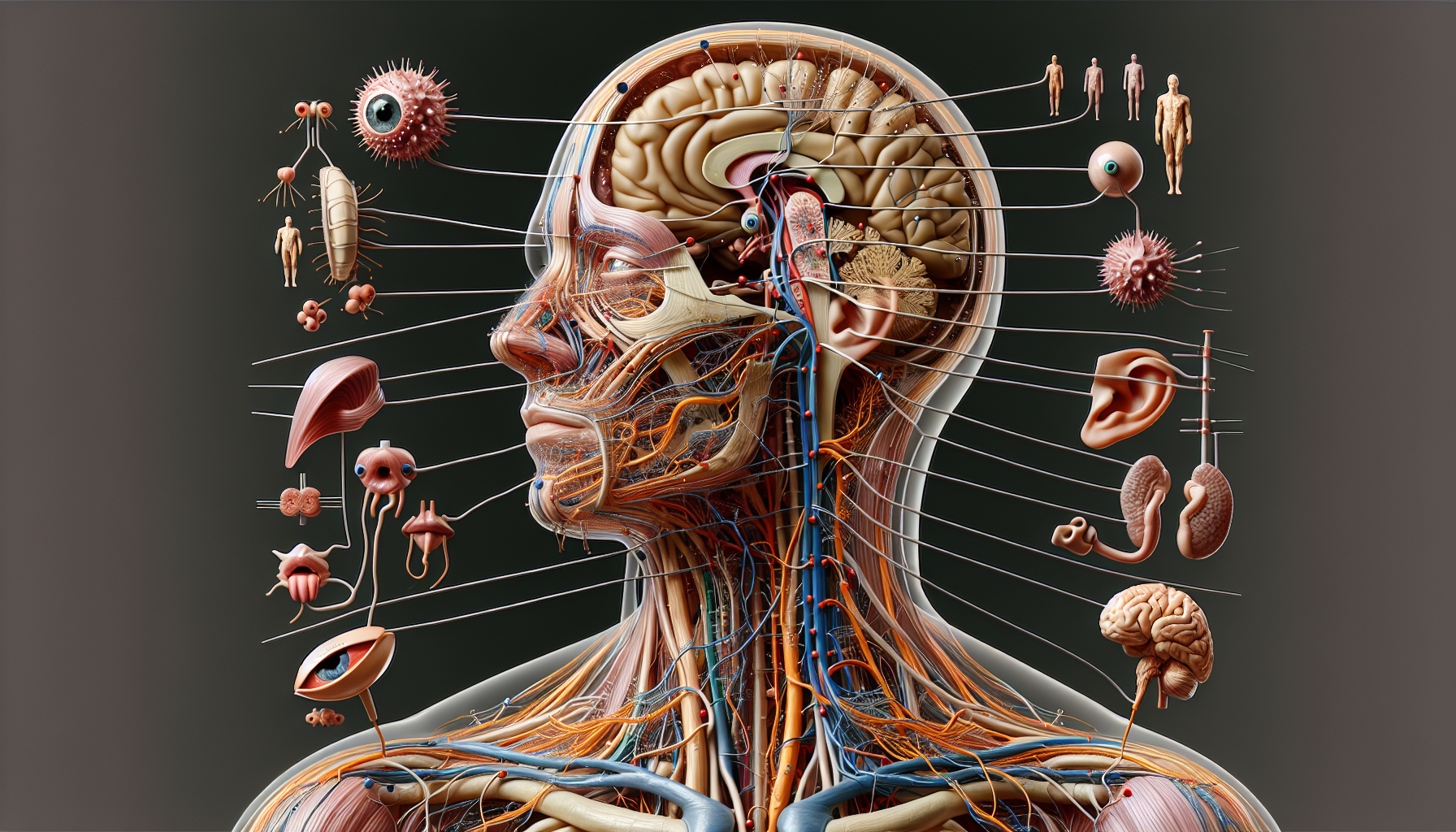
Our senses are the physiological method of perception, acting as the complex system that allows us to interact with and interpret our environment. Each sense—sight, smell, hearing, taste, and touch—is a gateway, providing a stream of information to the brain, which in turn helps us to understand and respond to the world around us. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the intricacies of each sense, their functions, and their importance in daily life.
