Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by the hardening and narrowing of the arteries due to the buildup of plaque, which can lead to serious cardiovascular complications. It is imperative for individuals to understand the nature of this disease, its risk factors, and the available treatment options to effectively manage and prevent its progression. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of atherosclerosis and guide you through the latest advancements in treatment.
What is Atherosclerosis?
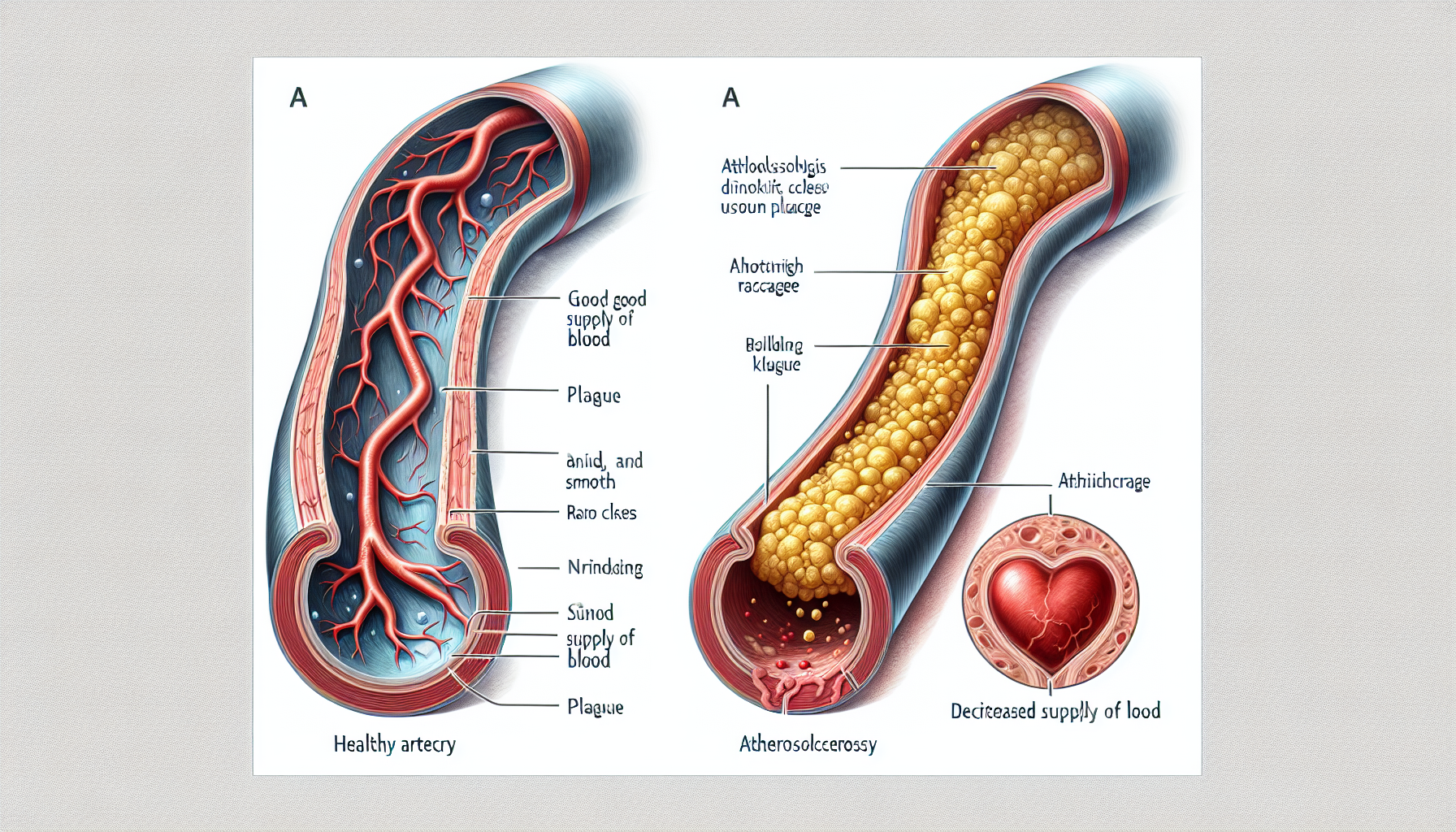
At its core, atherosclerosis is a slow, progressive disease that may start as early as childhood. Over time, the walls of the arteries become clogged with fatty substances, cholesterol, cellular waste products, calcium, and fibrin, forming a substance called plaque. This buildup can restrict blood flow and, in severe cases, can lead to the complete blockage of an artery. When arteries that supply blood to the heart are affected, it can result in coronary artery disease, angina, or heart attacks.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle. Genetics also play a role, with a family history of early heart disease being a significant indicator. For comprehensive information on managing cardiovascular risks, consider reading about Heart Health and Diabetes: Managing the Risks.
Signs and Symptoms
Atherosclerosis can be sneaky, often showing no symptoms until an artery is so narrowed or clogged that it can’t supply adequate blood to organs and tissues. Symptom manifestation depends on the affected arteries. If heart arteries are affected, symptoms may include chest pain or shortness of breath. Atherosclerosis in arteries leading to the brain can cause symptoms of a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing atherosclerosis involves reviewing medical history, conducting physical exams, and tests such as blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECG), stress tests, and cardiac catheterization. Advanced imaging technologies, including CT scans and MRIs, also play a pivotal role in diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Changes
The first line of defense against atherosclerosis involves making lifestyle changes. This includes following a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and quitting smoking. To explore how fitness can specifically benefit heart health and aid in the management of atherosclerosis, refer to the article on Fitness.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, and manage other contributing conditions. Antiplatelet medications can prevent clots from forming in narrowed arteries.
Surgical Procedures
In cases where atherosclerosis has led to significant blockages, surgical procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement or bypass surgery might be necessary. These procedures aim to restore adequate blood flow to the affected organs.
Preventative Measures
Preventative strategies for atherosclerosis include managing risk factors and adhering to a cardiovascular-friendly lifestyle. Monitoring blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels is essential. Furthermore, adopting a diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can make a significant difference.
Advancements in Treatment
The field of cardiovascular treatment is continuously evolving. New drugs, less invasive procedures, and innovative technologies are being developed to improve the outcomes for patients with atherosclerosis. Advancements in Cardiovascular Disease Treatment provides an in-depth look into current and emerging treatment options.
The Role of Supplements
While lifestyle changes and medications are the cornerstone of atherosclerosis treatment, some may consider the use of natural supplements. It’s critical to approach this option with caution and be aware of the promises and pitfalls involved. Natural Supplements for Heart Health: Promises and Pitfalls offers valuable insights into the role of supplements in heart health.
External Resources
For those seeking to delve deeper into the science and treatment of atherosclerosis, the following niche resources offer valuable information:
- The American Heart Association provides detailed information about cholesterol, a key player in the development of atherosclerosis.
- The Lancet’s commission on atherosclerosis is a treasure trove for the latest research and recommendations on managing the disease.
- ClinicalTrials.gov showcases ongoing clinical trials on atherosclerosis, offering insight into future treatment possibilities.
In conclusion, understanding and managing atherosclerosis requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication, and staying informed about new treatment options. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that best suits individual needs and circumstances. With the right knowledge and resources, managing atherosclerosis and leading a healthy life is within reach.