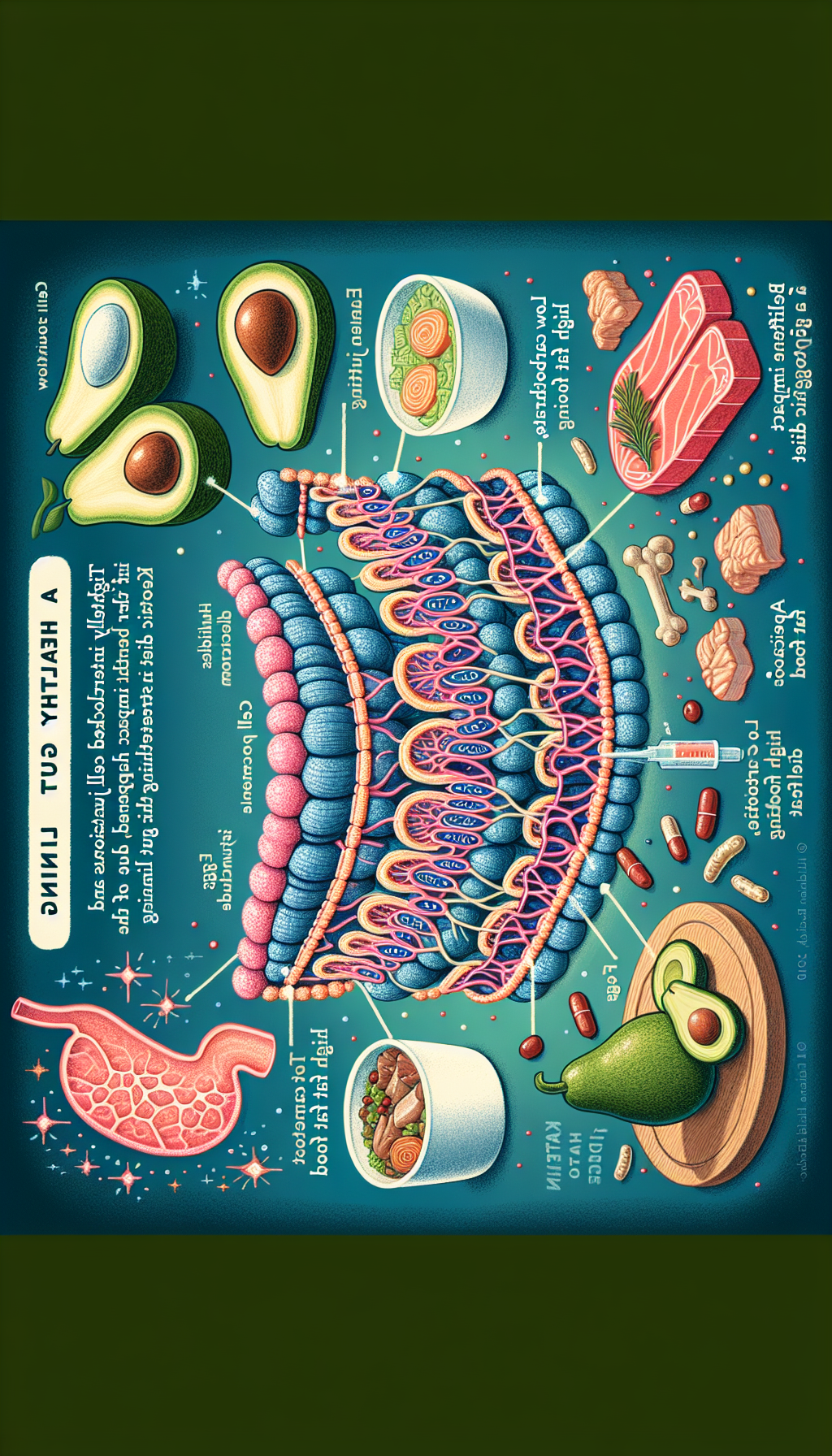
The Ketogenic diet, or ‘keto’ for short, has surged in popularity in recent years, drawing attention for its potential to induce rapid weight loss. But there’s more to this high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet than meets the eye. Emerging research suggests that keto may also have profound effects on the gut microbiota—the diverse community of microorganisms residing in our digestive tracts. These microscopic inhabitants play a crucial role in our overall health, influencing digestion, immune function, and even mood.
