Hydration plays an indispensable role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. It is a vital but often overlooked element that supports various functions within the gastrointestinal tract. Adequate water intake is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, and the elimination of waste. This comprehensive article delves into the significance of hydration for digestive health, outlines the consequences of dehydration, and provides practical advice for integrating proper hydration practices into daily life.
Understanding the Digestive System
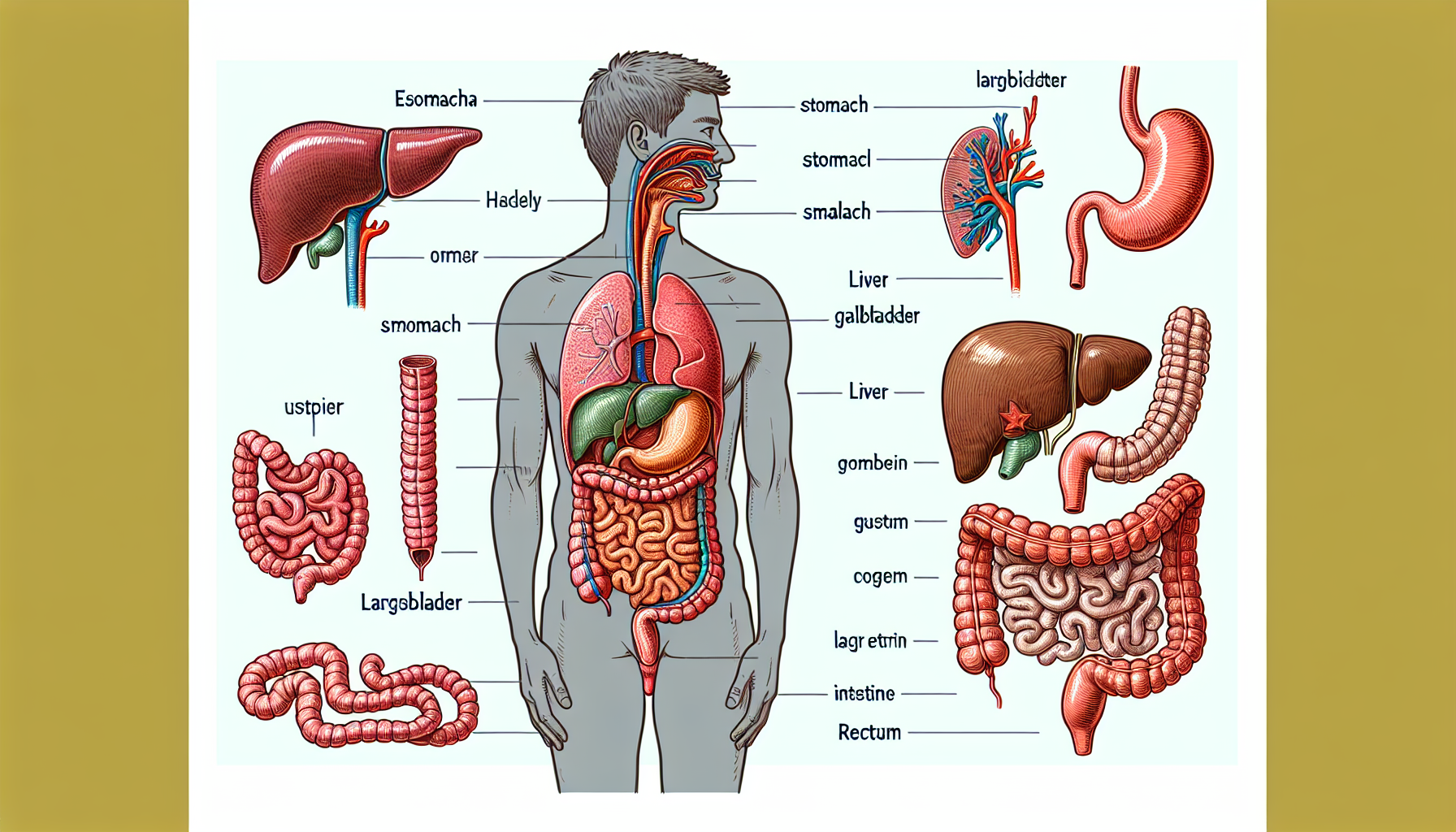
The digestive system is a complex network that breaks down food into nutrients, which the body uses for energy, growth, and cell repair. Water is the carrier that transports these nutrients to our cells. It is also instrumental in dissolving fats and soluble fiber, allowing these substances to pass through the intestines smoothly. Moreover, hydration aids in the production of saliva and gastric juices, which are essential for breaking down food.
