Achieving radiant and healthy skin is a common goal for many, but it’s not just about what you put on the surface. True skin health begins within, and vitamins play a crucial role in skin repair and maintenance. Understanding which vitamins are essential for skin health and how to incorporate them into your routine can make a significant difference in your skin’s appearance and resilience.
The Foundation of Skin Health
Skin is the body’s largest organ, and it serves as a barrier against environmental aggressors, such as UV rays and pollution. It’s also a reflection of our overall health, often showing the first signs of nutritional deficiencies or imbalances. Just like any other part of the body, the skin requires a range of nutrients to maintain its health and function.
For comprehensive skin health support, including vitamins in your diet and skin care regimen is essential. While the skin benefits from a variety of vitamins, there are a few key players that stand out for their reparative and protective properties.
Vitamin A: The Anti-Aging Ally
Vitamin A, and particularly its active form retinol, is renowned for its anti-aging effects. It promotes cell turnover, helps to even out skin tone, and stimulates collagen production, which is vital in maintaining skin elasticity. A deficiency in vitamin A can lead to dry, flaky skin, which is more susceptible to damage and aging.
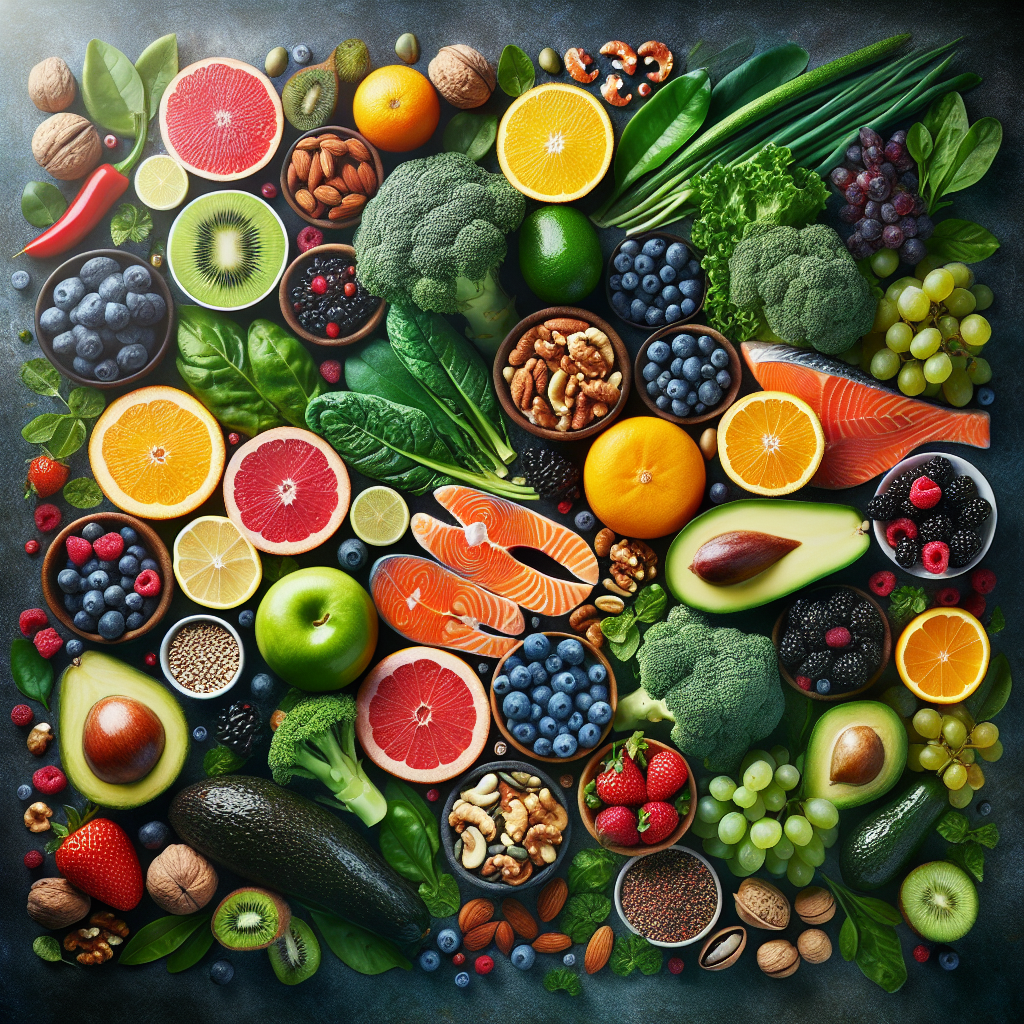
To boost your vitamin A intake, consider incorporating foods like sweet potatoes, carrots, and dark leafy greens into your diet. For topical application, retinol creams and serums can be particularly effective, although they should be introduced gradually to avoid irritation.
