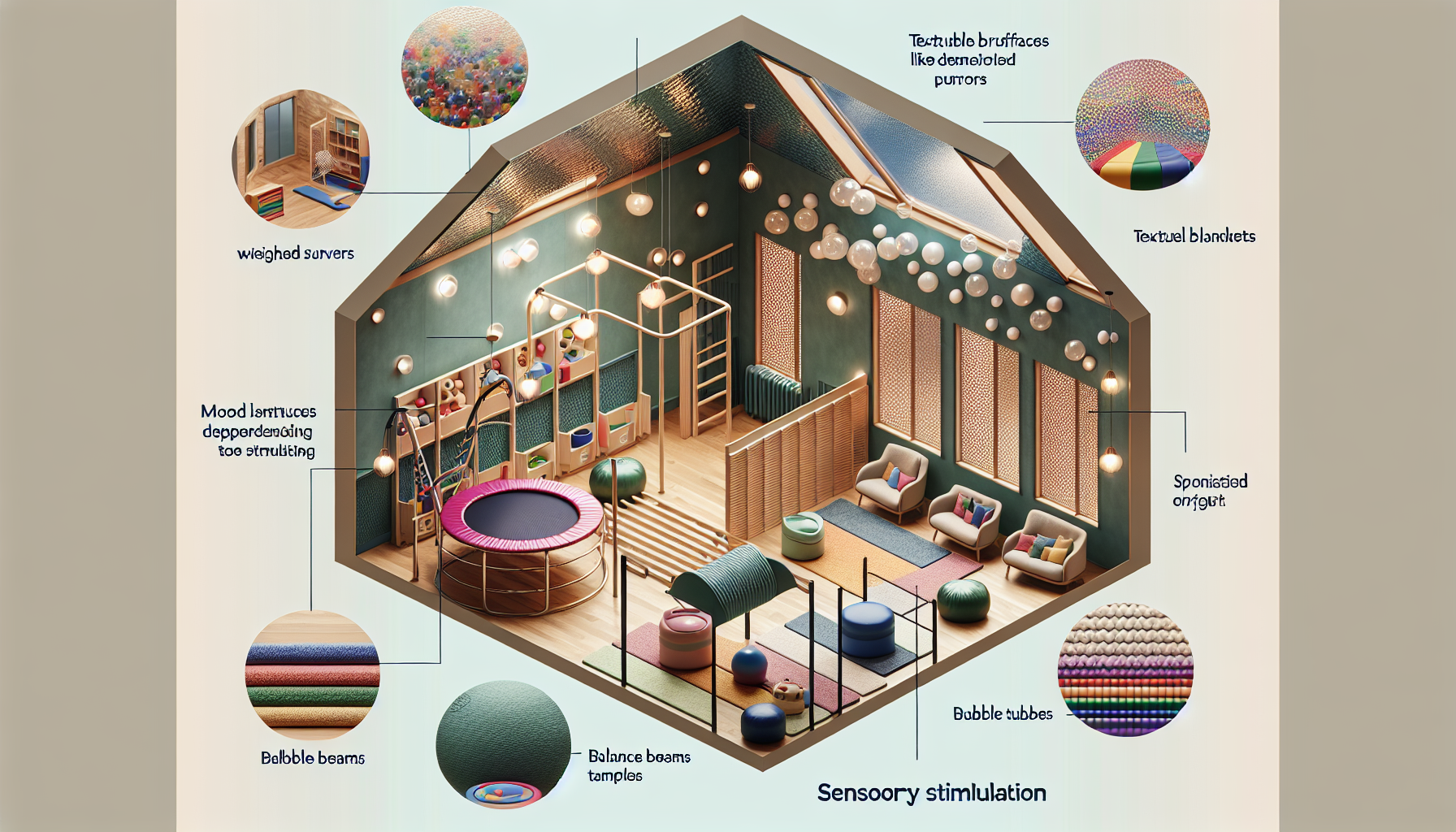
Sensory rooms, also known as multisensory environments, have gained traction in educational settings as a therapeutic tool with the potential to support students with sensory processing difficulties, as well as those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorders (ASD), and other special educational needs. These rooms are thoughtfully designed spaces that offer a variety of sensory experiences to help students regulate their sensory input, which can lead to improved focus, learning, and overall well-being. This article delves into the effectiveness of sensory rooms in educational institutions and explores how they can be an integral part of a holistic educational approach.
Understanding Sensory Health in Education
Before we can assess the impact of sensory rooms, it is vital to understand sensory health and its role in an educational context. Sensory health refers to the efficient processing and integration of sensory information received from one’s environment. It is the foundation upon which students can engage and interact with their surroundings, an essential aspect of the learning process. When sensory processing is inhibited or overloaded, it can lead to challenges that affect a student’s ability to learn and socialize effectively.