For an in-depth understanding of the digestive system and its functions, one can explore Understanding the Digestive System and Its Functions, which offers valuable insights into the processes that take place in our bodies during digestion.
The Link Between Hydration and Digestive Health
Water is essential for the mucosal lining of the intestines, keeping it moist and elastic. This is crucial for the smooth movement of food along the digestive tract. When the body is dehydrated, the intestine absorbs more water from food waste, which can lead to constipation. Chronic constipation can have severe health implications, including an increased risk of colorectal cancer and digestive discomfort.
Hydration also plays a role in maintaining the balance of good bacteria in the gut. A well-hydrated body ensures that the gut microbiome, a key component of gut health, functions optimally. To learn more about the importance of the gut microbiome, refer to Probiotics and Prebiotics: Nourishing a Healthy Gut Microbiome.
For those seeking to improve their digestive health through nutrition, Leveraging Nutrition Therapy for Optimal Digestive Health provides practical strategies and dietary advice.
Consequences of Inadequate Hydration
Dehydration can significantly affect digestive health. Insufficient water intake can lead to various issues such as:
- Constipation: Without enough water, stools become hard and difficult to pass.
- Acid Reflux: Dehydration can lead to a reduction in saliva production, which can increase the risk of acid reflux.
- Digestive Disorders: Chronic dehydration may contribute to the development of certain digestive disorders, such as gastritis and ulcers.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
The amount of water required can vary based on factors such as age, weight, climate, and physical activity. The U.S. National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine determined that an adequate daily fluid intake is about 3.7 liters for men and 2.7 liters for women. This includes all beverages and water-containing foods.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
To ensure you’re getting enough water for digestive health, consider the following tips:
- Start Your Day with Water: Begin each morning with a glass of water to kickstart your system.
- Carry a Water Bottle: Having water on hand encourages more frequent sipping.
- Eat Water-Rich Foods: Fruits and vegetables like watermelon, strawberries, and cucumbers are high in water content.
- Monitor Your Urine: Clear or light-yellow urine typically indicates good hydration.
- Limit Diuretics: Beverages like coffee and alcohol increase fluid loss.
For those interested in the potential benefits of CBD for wellness, including digestive health, SuperGreatCBD offers educational resources on CBD.
Hydration and Digestive Aids
Certain natural supplements and remedies can support hydration and digestive health. For instance, herbal teas like ginger and peppermint can promote hydration while soothing the digestive tract. Always consult with a healthcare provider before adding supplements to your regimen.
High-Quality External Resources
To further understand the connection between hydration and health, the following resources offer niche and specific insights:
- The Mayo Clinic provides guidelines on water intake and its importance for bodily functions.
- The Nutrition Source by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health offers detailed articles on water, hydration, and health.
Conclusion
Hydration is a key pillar of digestive health. It facilitates various digestive processes, prevents constipation, and supports the maintenance of a healthy gut microbiome. By understanding the critical role water plays in our digestive system and implementing strategies to stay adequately hydrated, we can contribute significantly to our overall well-being.
Remember that while hydration is vital, it is just one aspect of a comprehensive approach to digestive health. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and a healthy lifestyle are equally important in maintaining digestive wellness.