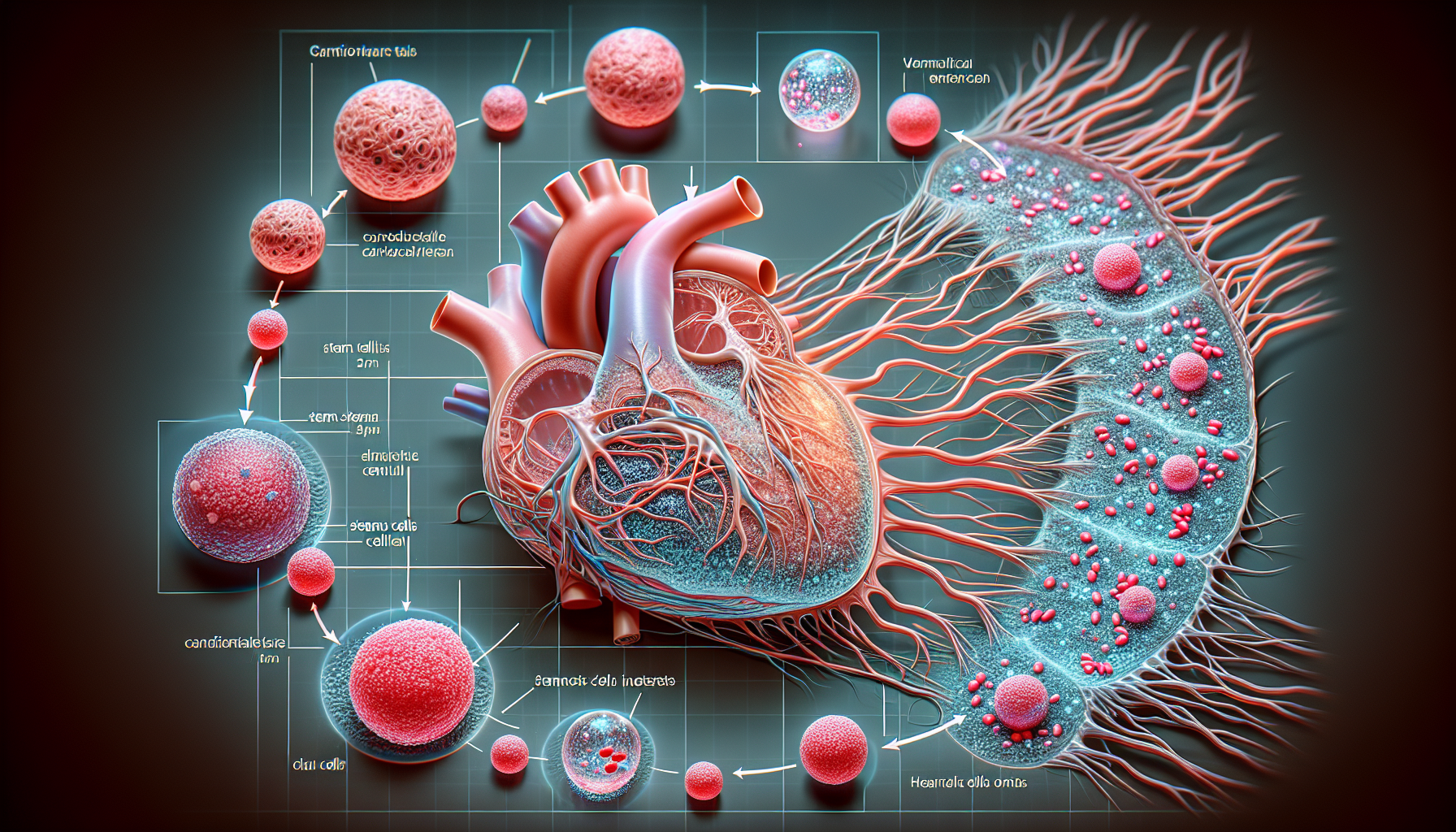
The quest for regenerative therapies to combat cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been an ongoing journey in the medical field, and stem cell therapy has emerged as a beacon of hope. With CVD remaining a leading cause of mortality globally, the integration of innovative treatments is not just a scientific pursuit but a necessity for improving patient outcomes. This article explores the cutting-edge realm of stem cell therapy and its potential to revolutionize the treatment of heart disease by enabling the regeneration of damaged heart tissue.
