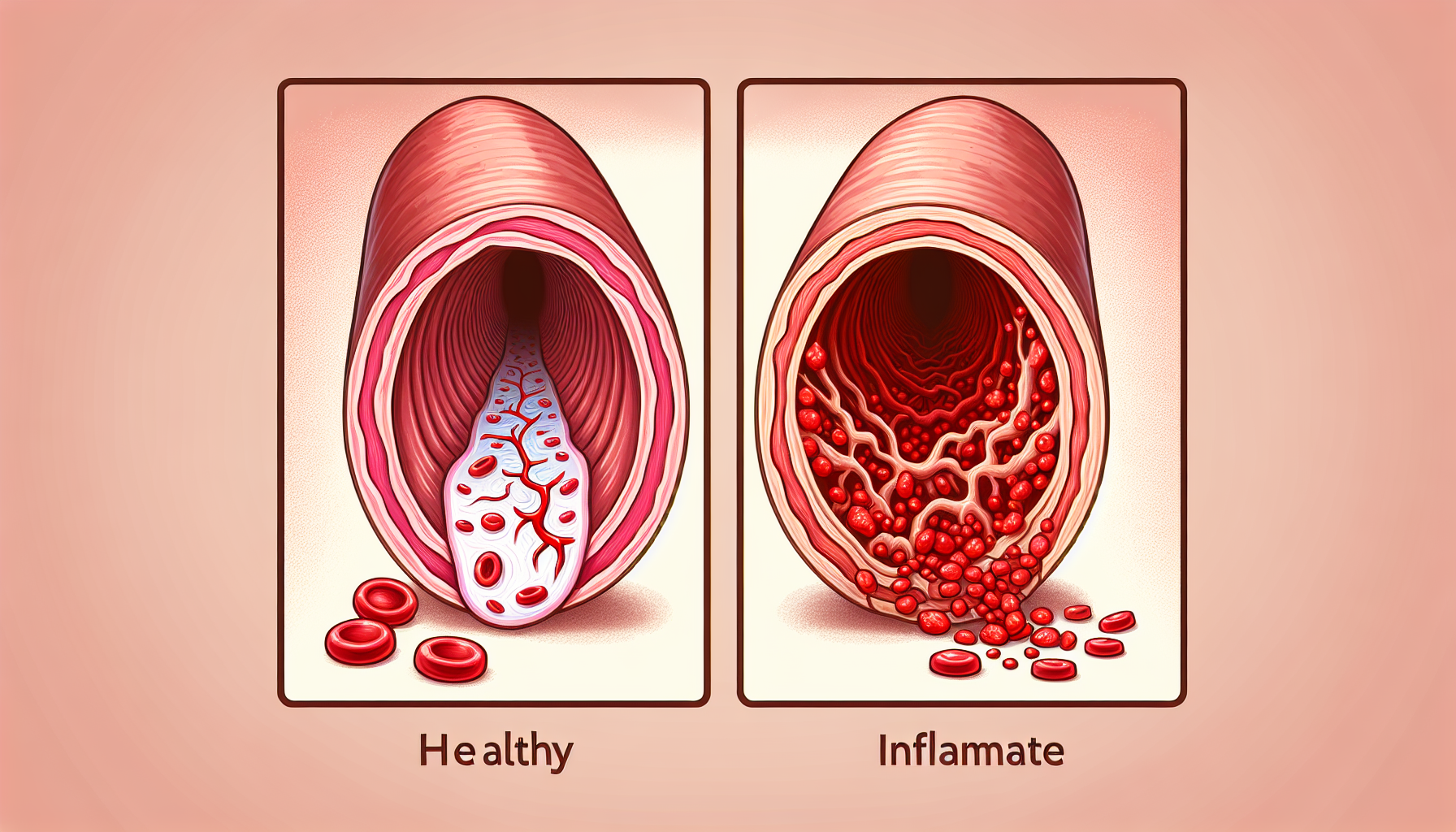
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged, pathological state of inflammation that can wreak havoc on body tissues, including the arteries, which are vital for maintaining cardiovascular health. Understanding the mechanisms by which chronic inflammation affects arterial health is crucial for both prevention and management of various heart diseases.
Chronic Inflammation: An Overview
Inflammation is a natural response of the body’s immune system to injury or infection. It is a defensive mechanism that eliminates harmful stimuli and initiates the healing process. However, when inflammation persists longer than necessary, it becomes chronic. This state can be triggered by various factors, such as persistent infections, autoimmune diseases, and exposure to irritants or industrial chemicals.
Chronic inflammation has been identified as a significant player in the development of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries. This plaque buildup can lead to blockages, which increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
How Chronic Inflammation Affects the Arteries
Inflammation can damage the inner walls of the arteries, leading to the development of atherosclerotic plaque. The damage caused by inflammation can also contribute to arterial stiffness, a condition where arteries lose their elasticity, making it harder for the heart to pump blood throughout the body.
The process of inflammation involves various immune cells and signaling molecules. Cytokines, which are proteins released by immune cells, play a central role in the inflammatory process. Some cytokines promote inflammation, leading to further damage to the arterial walls.
Identifying the Signs of Chronic Inflammation
Recognizing the signs of chronic inflammation is essential for early intervention. While some markers can be measured through blood tests, such as C-reactive protein (CRP), other signs can be more subtle and may manifest as fatigue, pain, or low-grade fever.
For more detailed insights into the broader impacts of chronic inflammation on health, visit Avix Health’s comprehensive take on Cardiovascular Health.
