Maintaining bone health is a critical aspect of overall wellness, especially as we age. Bones are the support system of the body, so it’s vital to keep them strong and healthy. Nutrition plays a significant role in bone health, and understanding which nutrients are necessary can help you keep your bones in top condition. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential nutrition tips for fostering healthy bones.
The Foundation of Bone Health
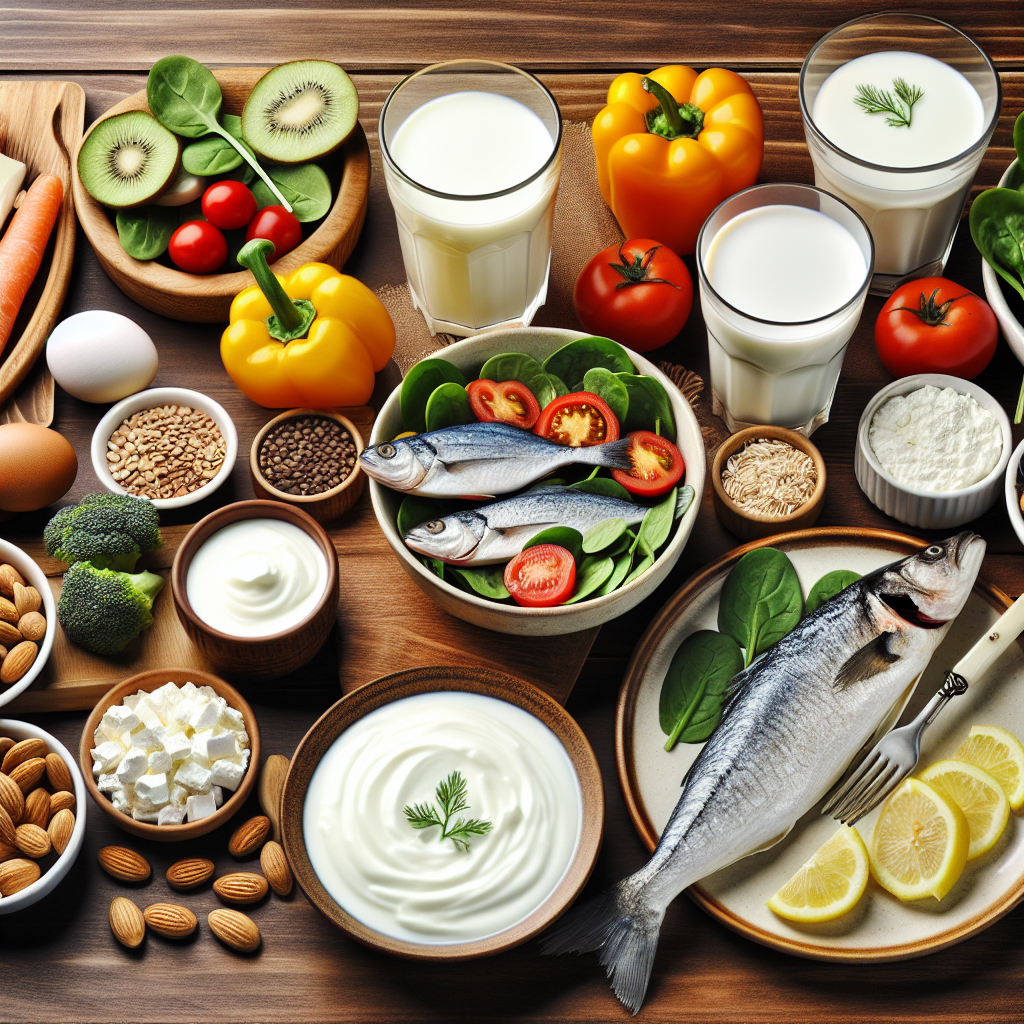
Bones are living tissue that continually undergoes a process of breakdown and renewal. For this renewal process to be effective, a balanced diet rich in specific nutrients is essential. The most well-known of these is calcium, a mineral that is vital for maintaining bone density and strength. However, calcium isn’t effective on its own; it works in tandem with other nutrients, such as vitamin D, which helps the body absorb calcium.
To ensure optimal bone health, it’s crucial to consume a variety of nutrients. For a more detailed understanding of how different factors influence bone health, consider exploring Bone Health for further information.
Calcium: The Building Block
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and is a critical building block of bone tissue. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are rich in calcium. For those who are lactose intolerant or vegan, other good sources of calcium include fortified plant-based milks, leafy green vegetables, and almonds.
Vitamin D: The Helper
Vitamin D is essential for bone health because it helps the body absorb calcium. Without sufficient vitamin D, our bones can become thin and brittle. The body naturally produces vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, but it can also be found in fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods.
Magnesium and Phosphorus: Supporting Roles
Magnesium and phosphorus are two more minerals that play a significant role in bone health. Magnesium aids in the structural development of bones, while phosphorus is crucial for the formation of bone and teeth. Foods high in magnesium include nuts, seeds, whole grains, and green leafy vegetables. Phosphorus-rich foods include dairy, fish, and lentils.
Balancing Diet and Lifestyle
While nutrition is foundational, other lifestyle factors also contribute to bone health. Regular exercise, especially weight-bearing and resistance activities, strengthens bones. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can adversely affect bone density, so it’s advisable to avoid these habits.
For further insight into how lifestyle affects your skeletal system, the article on the Impact of Lifestyle on Bone Health provides valuable information.
The Role of Hormones in Bone Density
Hormones play a crucial role in regulating bone density. Estrogen in women and testosterone in men are particularly important for bone health. As we age, changes in these hormone levels can lead to decreased bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
Postmenopausal women are at a higher risk for osteoporosis due to the sudden decrease in estrogen levels. It’s essential to manage hormone levels through diet, lifestyle, and, where appropriate, medication. Learn more about this topic by reading about Bone Health for Postmenopausal Women.
The Genetic Link
While diet and lifestyle are controllable factors, genetics also play a role in determining bone health. Some people are genetically predisposed to having higher bone density and strength. To understand the influence of genetics on your bone health, consider reading about The Role of Genetics in Bone Health.
Nutritional Supplements for Bone Health
Sometimes, diet alone may not provide all the nutrients necessary for optimal bone health. In such cases, supplements can be beneficial. Calcium and vitamin D supplements are commonly recommended, especially for those at risk of bone diseases like osteoporosis.
However, before starting any supplement regimen, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help determine the right dosage and ensure that supplements do not interfere with other medications.
External Resources for In-Depth Information
To supplement the information provided here, here are some niche and specific external resources that can help you understand and support your bone health:
- International Osteoporosis Foundation: Provides a wealth of information on bone health, including resources for preventing and managing osteoporosis.
- National Institutes of Health – Calcium: Offers detailed information on calcium, including dietary sources and how much you need by age and gender.
- Vitamin D Council: A nonprofit organization that educates on vitamin D, sun exposure, and health.
- National Osteoporosis Foundation Exercise Recommendations: Provides exercise recommendations for maintaining strong bones and preventing fractures.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy bones is a multifaceted endeavor that incorporates proper nutrition, lifestyle choices, and an understanding of your personal health factors, including genetics and hormonal balance. By consuming a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding detrimental habits like smoking, you can significantly contribute to the health of your bones.
Remember that while these tips are a good starting point, individual needs may vary. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. By taking proactive steps today, you can support the strength and vitality of your bones for years to come.