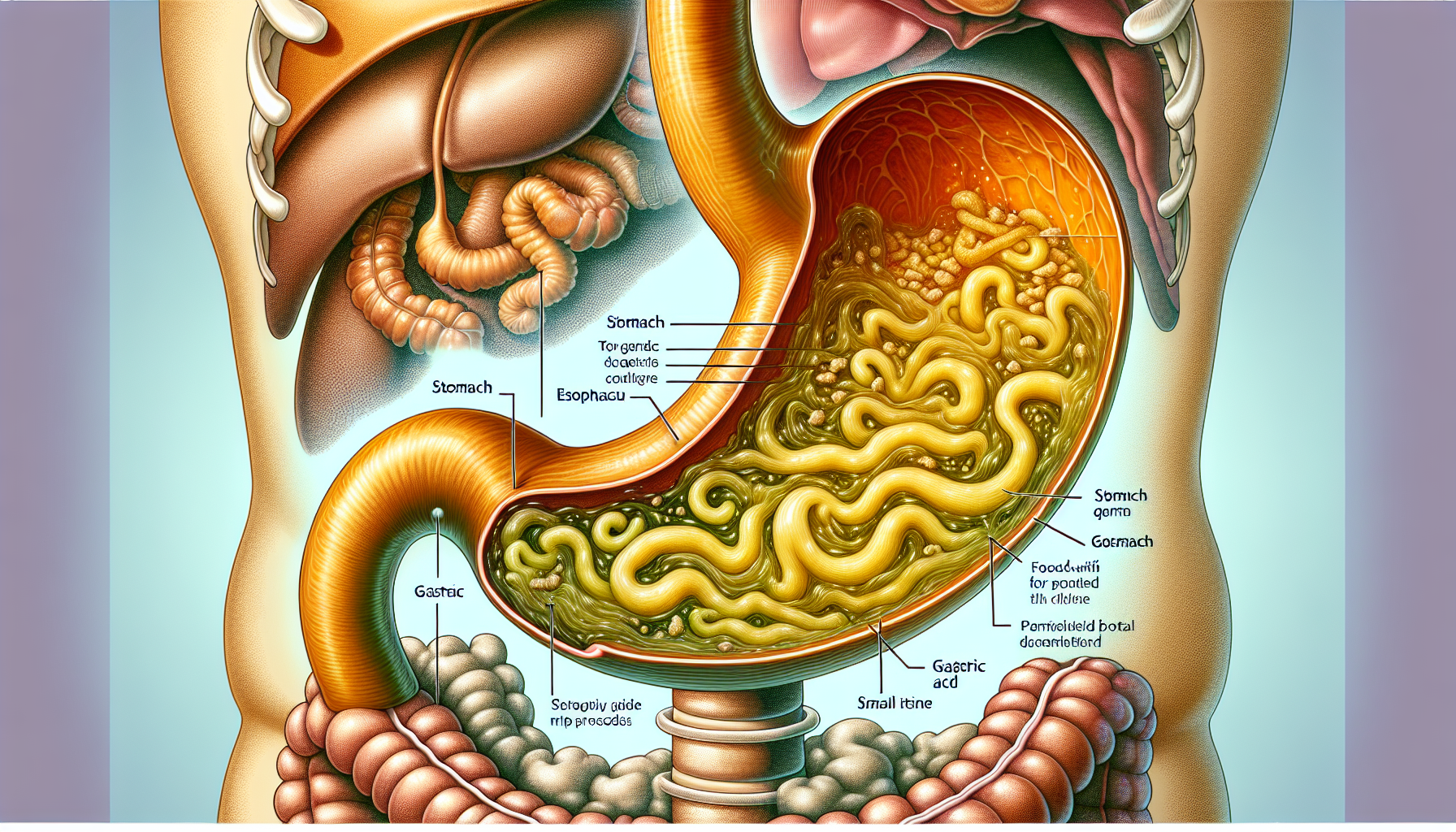
Stomach acid, clinically known as gastric acid, plays a pivotal role in our digestive health. Often overlooked or misunderstood, the significance of stomach acid extends beyond merely breaking down food. It is a critical component in a complex system that affects nutrient absorption, gut flora balance, and even our overall well-being.
