Enzymatic therapy has become a cornerstone in the pursuit of digestive wellness, offering an alternative and supportive approach to maintaining optimal gut health. This comprehensive article will explore the multifaceted role of digestive enzymes, their therapeutic potential, and how they can be integrated into daily health regimens.
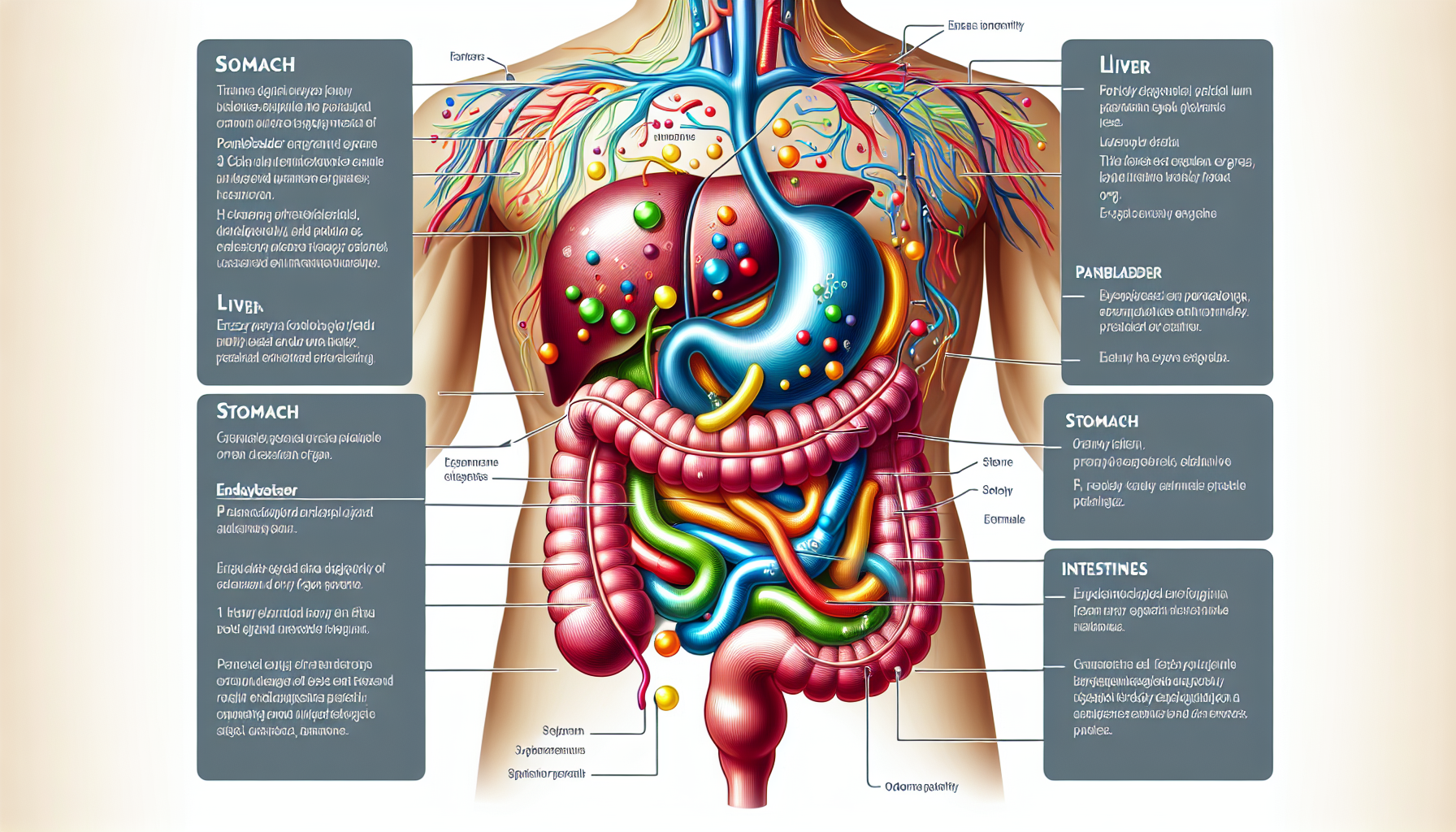
Digestive enzymes are biocatalysts that facilitate the breakdown of food into absorbable nutrients. Produced naturally by the body, these enzymes are crucial for proper digestion and nutrient absorption. However, certain conditions and lifestyle factors can disrupt enzyme production, leading to digestive discomfort and nutrient malabsorption. Enzymatic therapy, which involves the supplementation of natural enzymes, can help restore balance and support digestive health.
