Bone density is a crucial aspect of overall health and has a significant impact on the risk of developing various lifestyle diseases. This article explores the intricate relationship between bone health and chronic conditions, emphasizing the importance of maintaining optimum bone density through lifestyle choices.
Understanding Bone Density and Its Importance
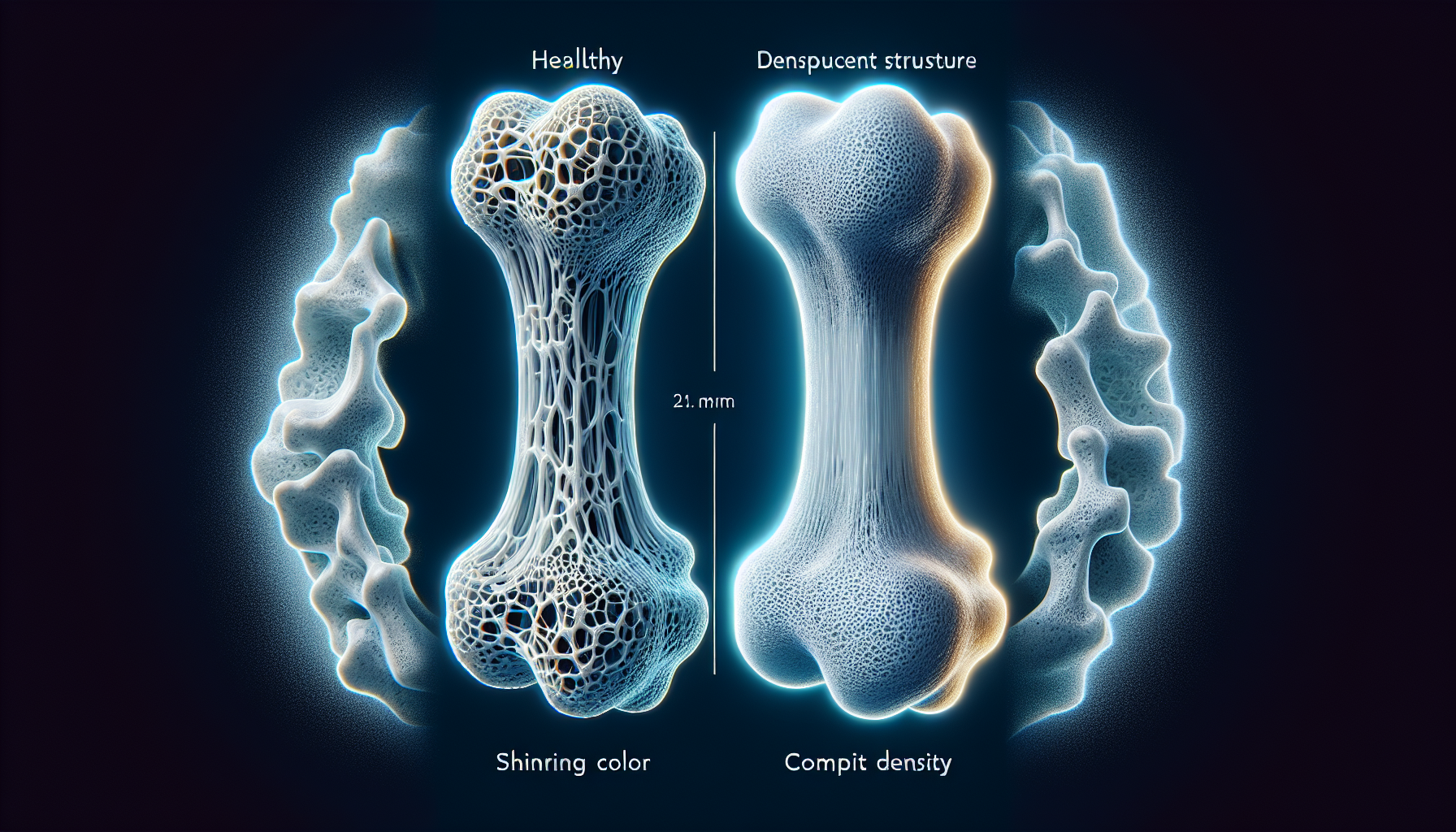
Bone density refers to the amount of mineral matter per square centimeter of bones and is a key indicator of bone strength and health. Healthy bones support our structure, protect vital organs, and store minerals that are essential for bodily functions. When bone density is compromised, it can lead to conditions such as osteoporosis, making bones fragile and more susceptible to fractures.
