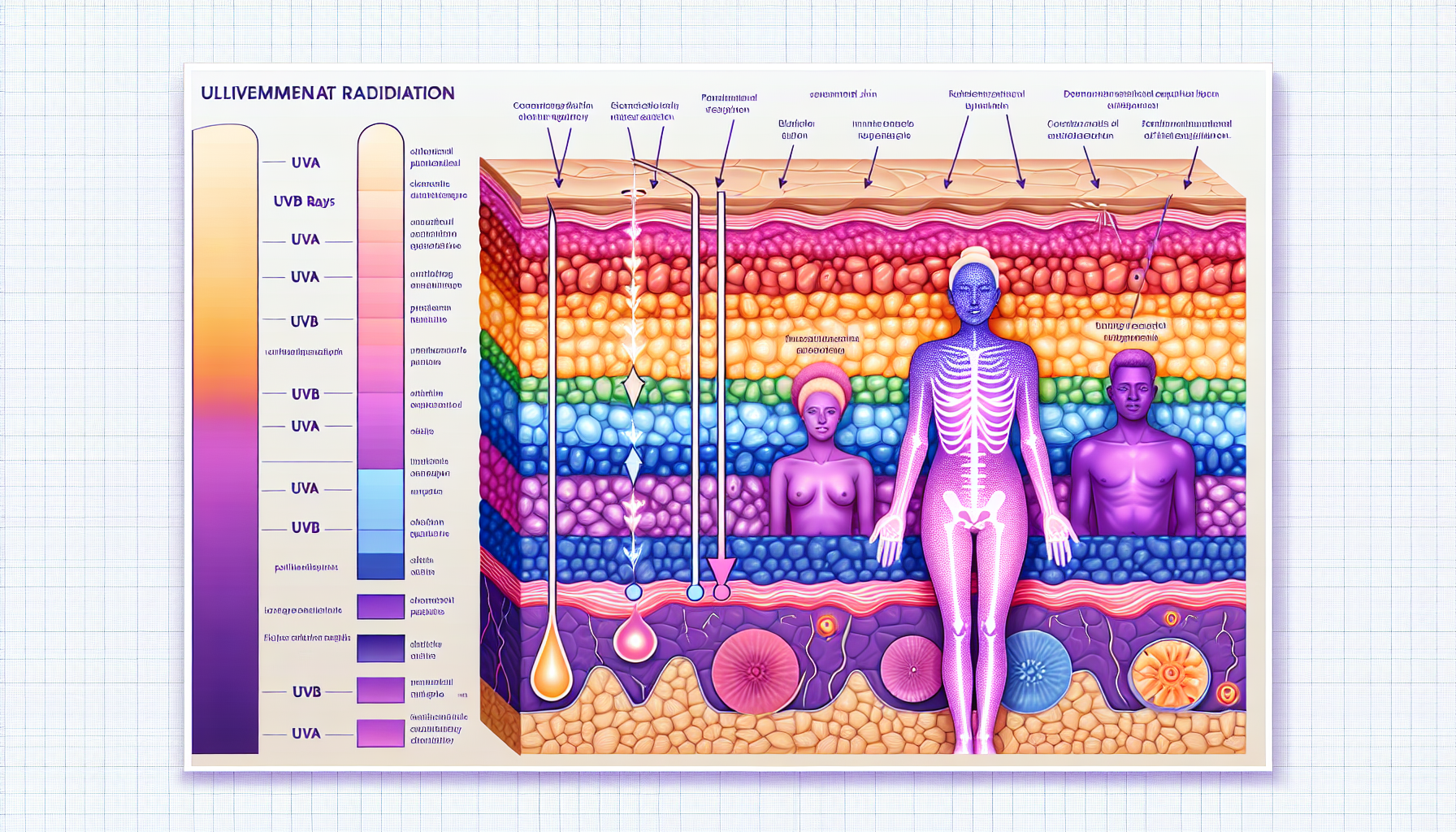
The skin, the largest organ of the human body, serves as the first line of defense against numerous environmental aggressors, among which ultraviolet (UV) radiation is one of the most significant. The sun emits a range of electromagnetic radiation, and the part that reaches the earth’s surface is primarily composed of UVA and UVB rays. While exposure to sunlight is beneficial for processes like Vitamin D synthesis, excessive UV radiation can lead to adverse effects on skin health.
The Science of UV Radiation and Skin Interaction
UV radiation is classified into three types based on wavelength: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVC is mostly absorbed by the ozone layer and does not reach the earth. However, UVA and UVB penetrate the atmosphere and play a crucial role in conditions such as premature skin aging, DNA damage, and skin cancers.
UVA Rays
UVA rays account for approximately 95% of the UV radiation reaching the earth’s surface and are present with relatively equal intensity during all daylight hours throughout the year. They can penetrate clouds and glass and can penetrate deeper into the skin layers, leading to the immediate tanning effect as well as contributing to skin aging and wrinkling.
UVB Rays
UVB rays are the chief cause of skin reddening and sunburn and tend to damage the skin’s more superficial epidermal layers. They play a key role in the development of skin cancer and contribute to tanning and photoaging. Unlike UVA, the intensity of UVB rays varies by season, location, and time of day.
Health Implications of UV Exposure
Skin Aging
Prolonged exposure to UV rays can accelerate the natural aging process of the skin, leading to what is known as photoaging. This includes the development of wrinkles, leathery texture, and loss of elasticity. For a comprehensive understanding of skin health and aging, consider reading about advances in dermatological treatments and skin care.
