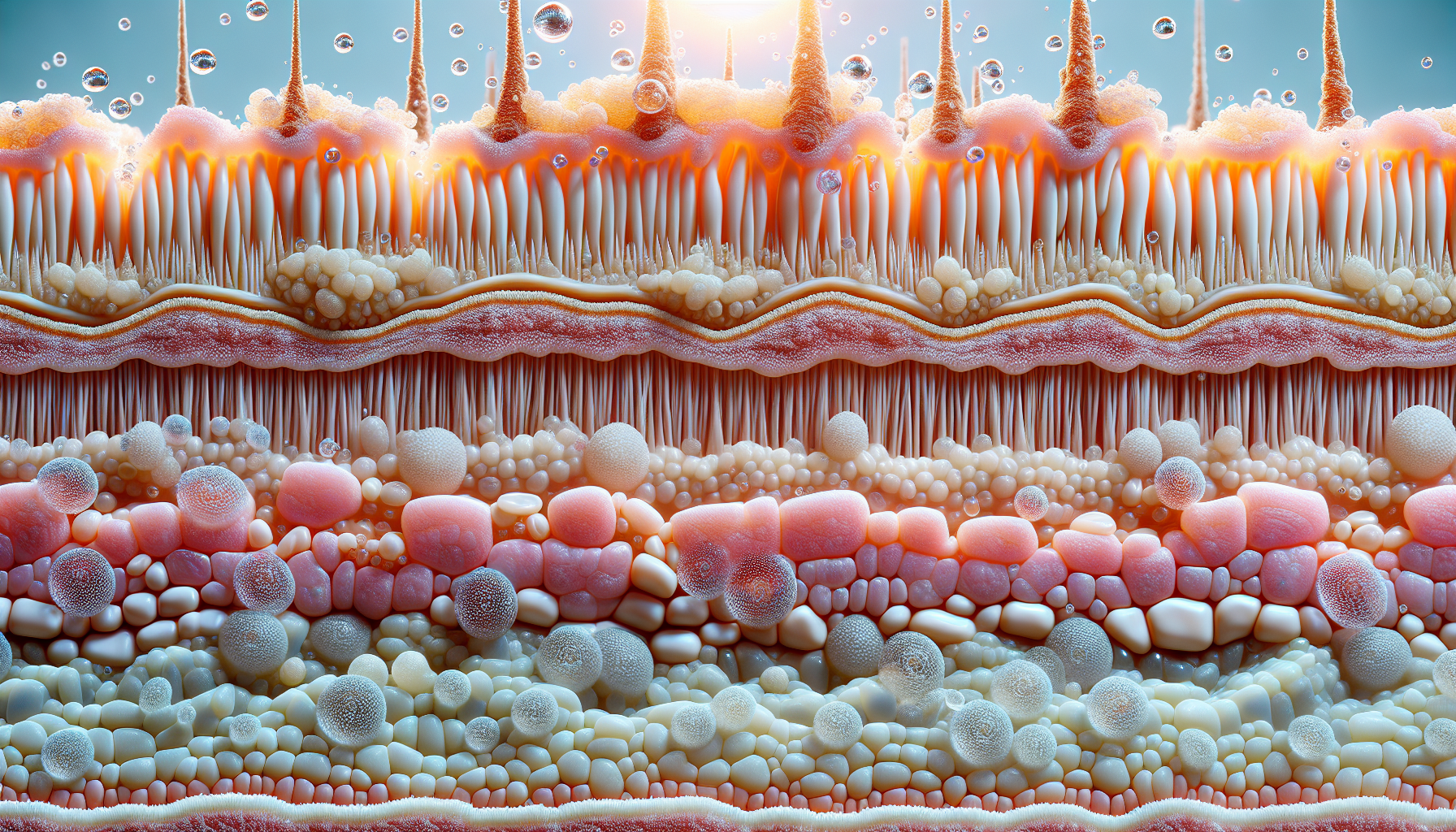
The skin is the largest organ of the body and serves as the first line of defense against environmental aggressors. It’s a complex ecosystem that requires balance and care to function optimally. One crucial aspect of skin health is the integrity of the skin barrier. A healthy skin barrier protects against irritants, allergens, and pathogens while retaining moisture and nutrients essential for skin vitality. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the functions of the skin barrier, signs of impairment, and strategies to restore and maintain its health.