Understanding Digestive Enzymes
Digestive enzymes are specific to the types of food they break down. Proteases split proteins into amino acids, lipases break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, and amylases convert carbohydrates into simple sugars. The body secretes these enzymes from the salivary glands, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine.
When enzyme production is insufficient, the digestion of specific food components can be hindered, resulting in symptoms such as bloating, gas, and discomfort. Enzymatic therapy aims to replenish the body’s enzyme levels through supplementation, thus aiding digestion and promoting a healthy gut environment.
The Therapeutic Potential of Enzymatic Therapy
Enzymatic therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with chronic digestive disorders such as pancreatic insufficiency, lactose intolerance, or conditions like celiac disease that affect nutrient absorption. By supplementing the body’s natural enzyme production, enzymatic therapy can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
For example, people with lactose intolerance can benefit from lactase enzyme supplements to help digest dairy products, while those with celiac disease may use enzymes that break down gluten. Moreover, as we age, natural enzyme production can decrease, making enzymatic therapy a valuable tool for age-related digestive issues.
Incorporating Enzymatic Therapy into Digestive Wellness
When considering enzymatic therapy, it’s essential to choose high-quality supplements that contain the appropriate enzymes for your dietary needs. It’s also important to take them correctly—usually with meals—to ensure they work effectively. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you determine the best approach for your individual health concerns.
For those looking to improve their digestive health through diet, incorporating enzyme-rich foods, such as pineapple (which contains bromelain) and papaya (rich in papain), can be a natural alternative to supplementation. Additionally, fermented foods are a great source of natural enzymes and can help support a healthy microbiome.
Beyond Digestion: The Wider Benefits of Enzymatic Therapy
Enzymatic therapy doesn’t only benefit the digestive system. By aiding digestion and nutrient absorption, it can have a positive impact on overall health. For instance, improved digestion may enhance energy levels and athletic performance, as the body becomes more efficient in utilizing nutrients for energy.
Moreover, there is emerging evidence to suggest that enzymatic therapy may play a role in managing inflammatory conditions and supporting cardiovascular health. Digestive enzymes can help break down inflammatory by-products in the gut, potentially reducing systemic inflammation and its impact on the heart and blood vessels.
Choosing the Right Enzymatic Therapy
When considering enzymatic supplements, it’s crucial to look for products that are specific to your needs. Enzymes derived from microbial sources are typically more stable across a broader pH range, making them effective throughout the digestive tract. High-quality supplements will also be free from additives and sourced from reputable manufacturers.
External Resources for Further Reading
For those interested in the scientific basis of enzymatic therapy, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases offers a wealth of information on digestive diseases and how enzymes play a role in their management. Additionally, the American Nutrition Association provides resources on nutrition and its impact on health, including the use of enzyme supplements.
Navigating Potential Challenges
While enzymatic therapy can be an effective adjunct to digestive wellness, it is not without its challenges. The key is to understand that enzymes are specific in their action and that supplementing with the wrong type may not provide the desired benefits. It’s also important to be aware of the quality and source of enzyme supplements to avoid potential allergens or contaminants.
The Future of Enzymatic Therapy
Research into enzymatic therapy is ongoing, with studies exploring its potential in improving digestive health and managing conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The future may see more personalized enzyme therapies tailored to individual digestive profiles and dietary patterns.
Conclusion
Enzymatic therapy is a powerful tool in maintaining digestive wellness and enhancing overall health. By supporting the body’s natural digestive processes, enzyme supplements can help alleviate discomfort, improve nutrient absorption, and contribute to a better quality of life. As research continues to shed light on the benefits and applications of enzymatic therapy, it stands as a promising approach to digestive health maintenance.
For those looking to integrate enzymatic therapy into their health regimen, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it aligns with personal health needs and goals. With the right approach, enzymatic therapy can be a valuable addition to a comprehensive wellness strategy.