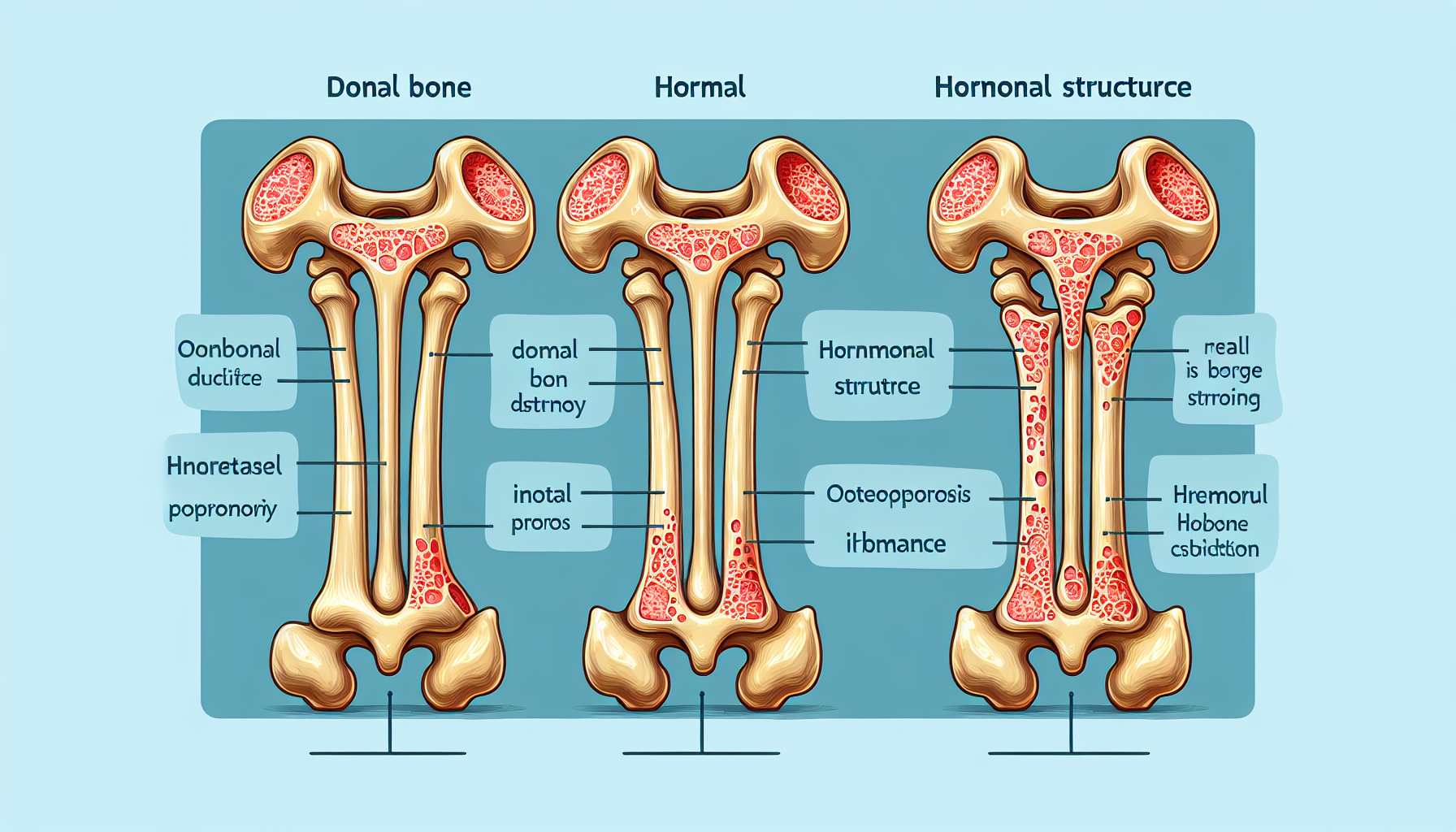
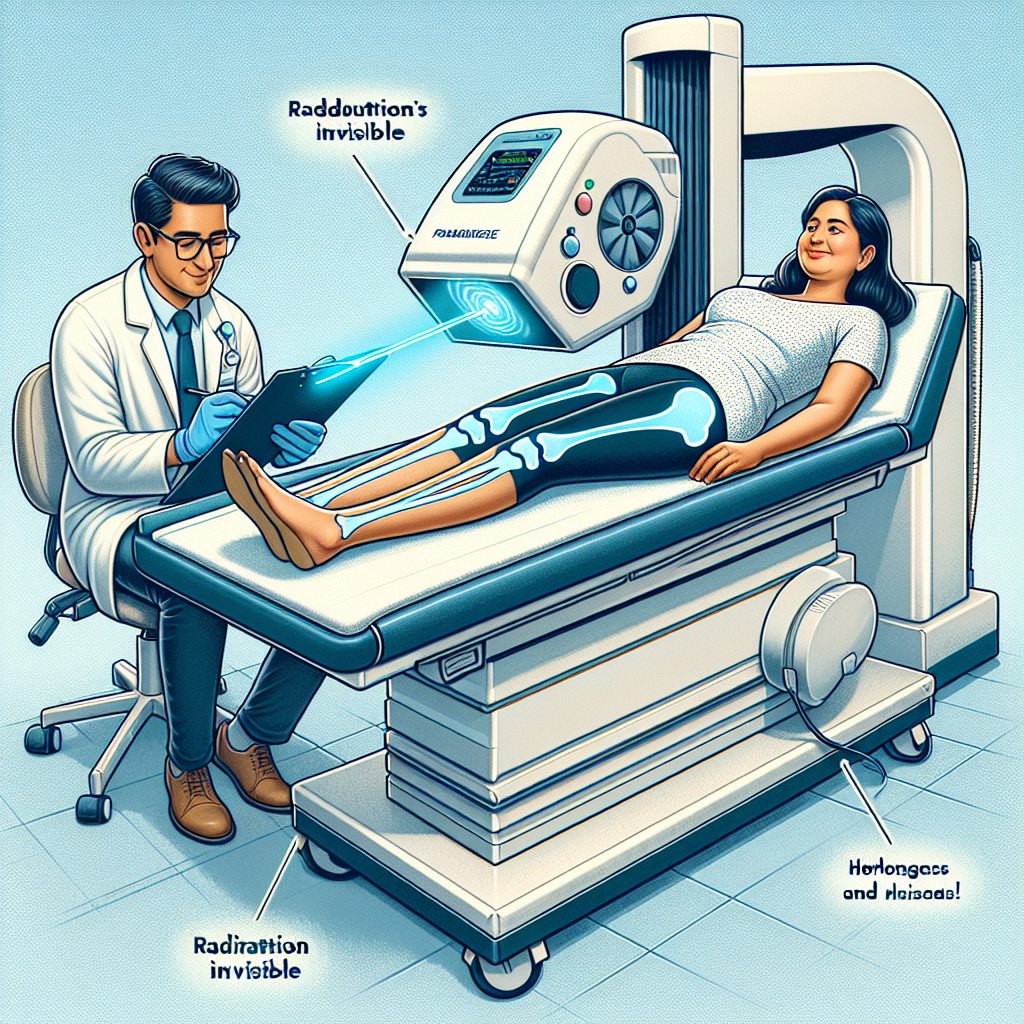
Our bones are the framework of our body, providing structure, safeguarding organs, anchoring muscles, and storing calcium. However, maintaining healthy bones goes beyond just getting enough calcium and vitamin D. It is a complex process influenced by an array of factors, with hormones playing a pivotal role. Understanding the hormonal impact on bone density is crucial for maintaining bone health throughout various stages of life.
The Role of Hormones in Bone Health
Bones are not static; they are living tissues that continuously remodel themselves. This remodeling process is regulated by hormones—chemical messengers that tell our cells what to do. Certain hormones stimulate bone formation, while others increase bone resorption, where bone is broken down and minerals are released into the blood.
Estrogen and Testosterone
Estrogen and testosterone are two hormones commonly associated with bone density. Estrogen, found in higher levels in women, protects bones by helping to balance the bone remodeling cycle, favoring bone formation. This is why women can experience a rapid decline in bone density after menopause when estrogen levels drop.
Testosterone, the primary male hormone, also plays a significant role in bone health. It stimulates the production of bone-forming cells and increases the absorption of calcium, a key mineral in bone. Lower levels of testosterone in men, which can occur naturally with aging, can lead to decreased bone density and strength.
Parathyroid Hormone and Calcitonin
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin are two other critical players in bone health. PTH is released when calcium levels in the blood are low, triggering the release of calcium from bones to balance blood levels. Conversely, calcitonin is secreted when calcium levels are high, working to store calcium in bones and improve bone density.
Hormonal Imbalances and Bone Density
Hormonal imbalances can adversely affect bone density. Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism, where excess PTH is produced, can lead to bone loss. Additionally, diseases that affect hormone levels, like hypogonadism in men or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women, can also impact bone health.
For more in-depth information on how these conditions affect bone health, consider reading about Bone Health at Different Life Stages.
Hormones and Bone Health at Different Life Stages
During childhood and adolescence, growth hormone and sex hormones are crucial for achieving peak bone mass. In adulthood, maintaining a balance of bone-forming and resorbing hormones is key to preserving bone density. As we age, changes in hormone levels can accelerate bone loss, making us susceptible to fractures.