For a deeper understanding of skincare routines that complement vitamin A’s benefits, you might want to read about how to build a skin care routine for combination skin.
Vitamin C: The Brightening Booster
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that protects the skin against free radical damage from exposure to UV rays and pollution. It also plays a role in collagen synthesis and can help lighten hyperpigmentation, leading to a brighter and more even complexion.
While citrus fruits are well-known sources of vitamin C, vegetables such as bell peppers and broccoli are also rich in this essential nutrient. Topical vitamin C serums can provide a direct dose of antioxidant protection and should be applied in the morning before sunscreen for optimal defense against daily environmental stressors.
To further explore the role of antioxidants in skin care, visit using antioxidants to prevent skin damage.
Vitamin E: The Protective Partner
Vitamin E complements vitamin C as it helps stabilize it and extends its effectiveness. It also nourishes the skin barrier, providing moisture and reducing inflammation. Vitamin E is particularly beneficial for healing scars and improving skin texture.
Nuts, seeds, and green leafy vegetables are good sources of vitamin E. It’s also commonly found in moisturizers and oils, where it helps to soothe and protect the skin, especially when combined with vitamin C.
For an in-depth look at a vital aspect of skin health, read about the role of collagen in maintaining a youthful appearance.
Vitamin D: The Sun’s Gift
Often called the "sunshine vitamin," vitamin D is synthesized by the skin when exposed to sunlight. It’s known for its role in bone health, but it also contributes to skin cell growth and repair. Vitamin D can help combat symptoms of skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema.
While moderate sun exposure can provide you with vitamin D, it’s also found in fatty fish, fortified foods, and supplements. Remember to always balance sun exposure with sun protection to prevent skin damage.
For more on how to safely get vitamin D from the sun while protecting your skin, consider the comprehensive guide on skin health.
Vitamin B3: The Regulator
Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, is gaining popularity in skin care due to its wide range of benefits. It helps regulate oil production, reduces inflammation, and can improve the skin’s barrier function. It’s also been shown to reduce the appearance of pores and fine lines.
Whole grains, meat, fish, and eggs are all excellent sources of vitamin B3. Topical niacinamide is often found in serums and creams and can be used both morning and night for maximum benefit.
Other Skin-Supportive Nutrients
While vitamins are fundamental, other nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and minerals such as zinc and selenium also play critical roles in skin health. Omega-3s, found in fish oil and flaxseeds, are anti-inflammatory and can help maintain skin’s moisture levels. Zinc aids in skin healing and sebum regulation, whereas selenium protects against oxidative damage.
External Resources for Further Reading
- The National Institutes of Health provides an extensive overview of vitamin A and its importance in skin health.
- A clinical study on the effects of niacinamide on the skin’s barrier function offers insight into vitamin B3’s benefits.
- For those interested in antioxidants, the Linus Pauling Institute presents detailed information on vitamin C’s role in skin health.
Integrating these vitamins into your diet, along with topical applications where appropriate, can significantly improve your skin’s health and appearance. Remember to consult with a healthcare provider or dermatologist before making significant changes to your diet or skin care regimen, especially if you have underlying skin conditions or are taking other medications.
Conclusion
Attaining healthy, glowing skin is a multifaceted endeavor that involves more than just the right creams and cleansers. Incorporating the key vitamins discussed here—A, C, E, D, and B3—into your routine can provide your skin with the essential nutrients it needs to repair, protect, and thrive. Pair these nutrients with a balanced diet, adequate hydration, and sun protection, and you’ll be well on your way to a vibrant and youthful complexion.