The Vital Role of Sensory Health
Sensory health is a critical aspect of overall well-being, encompassing the proper functioning of all the five senses. It is an area that deserves attention and care, similar to other aspects of health like cardiovascular health, brain health, and digestive health. A disturbance in sensory health can significantly impact daily life, as detailed in the article How Sensory Processing Disorders Affect Daily Life.
Sight: The Window to the World
Sight, or vision, is perhaps the most relied upon of the five senses. The eyes capture light and convert it into electrochemical impulses that travel through the optic nerves to the brain. The brain then interprets these impulses as images.
Eye Health and Vision
Maintaining eye health is essential for clear vision. Regular eye exams, protection from excessive light, and a diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E are all crucial. For an in-depth look at how nutrition affects eye health, the article on Nutrition and Its Impact on Sensory Health provides valuable insights.
Visual Perception and Cognitive Function
There is a strong connection between what we see and our cognitive processes. Studies on visual perception underscore this link, showing how sight influences memory and learning. An informative resource on this topic can be found at the Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, which offers cutting-edge research on vision science.
Hearing: The Symphony of Sounds
Hearing enables us to detect and interpret sounds by converting vibrations in the air into electrical signals that are recognized by the brain. It plays a vital role in communication, learning, and alertness to our surroundings.
Auditory Health and Hearing Loss Prevention
Protecting our ears from prolonged exposure to loud noises and infections is crucial in preventing hearing loss. The Hearing Health Foundation provides resources and research on hearing loss prevention and treatment.
The Importance of Hearing in Social Interaction
Hearing connects us to others and aids in social interaction. The loss of this sense can lead to isolation and affect mental health. The article on The Connection Between Cardiovascular Health and Cognitive Function touches on these aspects of wellness.
Smell: The Scent of Memory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is directly linked to the limbic system of the brain, which is involved in memory and emotion. This is why certain smells can trigger vivid memories or strong emotional responses.
Olfactory Health and Disease Detection
A healthy sense of smell is important not just for enjoyment but also for detecting hazards such as smoke or gas leaks. Interestingly, olfactory dysfunction can be an early sign of neurodegenerative diseases. Insightful research on this can be found at the Monell Chemical Senses Center.