Strategies to Mitigate Chronic Inflammation
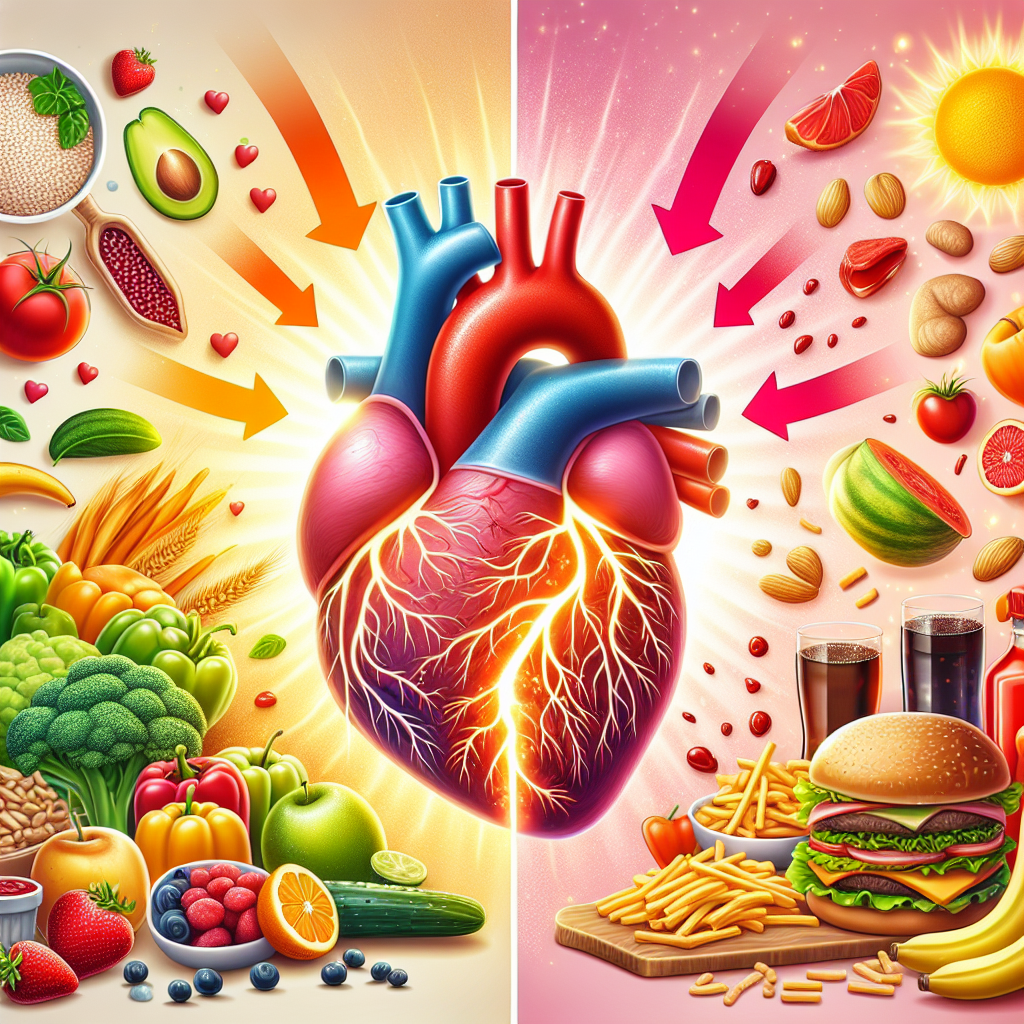
To manage chronic inflammation and protect arterial health, a multifaceted approach is recommended. This includes lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding smoking. Anti-inflammatory medications and supplements may also play a role in reducing inflammation.
Diet and Arterial Health
A diet rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help combat the oxidative stress associated with chronic inflammation. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseed, are also known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
For a deep dive into diet’s role in cardiac recovery and how it helps manage inflammation, one might explore "Evaluating the Role of Diet in Cardiac Disease Recovery" on Avix Health.
Exercise as a Key Component
Regular aerobic exercise has been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects. Activities such as walking, cycling, and swimming can help maintain the health of arteries by reducing inflammation and improving blood flow.
Engaging content on the "Importance of Aerobic Exercise in Hypertension Management" is available at Avix Health to understand the relationship between exercise and heart health further.
Stress Management
Chronic stress is a known contributor to inflammation. Effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises, can help reduce the body’s inflammatory response.
To understand the impact of stress on cardiovascular health, consider reading about "The Effects of Chronic Stress on Cardiovascular System" available on Avix Health.
Monitoring and Medical Intervention
Regular health check-ups and monitoring of blood markers can help in detecting and managing chronic inflammation early. In certain cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications like statins, which have anti-inflammatory properties, in addition to their cholesterol-lowering effects.
Advanced Therapies and Research
New therapies targeting specific inflammatory pathways are under investigation. These therapies aim to reduce cardiovascular risk by directly addressing the inflammatory processes involved in artery damage.
For additional resources that support the points made regarding inflammation and arterial health, consider visiting the following niche websites:
- The American Heart Association provides a wealth of information on heart disease and its relationship with inflammation.
- The Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology journal offers cutting-edge research articles on the role of inflammation in vascular diseases.
- The Inflammation Research Foundation is dedicated to advancing scientific knowledge on the effects of inflammation on diseases, including cardiovascular conditions.
Conclusion
Chronic inflammation poses a significant threat to arterial health and, by extension, cardiovascular well-being. It is imperative to understand the underlying mechanisms of chronic inflammation and its detrimental effects on the arteries to implement effective prevention and treatment strategies. By combining a heart-healthy lifestyle with regular medical monitoring and advanced therapeutic options, we can mitigate the risks associated with chronic inflammation and promote overall arterial health.
The journey to understanding and combating the impact of chronic inflammation on arterial health is ongoing, and with concerted efforts from individuals, healthcare providers, and researchers, we can look forward to a future with better cardiovascular outcomes.