For postmenopausal women, the decline in estrogen is a significant factor in the development of osteoporosis. Strategies to manage bone health during this stage can be found in the article on Bone Health for Postmenopausal Women.
Strategies to Support Hormonal Balance for Bone Health
Nutrition and Diet
A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients is essential for supporting hormonal balance and bone health. The link between diet and bone health is explored in detail at The Link Between Diet and Bone Health.
Lifestyle Choices
Exercise, particularly weight-bearing and strength-training exercises, can help increase bone density. Additionally, avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are important, as these can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to bone loss.
Further insights into how lifestyle affects bone health can be found in Impact of Lifestyle on Bone Health.
Medication and Supplements
In some cases, medication or supplements may be necessary to manage hormonal imbalances affecting bone density. Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can be beneficial for postmenopausal women, while testosterone replacement may help men with low levels due to hypogonadism.
Discover more about effective supplements for bone health at Bone Health Supplements: What Works?.
Monitoring and Testing Bone Density
Regular bone density tests can help monitor bone health and detect early signs of bone loss. Understanding these tests can empower individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining strong bones.
For an understanding of these tests, read about Understanding Bone Density Tests.
External Resources for Further Reading
- International Osteoporosis Foundation provides comprehensive resources on bone health, including hormonal factors.
- The Endocrine Society offers insights into how endocrine disorders affect bone density.
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases for in-depth information on bone diseases and how hormones are involved.
- The Hormone Health Network for detailed educational materials about hormones and bone health.
- Peer-reviewed articles on PubMed for scientific studies on the relationship between hormones and bone density.
By embracing a holistic approach that includes diet, exercise, lifestyle choices, and understanding hormonal influences, we can better manage our bone health and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. It’s important to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice, as they can provide guidance tailored to individual health needs and hormonal profiles.