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease and the Need for Regeneration
Cardiovascular diseases encompass a range of disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels, often leading to acute events like heart attacks and chronic conditions such as heart failure. The essence of these conditions lies in the damage to or death of heart muscle cells (cardiomyocytes), which have limited capacity to regenerate. This limitation poses a significant challenge in healing and restoring heart function after injury.
The traditional approach to managing heart disease has focused on controlling symptoms and preventing further deterioration through lifestyle changes, medication, and in some cases, surgical interventions. While these strategies are valuable, they do not address the core issue of lost or damaged cardiomyocytes. Hence, the interest in regenerative medicine, particularly stem cell therapy, has surged as it offers a potential means to repair and replace the affected heart tissue.
Stem Cells: The Building Blocks of Regeneration
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. They have the unique ability to develop into many different cell types and, importantly, to self-renew and produce more stem cells. Two key types of stem cells are used in cardiovascular regeneration:
- Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs): These are pluripotent stem cells derived from embryos and can differentiate into any cell type in the body, including cardiomyocytes.
- Adult Stem Cells (ASCs): Found in small numbers in most adult tissues, such as bone marrow or fat, these cells are multipotent and can generate a limited range of cells.
The use of stem cells in cardiac therapy aims to harness these properties to regenerate damaged heart tissue, either by directly differentiating into cardiomyocytes or by stimulating the body’s own repair mechanisms.
The Process of Stem Cell Therapy in Cardiac Regeneration
Stem cell therapy for heart disease typically involves several steps:
- Stem Cell Harvesting: Stem cells are collected from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic).
- Stem Cell Culturing and Differentiation: The harvested stem cells are then cultured in a lab to increase their numbers and, if necessary, induced to differentiate into cardiomyocytes.
- Transplantation: The prepared stem cells are transplanted into the patient’s heart, usually via catheter-based delivery or during surgery.
- Integration and Regeneration: The transplanted stem cells integrate with the existing heart tissue and contribute to the repair and regeneration of damaged areas.
Clinical Trials and Research
Clinical trials and research are critical in evaluating the safety and efficacy of stem cell therapy in cardiac regeneration. Several early-stage clinical trials have shown promising results, with some patients experiencing improvements in heart function and a reduction in symptoms. The American Heart Association provides updates on ongoing research and trials related to stem cell therapy and CVD.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the potential, stem cell therapy faces challenges, such as ensuring the survival of transplanted cells in the harsh environment of a damaged heart, avoiding immune rejection, and preventing abnormal heart rhythms. Addressing these issues is at the forefront of current research.
For a comprehensive understanding of cardiovascular health and its management, readers can delve into Cardiovascular Health.
Related Health Considerations
While stem cell therapy focuses on the heart itself, overall health plays a crucial role in the success of any treatment. Factors such as bone health, which influences the availability and quality of bone marrow-derived stem cells, and lifestyle factors like diet and exercise, which impact cardiovascular health, are integral to consider.
Further, exploring the importance of potassium in maintaining heart health can provide insights into the dietary aspects of cardiovascular wellness. Understanding the impact of hypertension on the heart is also critical, as high blood pressure can affect the outcomes of regenerative therapies.
Broader Implications and Supportive Care
Stem cell therapy is not a standalone treatment; it is part of a broader strategy that includes preventive care, proper nutrition, and management of related health conditions. For instance, the interplay between heart health and immune system is significant, as a robust immune response is essential for healing and combating infections post-therapy. Information on this can be found in the article Heart Health and Immune System: Interplay and Implications.
Moreover, the European Society of Cardiology offers resources and guidelines that support the points made about the broader implications of cardiovascular health management.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy represents a transformative approach to treating cardiovascular disease by enabling the regeneration of heart tissue. While challenges remain, the progress in this field provides hope for those suffering from CVD, and continued research is paving the way for more effective treatments. By integrating stem cell therapy with comprehensive health management, the future of cardiovascular care looks promising.
For patients and healthcare providers alike, staying informed and engaged with the latest advancements is key. High-quality resources such as The National Institutes of Health offer valuable information on the latest research in stem cell therapy and cardiovascular health.
As we move forward, the integration of cutting-edge treatments like stem cell therapy with holistic health care will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in improving outcomes for heart disease patients worldwide.