Smell and Taste: A Complementary Duo
Our sense of smell works closely with taste to create the perception of flavor. This is explored in the context of nutrition in the article Improving Vascular Health Through Targeted Nutrition.
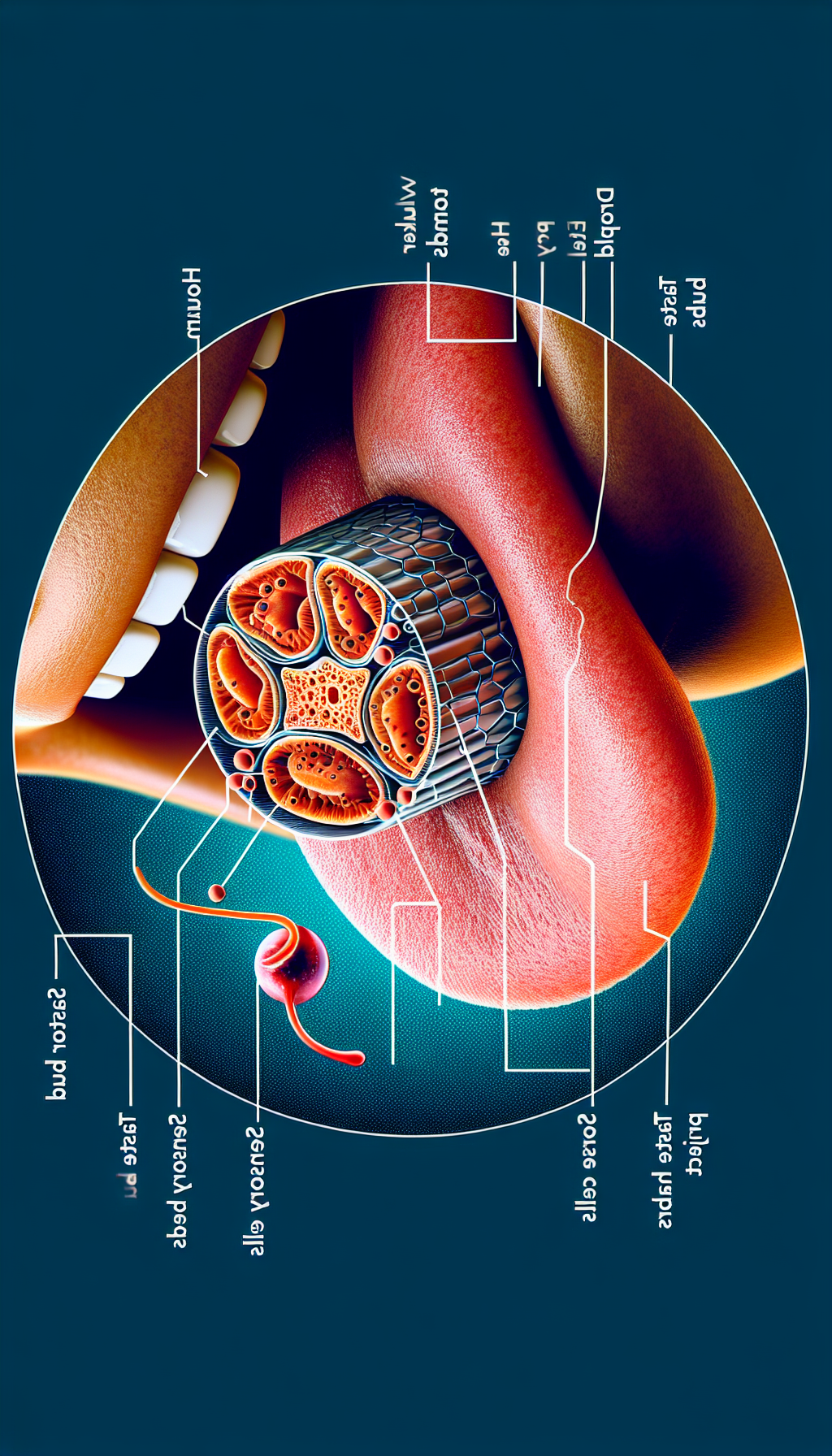
Taste: The Flavor of Life
Taste buds on the tongue detect five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. This sense helps us enjoy food, but it also has a protective function, helping us to avoid spoiled or toxic substances.
Taste Disorders and Nutritional Impact
Taste disorders can alter eating habits and impact nutritional intake. For those seeking to understand the relationship between diet and taste, the Taste and Smell Clinic in Washington, D.C. offers specialized insights.
Touch: The Feel of Reality
Touch is mediated by a network of nerves that send information to the brain about pressure, temperature, and pain. It is essential for tasks requiring dexterity and is also a key component in emotional bonding.
The Significance of Touch in Human Development
The importance of touch in early childhood development and the role of sensory-friendly environments are discussed in the article Sensory-Friendly Environments for Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Chronic Pain and Sensory Processing
Chronic pain conditions can affect the sense of touch. Organizations like the International Association for the Study of Pain provide resources for understanding and managing pain.
Sensory Integration and Overall Health
The integration of sensory information is vital for daily activities and overall health. It is important to recognize the signs of sensory processing issues and seek appropriate therapy if needed. Sensory health is as significant as maintaining bone health or managing medication and supplements.
The Role of Sensory Health in Aging
As we age, sensory functions may decline, which is why it is crucial to adopt strategies to maintain sensory health. The article Sensory Health and Aging: How to Adapt and Thrive provides valuable advice for older adults.
The Future of Sensory Health
Innovations in technology are continually shaping the future of sensory health. For those interested in the technological advancements in this field, Innovations in Sensory Health Technology offers a fascinating perspective.
Conclusion
Our senses are vital to our experience of life, and maintaining their health is integral to our overall well-being. From enjoying the subtleties of flavor to navigating the complexities of social interaction, our senses play a crucial role. By understanding and caring for our senses, we ensure a richer, more engaged experience of the world. For more information on how to maintain and improve sensory health, explore the wealth of resources available on Avix Health and other specialized platforms dedicated to health and wellness.