency)
- Avoiding NSAIDs and seeking alternatives for pain relief
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake
Adopting a holistic approach to health can also be beneficial. For instance, maintaining Digestive Health is crucial for preventing and managing gastric ulcers effectively.
Complications of Gastric Ulcers
Without proper treatment, gastric ulcers can lead to complications such as bleeding, perforation, and gastric obstruction. It’s vital to recognize the signs of these complications, which include sudden, severe abdominal pain, fainting, and unexplained weight loss.
Complementary Therapies
Some individuals find relief through complementary therapies such as:
- Probiotics (Using Probiotic Foods to Naturally Improve Gut Health)
- Herbal remedies like licorice and slippery elm
- Specific vitamins or supplements (Connection Between Vitamin D and Gut Health)
However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new therapy to ensure it’s safe and appropriate for your situation.
Preventing Gastric Ulcers
Prevention is always better than cure. Steps to prevent the development of gastric ulcers include:
- Avoiding the overuse of NSAIDs
- Eating regular, balanced meals
- Managing stress effectively
- Regular check-ups, especially if you have a family history of ulcers
Seeking Support
Living with gastric ulcers can be challenging, but support is available. Whether it’s through healthcare providers, support groups, or educational resources, don’t hesitate to seek help (The Benefits of Digestive Health Support Groups).
Conclusion
Gastric ulcers are a common and treatable condition. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment can lead to a significant improvement in quality of life. By combining medical interventions with lifestyle changes and possibly complementary therapies, individuals can manage their symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
For further reading on the role of diet and supplements in managing digestive disorders, consider exploring resources such as the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Remember, while this guide provides a comprehensive overview of gastric ulcers, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.