The decline in bone density is a natural part of aging, but it can be exacerbated by lifestyle factors, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and other habits that contribute to the development of lifestyle diseases like diabetes and heart disease. Understanding the relationship between these conditions and bone health is vital for prevention and management.
Lifestyle Diseases and Their Impact on Bone Health
Lifestyle diseases are non-communicable diseases that are primarily caused by unhealthy behaviors. Some of the most common lifestyle diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes, have been linked to decreased bone density.
For instance, cardiovascular health is deeply intertwined with bone health. Atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the build-up of plaque in the arteries, can limit the blood flow to bones, affecting their ability to remodel and maintain density. Those concerned about their cardiovascular health may find valuable information on Avix Health’s cardiovascular health resource.
Furthermore, obesity is often associated with inflammation and hormonal changes that can adversely affect bone turnover rates. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, can lead to lower bone quality and a higher risk of fractures, despite often presenting higher bone density readings.
Strategies for Maintaining Bone Density
Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients is fundamental for maintaining bone density. Calcium is the primary building block of bone tissue, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium effectively. Incorporating foods like dairy products, leafy greens, and fatty fish into the diet can help meet these nutritional requirements.
Exercise
Regular weight-bearing and resistance training exercises are highly beneficial for bone health. Activities such as walking, jogging, and lifting weights can stimulate bone formation and slow down the rate of bone loss.
Lifestyle Modifications
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are crucial steps in preserving bone density. Both tobacco and excessive alcohol can interfere with the balance of calcium in the body and the function of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for forming new bone.
Medical Interventions
For those already experiencing bone density loss, medications and supplements can play a role in management. Bisphosphonates, for example, can help slow the rate of bone loss, and supplements like calcium and vitamin D can aid in maintaining bone health.
The Role of Omega-3s in Bone Density and Joint Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have a positive impact on bone density. They help reduce inflammation in the body, which can contribute to bone loss. For an in-depth look at how omega-3s support bone and joint health, consider reading The Role of Omega-3s in Bone Density and Joint Health.
Addressing Bone Density Decline in Menopause
Women are particularly susceptible to bone density loss during menopause due to hormonal changes. Strategies designed to combat this decline, such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) and lifestyle adjustments, are critical. More information on managing bone health during menopause can be found in Strategies to Combat Bone Density Decrease in Menopause.
External Resources for Further Information
- The National Osteoporosis Foundation provides a comprehensive guide on bone density and osteoporosis.
- The International Osteoporosis Foundation offers global statistics and resources on bone health.
- The Bone Health and Osteoporosis Foundation is a resource for understanding the link between diet, exercise, and bone health.
The Impact of Hyperthyroidism on Bone Density
Thyroid health is another critical factor in maintaining bone density. Hyperthyroidism can accelerate bone turnover, leading to a decrease in bone density over time. Understanding the effects of thyroid conditions on bone health is crucial, as detailed in Understanding the Effects of Hyperthyroidism on Bone Density.
Conclusion
Bone density plays a significant role in overall health and is closely linked to the prevalence of lifestyle diseases. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of harmful habits, individuals can significantly improve their bone health and reduce the risk of developing chronic conditions. Medical interventions and targeted therapies can also aid in managing bone density loss when necessary. Maintaining healthy bones is not just about preventing fractures; it is about sustaining a quality of life that allows for active and fulfilling living.