Sleep is a critical component of our daily lives, a time when our body and mind undergo essential restorative processes. In the realm of neuroscience, the study of brain wave activity during sleep has provided fascinating insights into how our brains work and recover. Understanding the relationship between sleep and brain wave activity is not only crucial for academic purposes but also has practical implications for improving overall brain health.
The Science of Sleep and Brain Waves
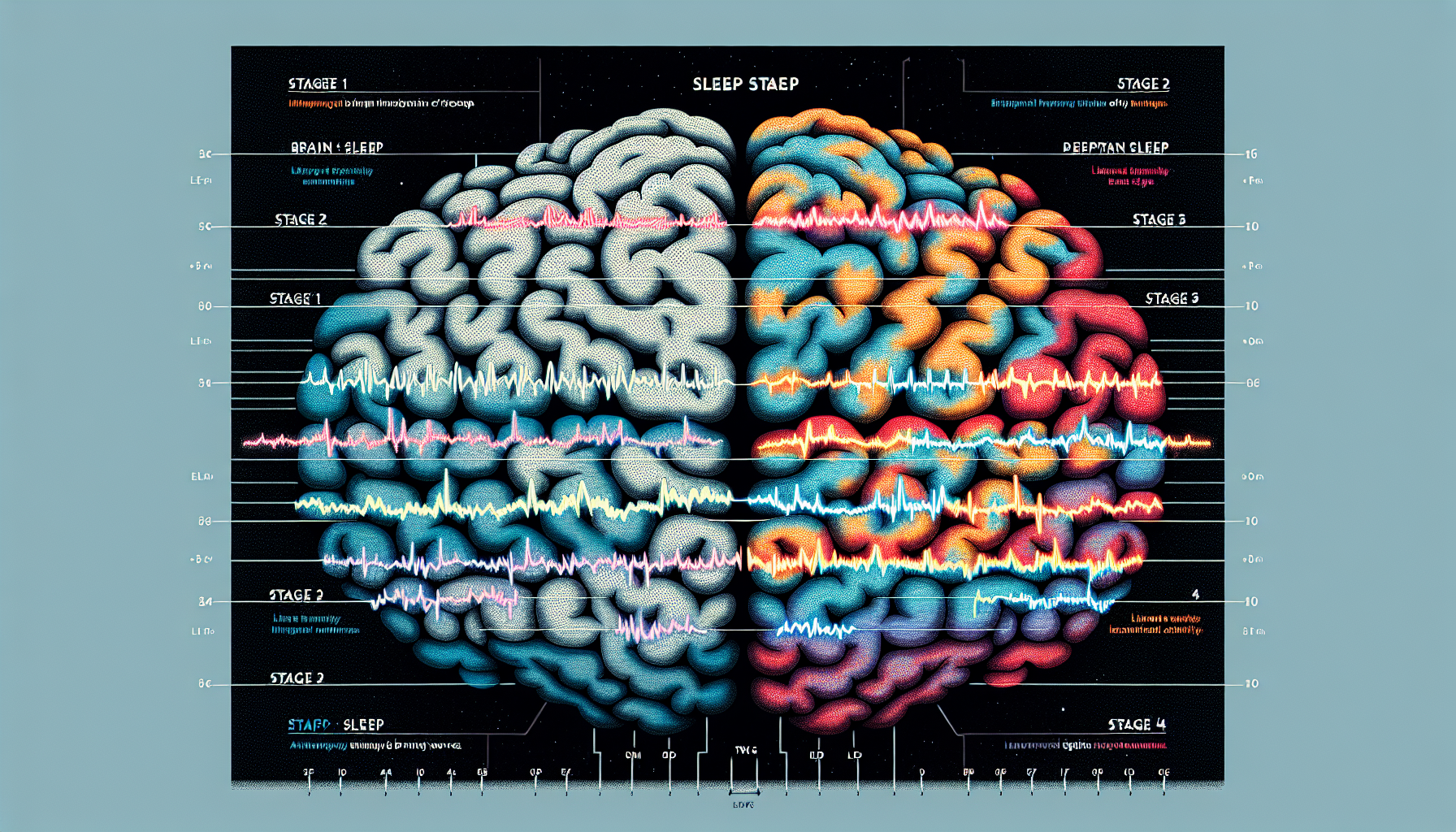
Sleep is divided into several stages, each characterized by unique brain wave patterns. These stages range from light sleep to deep sleep and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. During the night, a person typically cycles through these stages multiple times.