Keto Basics and Its Impact on Digestive Health
At its core, the ketogenic diet alters the body’s energy metabolism by restricting carbohydrates, forcing the body to burn fat for fuel—a state known as ketosis. This dramatic shift not only affects weight but may also lead to changes in gut flora composition. A study published in the journal ‘Cell’ found that the gut microbiota undergoes significant changes when the host is in a state of ketosis, which could have various health implications.
The Ketogenic Shift: A Microbial Perspective
The reduction of carbohydrate intake on a ketogenic diet reduces the availability of sugars that some gut bacteria thrive on. In contrast, an increase in fat consumption can favor bacterial species capable of metabolizing these compounds. For instance, certain beneficial bacteria, like those from the genus Bacteroides, are known to flourish in a fat-rich environment, as noted in a research article published in ‘Frontiers in Microbiology’.
Furthermore, a ketogenic diet can influence gut health by impacting the body’s bile acid composition. Bile acids are not only crucial for the digestion and absorption of fats but also act as antimicrobial agents that can shape the gut microbiota. A study in ‘Gastroenterology’ journal highlights that these changes in bile acid composition can selectively inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic bacteria while promoting the proliferation of beneficial ones.
Keto and Digestive Wellness
The potential benefits of a ketogenic diet on digestive wellness extend beyond the microbiota. By reducing inflammatory foods, such as sugars and certain starches, the keto diet can help in managing digestive inflammation. This is particularly relevant for individuals with conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Moreover, for insights on managing digestive health effectively, readers may find the article on Strategies for Improving Liver Detoxification for Digestive Health particularly enlightening.
The Role of Ketogenic Diet in Reducing Gut Inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can lead to a host of problems, from discomfort to more serious conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. The ketogenic diet’s reduction in sugar intake is one of the mechanisms by which it can lower inflammation. By limiting food for potentially harmful bacteria that thrive on sugars, the diet can reduce bacterial overgrowth and the associated inflammatory response. Readers may also explore The Role of Chronic Inflammation in Gut Diseases for a more in-depth understanding of inflammation’s impact on gut health.
Enhancing Gut Barrier Function through Keto
The gut barrier is our first line of defense against pathogens, and its integrity is vital for maintaining overall health. A compromised gut barrier can lead to ‘leaky gut syndrome’, where harmful substances leak into the bloodstream, potentially leading to autoimmune conditions and chronic inflammation. The ketogenic diet has been suggested to enhance gut barrier function, as indicated by research demonstrating the diet’s ability to increase levels of "tight junction proteins," which are crucial for a robust and functional gut lining.
The Importance of Prebiotics in a Ketogenic Diet
While a ketogenic diet can benefit the gut microbiota, the restriction of carbohydrates may limit the intake of prebiotic fibers—essential food for healthy bacteria. It’s important to include keto-friendly, fiber-rich foods such as avocados, leafy greens, and flaxseeds to maintain a balanced microbiome. For those looking to delve deeper into the significance of these foods, the article on The Importance of Prebiotic Foods in Gut Health offers valuable insights.
Considerations and Challenges
Despite its potential benefits, the ketogenic diet is not without its challenges. A drastic change in diet can initially cause discomfort as the body adapts to new fuel sources. Moreover, the diet’s restrictive nature may make it difficult to maintain long-term, potentially leading to nutritional deficiencies if not carefully managed. Before embarking on a ketogenic diet, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and goals.
Conclusion
The ketogenic diet’s impact on gut flora is a promising area of research, offering potential benefits for digestive health and beyond. By reshaping the microbiota, reducing inflammation, and enhancing gut barrier function, keto may play a role in promoting a healthier digestive system. However, it’s essential to approach this diet with careful consideration and the guidance of a healthcare provider. As the understanding of the gut microbiome continues to evolve, the ketogenic diet’s place in digestive wellness will undoubtedly become clearer.
For individuals interested in the intersection of diet and digestive health, Avix Health offers a wealth of resources. From understanding the role of exercise in promoting healthy gut motility to exploring the effects of stress on gut microbiota, the journey to digestive wellness is multifaceted and deeply personal. By considering the latest research and seeking professional advice, one can tailor their approach to diet and lifestyle for optimal gut health and overall well-being.