Omega-3 fatty acids are crucial components of cell membranes throughout the body and affect the function of the cell receptors in these membranes. They provide the starting point for making hormones that regulate blood clotting, contraction and relaxation of artery walls, and inflammation. Moreover, they bind to receptors in cells that regulate genetic function. Likely due to these effects, omega-3 fats have been shown to help prevent heart disease and stroke, may help control lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis, and may play protective roles in cancer and other conditions.
The Importance of Omega-3s for Cardiovascular Health
The heart is perhaps the organ most directly impacted by omega-3s due to their effect on the complex cardiovascular system. The anti-inflammatory properties of omega-3 fatty acids are particularly beneficial, as inflammation is a key component in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis – the process that underlies most cardiovascular diseases. Cardiovascular Health is a multifaceted issue that requires a well-rounded approach, and omega-3 supplements can be a significant part of this strategy.
Omega-3s are known to have a positive effect on blood pressure levels, as numerous studies have documented their ability to lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Additionally, they have been found to reduce triglycerides, a type of fat found in your blood that, in high levels, can increase the risk of heart disease.
One of the most well-documented benefits of omega-3 fatty acids is their ability to reduce the risk of arrhythmias – irregular heartbeats that can lead to sudden death. They also slow the growth rate of atherosclerotic plaque and lower blood pressure, further decreasing heart risks.
Sources of Omega-3s
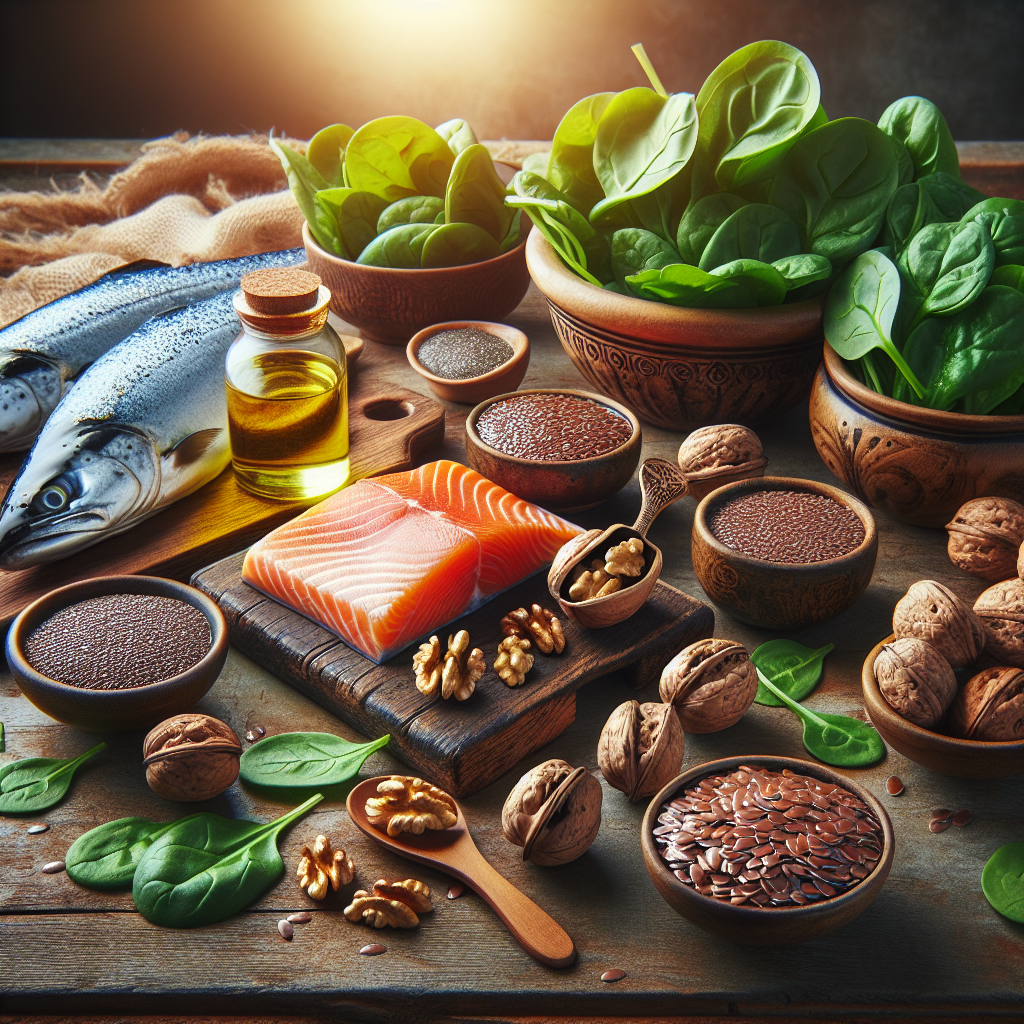
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids: ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) found in plant oils, and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), both commonly found in marine oils. Fish oil supplements, which contain EPA and DHA, have been the focus of omega-3 research, while ALA comes from flaxseed oil and other plant-based oils.
While it’s possible to get sufficient omega-3s through diet alone – fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources – many people turn to supplements to ensure they get enough.
Omega-3 Supplement Quality and Safety
Not all omega-3 supplements are created equal. The quality of fish oil is paramount, as it should be free of contaminants like mercury and PCBs. It’s also crucial that the oil is stabilized with vitamin E or other antioxidants to prevent spoilage and rancidity, which can negate any health benefits.
When considering omega-3 supplementation, it’s vital to look at the Impact of Supplements on Prescription Drug Effectiveness. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider, as omega-3s can interact with medications and affect clotting and blood pressure.
The Research Behind Omega-3 Supplements for Heart Health
Numerous studies have supported the cardiovascular benefits of omega-3s. A landmark study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that participants with the highest levels of omega-3 fatty acids in their blood had a 90% lower risk of sudden cardiac death compared to those with the lowest levels.
Another study, known as the Gissi-Prevenzione trial, showed that heart attack survivors who took fish oil supplements significantly reduced their risk of another heart attack, stroke, or death from heart disease.
These findings are supported by a systematic review by the Cochrane Library, which concluded that omega-3 fatty acid supplements are associated with a modest reduction in death from heart disease.
The Synergy of Diet, Medication, and Supplements
Omega-3 supplements should not be taken in isolation but as part of a comprehensive approach to heart health. This includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and, when necessary, medication. Understanding the Nutrient Timing: The Intersection of Diet, Medication, and Supplements is essential to maximize the benefits of all these components.
Omega-3s Beyond Heart Health
While the benefits of omega-3 supplements for heart health are significant, their impact extends to other areas of health as well, such as Mental Wellness and Brain Health. The anti-inflammatory and cell-protective properties of omega-3s play roles in cognitive function and emotional balance.
Conclusion
In summary, omega-3 supplements offer a wide range of cardiovascular benefits, from lowering blood pressure and triglyceride levels to reducing the risk of arrhythmias and slowing the progression of atherosclerotic plaque. They are a vital part of a heart-healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, physical activity, and appropriate medical care. However, it’s important to choose high-quality supplements and to consider the interaction with other medications and lifestyle factors. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
The impact of omega-3s on heart health is an excellent example of how targeted nutritional supplementation can support and enhance overall health outcomes. As research continues to evolve, the integration of these supplements into broader health strategies will likely become even more refined, benefiting patients and the healthcare system alike.