The Role of Sensory Rooms
Sensory rooms provide a safe space where students can engage in activities that help modulate their sensory intake. These activities may include tactile stimulation, visual or auditory experiences, and proprioceptive or vestibular input. Such environments are designed to be calming and therapeutic, offering a respite from potential overstimulation in typical classroom settings.
Evaluating Effectiveness
When evaluating the effectiveness of sensory rooms, several factors come into play. The primary goal of these rooms is to offer students a way to self-regulate, which can lead to improved attention, behavior, and learning outcomes. Research has shown that when students are given the opportunity to engage in sensory-based interventions, there can be noticeable improvements in these areas.
Impact on Learning and Behavior
One of the most significant benefits of sensory rooms is the potential impact on student behavior and learning. Students with sensory processing challenges may exhibit behaviors that are disruptive to themselves and others. Sensory rooms can offer a controlled environment where they can manage their sensory needs and return to the classroom more focused and calm. This can lead to a reduction in disruptive behaviors and an increase in engagement with academic tasks.
Social and Emotional Benefits
The influence of sensory rooms extends beyond academic performance. These spaces can also support the social and emotional development of students. By providing a space where students feel secure, sensory rooms can help promote self-awareness and self-esteem. The positive reinforcement of managing one’s sensory needs can empower students, giving them a sense of control and improving their social interactions both within the sensory room and in the broader school environment.
Customization and Accessibility
The effectiveness of a sensory room is closely tied to its design and how well it caters to the individual needs of students. A well-designed sensory room should be customizable and adaptable, allowing for a personalized experience for each user. This means that the room should have a variety of equipment and activities that can be modified to suit different sensory preferences and requirements.
Relevant Research and Resources
To further understand the impact of sensory rooms, it is beneficial to look at niche and specific resources that provide insight into their use and effectiveness:
- A study by the American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA) examines how sensory integration therapy, often conducted in sensory rooms, can improve educational outcomes for children with ASD. (AOTA)
- Research published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders investigates the relationship between sensory processing and social-communication in children with and without ASD, shedding light on the importance of addressing sensory needs in educational settings. (SpringerLink)
- The STAR Institute for Sensory Processing Disorder provides valuable resources on sensory processing and the role of sensory rooms in managing sensory processing challenges. (STAR Institute)
Linking Sensory Rooms with Broader Educational Strategies
To maximize the benefits of sensory rooms, it is essential to integrate them with broader educational strategies and approaches. For instance, sensory-based strategies for improving memory and cognition can complement the use of a sensory room by providing students with tools to enhance learning and retention of information.
Similarly, understanding the role of sensory integration in autism spectrum disorders can guide educators in creating effective sensory room interventions for students on the autism spectrum.
Furthermore, implementing sensory-friendly solutions for workplace productivity can serve as an extension of the principles applied in sensory rooms, preparing students with the skills to navigate sensory challenges in future work environments.
Best Practices for Sensory Room Implementation
There are several best practices to consider when implementing sensory rooms in educational institutions:
- Assessment and Individualization: Conduct thorough assessments of student needs to ensure the sensory room is tailored to provide the most benefit for its users. Individualization is key to effective sensory intervention.
- Professional Guidance: Involve occupational therapists or other professionals trained in sensory health to ensure the room’s design and the activities offered are appropriate and beneficial.
- Training and Supervision: Educators and support staff should receive training to understand how to best utilize the sensory room and supervise students effectively.
- Integration with Curriculum: Sensory room activities should be integrated with the curriculum and individual education plans (IEPs) to support educational goals.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Regularly monitor and evaluate the use of the sensory room to measure its impact and make any necessary adjustments.
Future Directions
As the awareness and understanding of sensory processing issues continue to grow, the role of sensory rooms in educational institutions is likely to expand. Future research and innovation will focus on optimizing the design and use of these spaces to support a wider range of sensory needs and further integrate sensory health into the educational framework.
Conclusion
Sensory rooms represent a valuable asset in educational institutions, offering students with sensory processing challenges a dedicated space to manage their sensory input, which can lead to improved focus, behavior, and learning outcomes. When implemented correctly and integrated with broader educational strategies, sensory rooms can have a profound impact on students’ educational experiences, equipping them with the skills necessary to thrive both academically and socially.
By fostering environments that address the holistic needs of students, including their sensory health, educational institutions can create more inclusive, effective, and nurturing spaces for learning and growth.