The Stages of Sleep
- NREM Stage 1: This is the lightest stage of sleep where alpha waves are prominent, and the transition to theta waves begins.
- NREM Stage 2: Characterized by the presence of sleep spindles and K-complexes amidst theta wave activity.
- NREM Stage 3: Often referred to as deep sleep, delta waves dominate this stage.
- REM Sleep: Beta waves, similar to an awake state, are most prevalent here, and this is when most dreaming occurs.
Each stage of sleep plays a role in brain health and function, including memory consolidation, neurogenesis, and neurotransmitter balance.
The Role of Sleep in Memory and Cognitive Function
A deep dive into the relationship between sleep quality and memory consolidation reveals the intricate processes our brains undertake during sleep. It’s during the deep sleep stage that our brains consolidate memories, transferring information from short-term to long-term storage. This process is facilitated by the slow delta waves of NREM sleep, which allow neurons to coordinate and strengthen the neural pathways that form memories.
Sleep’s Impact on Neurogenesis and Brain Repair
Sleep, particularly the deep sleep stage, also fosters neurogenesis—the creation of new neurons. This aspect of brain repair is crucial for maintaining cognitive function and resilience. Strategies that boost neurogenesis, such as aerobic exercise and a nutritious diet, can be complemented by quality sleep to maximize brain repair. For more on this subject, consider reading about strategies to boost neurogenesis and brain repair.
Brain Wave Entrainment and Cognitive Enhancement
Brain wave entrainment is a method used to stimulate the brain into entering a specific state by using pulsing sound, light, or electromagnetic fields. The concept of entrainment suggests that the brain can be encouraged to alter its wave patterns, potentially leading to cognitive enhancements. This technique is explored in greater depth in the article on cognitive enhancements through brainwave entrainment techniques.
External Resources on Sleep and Brain Wave Activity
To further your understanding of the relationship between sleep and brain wave activity, consider these niche resources:
- A scholarly article on the effects of sleep deprivation on brain function providing a comprehensive look at how lack of sleep can disrupt normal brain wave patterns and cognitive processes.
- An in-depth review of brain wave entrainment detailing its potential therapeutic applications and mechanisms.
- A clinical study on the role of deep sleep and memory offering insights into how slow-wave sleep contributes to memory consolidation.
Practical Applications: Enhancing Sleep for Better Brain Health
Given the importance of sleep in maintaining and enhancing brain function, it is crucial to adopt habits that promote healthy sleep patterns. Here are several strategies that can help:
- Maintain a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a restful environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool to facilitate easier sleep.
- Limit exposure to screens before bedtime: The blue light emitted by phones, tablets, and computers can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Exercise regularly: Physical activity can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep.
- Mind your diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.
The Importance of Sleep in Brain Health Maintenance
For a holistic approach to brain health, it is imperative to consider the broader context of lifestyle choices. Brain health maintenance encompasses various aspects such as diet, physical exercise, and mental stimulation, all of which are influenced by the quality of sleep.
Conclusion
The exploration of sleep and brain wave activity opens up avenues for enhancing cognitive function and overall brain health. By understanding the intricate dance of brain waves during sleep, we can better appreciate the complex nature of our brains and the critical role sleep plays in maintaining its health. As research continues to unfold, the potential to optimize brain function through improved sleep is an exciting prospect for anyone looking to enhance their mental acuity and well-being.
By integrating the knowledge gained from the study of sleep and brain wave activity with practical sleep hygiene practices, we can work towards a future where cognitive decline is no longer an inevitable part of aging, but rather a challenge that can be effectively managed and mitigated.