Understanding the Skin Barrier
The skin barrier, primarily located in the outermost layer of the skin known as the stratum corneum, consists of cells (corneocytes) embedded in a lipid matrix. This structure acts as a brick wall, with the corneocytes being the bricks and the lipids representing the mortar. The integrity of this barrier is vital for skin health, as it prevents transepidermal water loss (TEWL) and blocks the entry of harmful substances.
For a deeper understanding of skin health and its various components, consider exploring Avix Health’s comprehensive discussion on skin health.
Signs of a Compromised Skin Barrier
A damaged skin barrier can manifest in several ways, including:
- Increased dryness or dehydration
- Sensitivity to products or environmental factors
- Inflammation and redness
- Itchiness and discomfort
- Flakiness or rough texture
- Susceptibility to infections
- Aggravation of skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it may be indicative of a compromised skin barrier.
Factors That Affect Skin Barrier Health
Various factors can impact the health of the skin barrier, such as:
- Over-exfoliation or harsh skincare products: Stripping the skin of its natural oils can weaken the barrier.
- Environmental stressors: Pollution, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures can damage the skin.
- Lifestyle choices: Poor diet, inadequate sleep, and high-stress levels can negatively affect skin health.
- Aging: Natural aging processes lead to a decline in lipid production, thinning the skin barrier.
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals are naturally prone to weaker skin barriers.
To gain insight into how lifestyle factors like diet affect skin over time, delve into the article on How Diet Affects Skin Health Over Time.
Strengthening and Repairing the Skin Barrier
Repairing and reinforcing the skin barrier involves a multifaceted approach. Here are some strategies:
Gentle Cleansing
Opt for mild cleansers with a pH close to that of the skin to avoid disrupting the acid mantle. Harsh soaps can strip essential lipids and proteins, leading to barrier damage.
Adequate Hydration
Moisturizing is crucial for a healthy skin barrier. Look for products with ingredients like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and ceramides, which help to retain water and repair the lipid matrix.
Balanced Diet
A diet rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can support skin barrier function. Foods like berries, nuts, and leafy greens are excellent choices.
Sun Protection
UV radiation can deteriorate the skin barrier, making sunscreen an essential part of any skin care routine. Be sure to select a broad-spectrum sunscreen and reapply regularly.
For further reading on the benefits of sunscreen, check out the article The Importance of Sunscreen for All Skin Types.
Avoiding Irritants
Limit exposure to irritants such as fragrances, alcohol, and certain preservatives, which can trigger inflammation and barrier damage.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can impair barrier function by increasing inflammation and disrupting the skin’s ability to repair itself. Practices like meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep can help manage stress levels.
Professional Treatments
Seeking professional guidance can be beneficial. Dermatologists may recommend treatments like hydrafacials or medical-grade moisturizers to enhance barrier repair.
External Resources for Further Research
To supplement your understanding of skin barrier health, consider these high-quality niche resources:
- International Journal of Molecular Sciences – Features research on the molecular mechanisms involved in skin barrier function and repair.
- National Eczema Association – Provides insights on managing eczema and related skin barrier issues.
- Skin Cancer Foundation – Offers information on how sun exposure impacts the skin barrier and ways to protect it.
- American Academy of Dermatology – A resource for guidelines on skincare practices that promote a healthy skin barrier.
Conclusion
Maintaining the integrity of your skin barrier is essential for overall skin health and appearance. By understanding the factors that affect the skin barrier and implementing the strategies outlined above, you can help ensure your skin remains resilient, hydrated, and healthy. Remember that consistency is key, and it’s crucial to adapt your skincare routine to the changing needs of your skin.
For personalized advice, always consult with a dermatologist who can provide tailored recommendations based on your unique skin type and concerns.
By nurturing your skin barrier, you not only enhance your skin’s appearance but also fortify its defense against the daily challenges it faces. Embrace the journey to healthier skin, and enjoy the confidence that comes with it.