Skin Cancer
UV radiation can cause mutations in the DNA of skin cells. Over time, these mutations can accumulate, leading to skin cancer, including melanoma, which is the most deadly form. To learn more about detecting and preventing this disease, refer to detecting and preventing skin cancer.
Immune Suppression
UV radiation can suppress the skin’s immune function, hindering the body’s ability to fight off certain skin cancers and infections.
Protective Measures Against UV Radiation
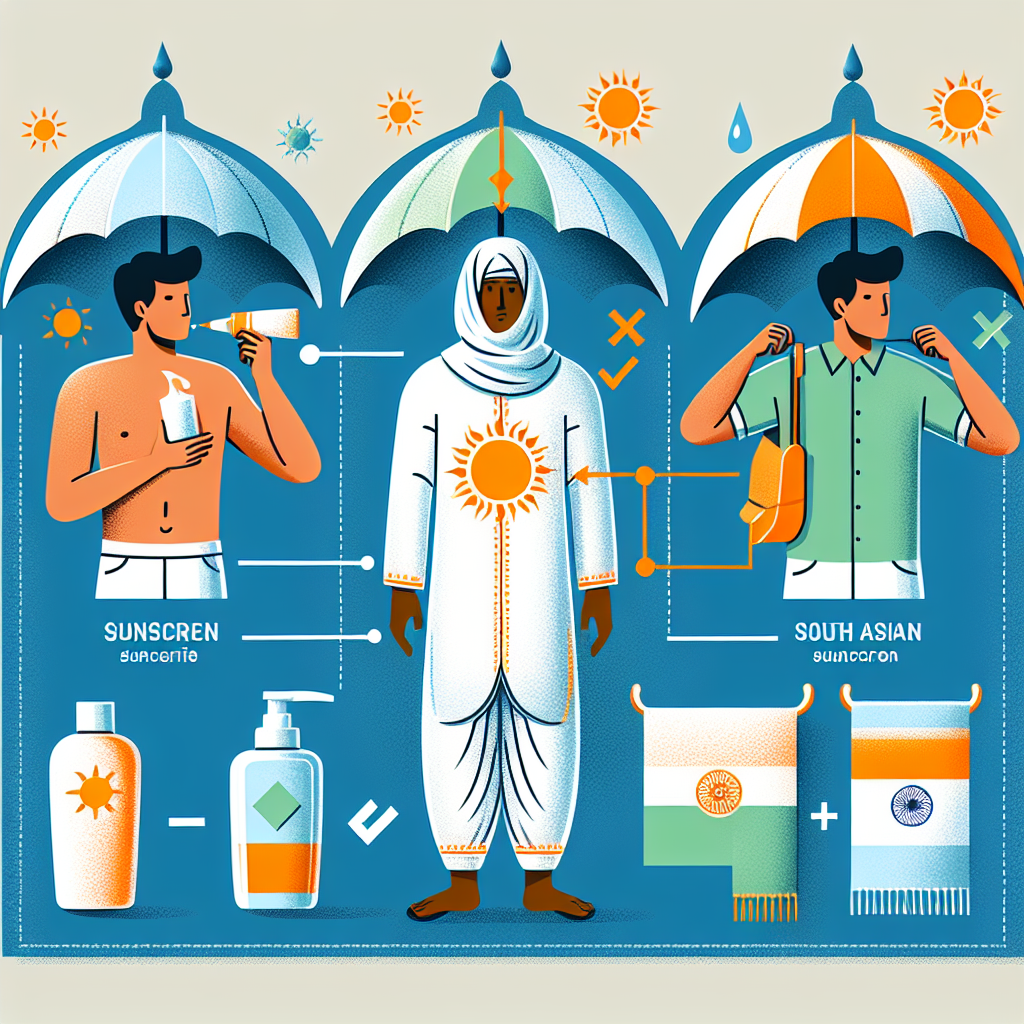
Sunscreen
Using broad-spectrum sunscreens that protect against both UVA and UVB rays is essential. The sunscreen should have a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30 and be reapplied every two hours or immediately after swimming or sweating.
Clothing
Wearing protective clothing and hats can shield the skin from UV rays. There are also laundry additives available that give clothing an additional layer of UV protection for a certain number of washings.
Timing
Avoiding the sun during peak hours, generally from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m., when UV radiation is strongest, can significantly reduce exposure.
Sunglasses
Wearing sunglasses that block 99% to 100% of UVA and UVB rays helps protect the eyes and the sensitive skin around them.
The Link Between UV Exposure and Other Health Aspects
UV radiation’s impact is not limited to the skin—it can also affect other aspects of health. For instance, there is a link between gut health and skin appearance, indicating that a holistic approach to health can potentially mitigate some of the adverse effects of UV exposure.
Moreover, considering the comprehensive care of your skin also involves understanding the importance of daily skin care routines which can help in maintaining the skin’s integrity against environmental stressors, including UV rays.
External Resources for Further Reading
- The World Health Organization provides resources on UV radiation and its health implications (WHO – Ultraviolet radiation).
- The Skin Cancer Foundation offers detailed information on how to protect your skin from UV damage (Skin Cancer Foundation – Prevention Guidelines).
- Research on the effects of UV radiation on skin cells is available through scientific publications like the Journal of Investigative Dermatology (Journal of Investigative Dermatology).
Conclusion
Understanding the effects of UV radiation on the skin is crucial for maintaining long-term skin health and overall well-being. By taking protective measures and educating ourselves about the risks and safe sun practices, we can enjoy the benefits of sunlight without compromising our skin’s health.
To delve deeper into related topics, such as maintaining bone health, which can be affected by vitamin D synthesis through sun exposure, please visit Avix Health on bone health.