The Function of Stomach Acid
Gastric acid is composed primarily of hydrochloric acid (HCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and sodium chloride (NaCl). The acidity of the stomach’s contents, which can reach a pH as low as 1.5, is essential for the activation of digestive enzymes like pepsin, which break down proteins into peptides.
Nutrient Absorption
One of the less celebrated roles of stomach acid is its contribution to the absorption of certain nutrients. For instance, it is essential for the absorption of vitamin B12, a nutrient found in meat and dairy products that is vital for nerve function and the production of DNA and red blood cells. Without adequate stomach acid, the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency increases significantly.
Protection Against Pathogens
Stomach acid acts as a barrier against pathogens that enter our system through food or drink. Its high acidity destroys harmful bacteria and viruses, reducing the likelihood of infections and food poisoning.
Gastrointestinal Balance
The acidity in the stomach also ensures the proper balance of gut flora by creating an environment conducive to beneficial bacteria and hostile to harmful ones. A balanced gut microbiota is linked to better digestive health and a stronger immune system.
For more on how to maintain a balanced gut microbiota, consider reading about Using Probiotic Foods to Naturally Improve Gut Health.
Conditions Related to Low Stomach Acid
A condition termed hypochlorhydria refers to low levels of stomach acid, which can lead to a range of health issues. Common symptoms include bloating, belching, heartburn, and indigestion. Long-term consequences can be even more severe, including:
- Increased risk of bacterial overgrowth such as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Impaired absorption of nutrients
- Greater susceptibility to infection
For those struggling with hyperacidity, learning Dietary Strategies to Manage Hyperacidity can be incredibly beneficial.
Factors Affecting Stomach Acid Production
Several factors can influence the production of stomach acid. These include age, lifestyle choices, medications, and certain medical conditions. For example, the use of antacids and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can reduce stomach acid levels. While these medications can provide short-term relief for conditions like heartburn and ulcers, long-term use can lead to decreased stomach acid and associated complications.
Age-Related Changes
As we age, our bodies naturally produce less stomach acid. This reduction can affect digestion and the absorption of key nutrients, emphasizing the importance of a diet that supports digestive health.
To gain insight into the broader context of digestive health, including the role of stomach acid, readers may find The Role of Fasting in Gut Health Renewal enlightening.
Diet and Lifestyle
The foods we eat and our lifestyle choices can also impact stomach acid production. Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to digestive issues. Conversely, a diet rich in whole foods, such as the Mediterranean diet, has been linked to improved digestive health and adequate stomach acid levels.
For those interested in how diet affects digestion, exploring the Digestive Benefits of Mediterranean Diet is highly recommended.
Enhancing Stomach Acid Production
There are ways to naturally encourage the production of stomach acid:
- Chewing food thoroughly: This simple act can stimulate the production of stomach acid.
- Mindful eating: Eating in a relaxed environment and focusing on your meal can improve digestion.
- Healthy diet: Incorporating foods like ginger, apple cider vinegar, and fermented vegetables can support stomach acid levels.
For additional insights into the digestive system and related health topics, readers can explore Digestive Health on Avix Health.
Conclusion
Stomach acid is a fundamental component of our digestive system, crucial for nutrient absorption, pathogen protection, and maintaining a healthy gut flora. Understanding its role and how to support healthy stomach acid levels can significantly impact our overall health.
For those looking to delve deeper into the subject, there are several niche resources that offer valuable information:
- Understanding the intricate role of stomach acid in digestion
- The relationship between gastric acid secretion and gastric flora
- The clinical significance of hypochlorhydria
Maintaining a healthy stomach acid level is a delicate balance. It’s crucial to be informed and proactive about our digestive health to ensure that our bodies are functioning optimally.