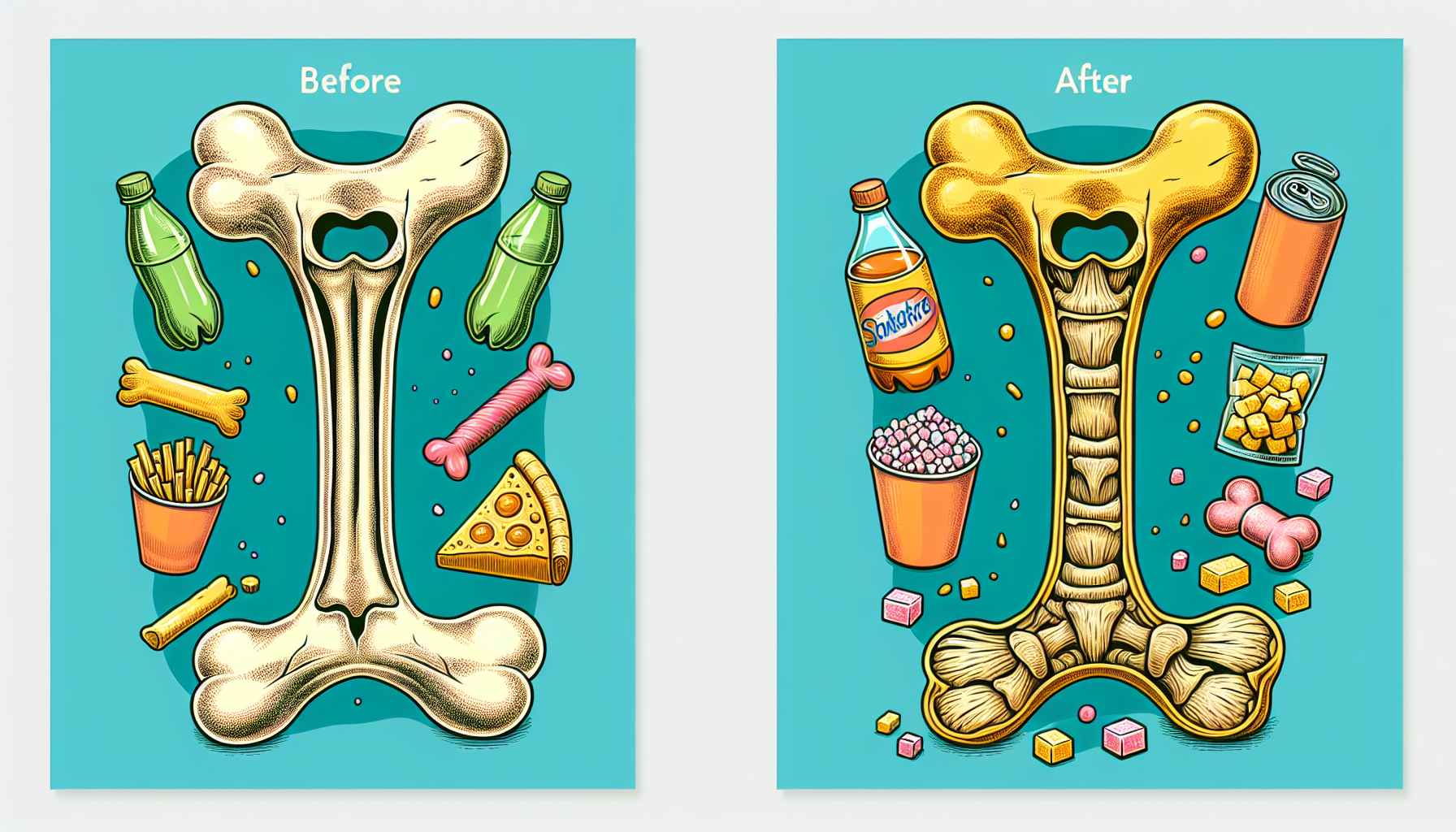
Excessive sugar intake is a growing concern in modern diets, with its implications reaching far beyond the commonly discussed risks of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Among the lesser-known consequences is the potential detriment to bone health. To understand this impact fully, we must delve into the complex interplay between dietary choices and the structural integrity of our skeleton.
Sugar’s Role in Bone Health
Bones are living tissues that require a balance of nutrients, including calcium and phosphate, to maintain their density and strength. This balance is not just about the nutrients we take in, but also about how our body processes and utilizes them. Sugars, particularly those added to foods during processing, can disrupt this balance in several ways.
Nutrient Absorption and Excretion
High sugar consumption can increase the excretion of calcium in the urine, effectively reducing the amount of calcium available to the bones. Additionally, diets high in sugar often displace healthier options that are rich in calcium and other bone-fortifying nutrients. This double-edged sword not only deprives the bones of necessary materials but also enhances their loss.
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress have been implicated in various health issues, including the weakening of bones. Sugars, especially in the form of high-fructose corn syrup, can heighten inflammatory responses in the body and create oxidative stress, potentially accelerating bone density loss.
Hormonal Disruptions
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. High sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s response to insulin is diminished. Since insulin also plays a role in bone remodeling—a process where old bone tissue is replaced with new—resistance to this hormone can interfere with normal bone maintenance, predisposing individuals to osteoporosis.
Exploring the Evidence
Research has begun to shed light on the connection between sugar and bone health. One study found that high sugar intake was associated with a decrease in bone density among adolescents, a critical period for bone development. Another suggested that diets high in sugar could lead to a reduction in bone strength and quality in adults.
For those seeking more in-depth information on bone health, Avix Health provides an extensive resource on the topic, which offers valuable insights into maintaining strong and healthy bones over a lifetime.
The Broader Dietary Picture
While sugar’s effect on bone density is significant, it is but one piece of the larger dietary puzzle. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly calcium and vitamin D, is essential for bone health. Foods like leafy greens, dairy products, and fortified cereals can provide these nutrients, while practices such as regular physical activity can also contribute to stronger bones.
Moreover, reducing the intake of other bone-depleting substances such as caffeine and alcohol, alongside sugar, can further bolster bone density.
Practical Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar intake does not have to be a daunting task. Simple changes can have a profound impact:
- Read Labels: Becoming aware of hidden sugars in processed foods by reading nutrition labels can help you make better choices.
- Choose Whole Foods: Opt for fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins over processed snacks and meals.
- Limit Sugary Beverages: Replace sodas and fruit juices with water, herbal teas, or infused water.
Beyond Diet: Lifestyle and Bone Health
Diet is not the only factor influencing bone health. Exercise, particularly weight-bearing activities like walking, running, and strength training, is crucial for stimulating bone growth and maintenance. Moreover, lifestyle choices such as smoking cessation and limiting alcohol intake can also have substantial benefits for bone density.
For those interested in the specific benefits of weight lifting for bone health, explore this Avix Health article which delves into how resistance training can fortify the skeletal system.
The Interplay of Other Health Factors
Bone health does not occur in isolation. It is deeply interconnected with other aspects of well-being, including cardiovascular health. For instance, diets high in sugar can lead to increased blood pressure and inflammation, indirectly affecting bone health by altering blood flow and nutrient delivery to bone tissues.
To understand more about the relationship between dietary choices and cardiovascular health, consider reading through the comprehensive guide provided by Avix Health’s cardiovascular health resource.
Seeking Guidance from Healthcare Providers
If you’re concerned about your sugar intake and its potential effects on bone density, consult with a healthcare provider. They can help you assess your dietary habits and bone health status, potentially through bone density imaging techniques. For a closer look at the advancements in this field, this article offers a summary of the latest imaging methods and their role in diagnosing and monitoring bone health conditions.
Resources for Further Reading
To expand your understanding of the relationship between dietary sugar and bone health, consider the following niche resources:
- The National Osteoporosis Foundation provides comprehensive information on bone health, including the effects of diet.
- The International Osteoporosis Foundation offers resources on preventing, diagnosing, and treating bone disorders.
- The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics features articles on nutrition, including the impact of sugar on health.
In conclusion, while sugar may be a sweet temptation, its excessive consumption can lead to long-term implications for bone health. By understanding the risks and adopting healthier dietary and lifestyle habits, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain strong bones and overall well-being.